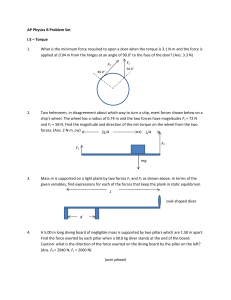
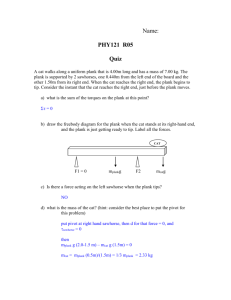
PED 030 P2 (L4-7) L4 • Plank exercise – prone position, holds a position that mimics the top of a push up, body held straight and rigid like a plank. Holding a straight body position on your forearms and toes. - • • • Goal is to maintain this position for as long as possible while keeping the body stable and avoiding any sagging or arching in the back. - Benefit – enhance stability and provides a esthetic appeal. -serve as a benchmark for evaluating sore muscles strength and stability. - building core strength and stability. - improve balance and coordination during everyday activities. - protect your lower back from injury. Robust core – Foundation of all coordinated and dynamic athletic movements. Reduce joint stress and improve posture. COMMON MISTAKES Arching your back – putting much pressure in the arms. Sagging your hips – a sigh it’s time to end your plank. Titling your head up – could strain the neck. • PLANK VARIATION Knee Plank (for beginners) • L5 • Straight-arm knee plank (for beginners) – a step up from knee plank. A bit more arm and core strength but is easier to perform than a traditional plank. • Forearm Plank – a great way to feel the burn. • Straight-arm (Full) Plank – increasing the difficulty, a straight arm plank, also known as full plank. • Forearm to Full Plank – a traditional plank. • Side Plank on forearm – largely targets your obliques, the muscles on the side of your torso, and your hip abductors. • Walking Plank – strengthen your core as well as your upper and lower body muscles groups. • Plank with shoulder tap – adds a extra challenge to the traditional straight-arm plank. • Reserve Plank – full-body exercise targets several muscle groups. Position yourself with your stomach towards the ceiling. • Spider-Man Plank –to feel the burn your obliques,, abs, and lower body. • Plank with alternating knee to elbow – targets obliques. • Plank with a row – targets your upper body. • Mountain Climber – activate your whole body. • Plank Jack – get your heart pumping during your strength routine. • Swiss ball Jackknife – excellent for building strength and stability. Advanced more and should be done the caution. Duration of regularly doing Plank EXERCISE (for beginners) – 10 seconds. 150 pound individual will burn about 3-4 calories 1min holding a plank. Maintaining a proper form is crucial in reducing the risk of injury and maximizing the benefit of the exercise. Proper form and alignment – important for safe and effective Plank exercises. How long to hold a plank exercise -20-30 seconds. L7 • Locomotor -ability o action of moving or travelling from one place to another. - Locomotor movements involves gross motor skills, include activities: o Walking o Running o Crawling o Jumping o Hopping o Skipping o Galloping - This movements requires coordination of various muscle groups and are often incorporate into physical education programs, sports, and fitness routine. - Improving cardiovascular endurance, strength, coordination, and overall physical fitness. - Important for functional mobility in daily life and foundational skills in physical development for children. IMPORTANCE o Physical fitness – walking, running, jumping, and Hopping requires the use of large muscle groups and help improve cardiovascular endurance, strength, and stamina. -contribute to improved physical fitness level, which are vital for maintaining overall health and well-being. o Motor skills development – fundamental gross motor skills that form the foundation for more complex movements. -enhance overall motor skills development, including coordination, balance, spatial awareness, and body control. - this skills are important for a child’s physical, cognitive, and social development. o Sports and Recreational activities – building blocks for participating in sports and recreational activities. -Help individual excel in these activities and promote a lifelong engagement in sports and recreational pursuit. COMMON MOVEMENT o o Running Jumping Hopping SPORTS Soccer Basketball Track an field Gymnastics Daily Life functionality – essential for functional mobility in everyday life. -enhance an individual’s ability to independently and safely perform various activities of daily living. -WALKING AND Running – necessary for navigating the environment, performing daily tasks, and participating in social and recreational activities. Fun and play – associated with play and can provide opportunities for children and adults to engage in enjoyable physical activity. -promote creativity, imagination, social interaction, and overall well-being. Locomotor skills are fundamental movements that are critical for physical development, functional mobility, sports participation, and overall well-being. Locomotor skills are fundamental movements that are essential for physical activity and promote physical literacy. EXAMPLE OF LOCOMOTOR EXERCISES THAT INVOLVE PHYSICAL MOVEMENT FROM ONE PLACE TO ANOTHER. o o o o o o o Walking – basic and natural form of Locomotor movement that can be done at different speeds and intensities. -It is a low-impact exercise that can be easily incorporated into daily routine. Running – more vigorous form of Locomotor movement that involves Faster and more dynamic strides. -It can be done on a treadmill, track, or outdoor terrain. - effective cardiovascular exercise that helps to improve endurance, strength, and coordination. Jumping – (Jumping jacks, box jumps, or burpees) – explosive movements that requires coordinated use of the legs, arms, and core. -effective for improving cardiovascular fitness, power, and coordination. Skipping – playful and dynamic Locomotor movement that involves alternating hops on one foot while moving forward. -a fun and challenging exercise that can help to improve coordination, balance, and leg strength. Hopping – (Single-Leg hops or lateral hops) - propelling the body off one fot and landing on the same foot or another foot. -Effective for improving balance, power, and agility. Galloping – a form of Locomotor movement that involves a combination of a step and an leap, often used in sports like basketball or soccer. -requires coordination of the arms, legs, and core. And can be practiced as a cardiovascular exercise or as part of agility training. Crawling – (bear crawls or crab walks) – moving on hands and feet while keeping the body close to the ground. -effective for strengthening the upper body, core, and improving coordination.