Uploaded by
Napasjutha Kongsonthana
Structures and Functions of Life: Textbook Chapter
advertisement

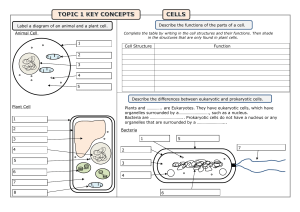
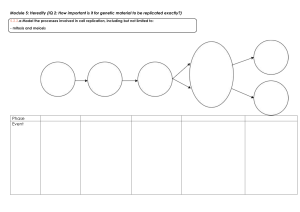
11 CHAPTER 2 Structures and Functions of Life 12 Question 1 - 3 refer to the following information. Tuberculosis is caused by the mycobacterium, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which kills approximately half of all infected patients. For many years, M. tuberculosis was susceptible to drug therapy; however, like many other disease-causing organisms, new drug-resistant strains of tuberculosis have emerged. Many theories have been postulated to explain the emergence of these resistant strains (also known as "superbugs") but most healthcare professionals blame the over-prescription of antibiotics as well as their misuse by patients. Today, before a tuberculosis patient can be treated, it is first necessary to find out which strain of bacterium is causing the disease and then to find a drug that will kill that particular strain., a new technique has been discovered that aids this process. Scientists can now insert luciferase, the enzyme that makes fireflies glow in the dark, into tuberculosis cells taken from the patient, which makes the tuberculosis cells glow in the dark (see Figure). 13 With their new glow-in-the-dark organisms, scientists can then test different drugs to see if they kill the bacteria (which stop glowing). This new test can be done in days, which is faster than previous tuberculosis tests which required up to five weeks. 1. If a tuberculosis cell with luciferase is treated with a drug but keeps on glowing, which of the following is most likely the case? A. A higher dosage of the drug is needed. B. The tuberculosis cell has been destroyed. C. The cell is resistant to that particular. D. Both A and C are correct. 2. What is likely to be the most important reason to save time on a tuberculosis test? A. The patient can begin effective drug therapy that much sooner. B. The scientist can perform twice as many tests and thus have more time for other experiments. C. The enzyme luciferase lasts almost indefinitely. D. Other types of bacteria have shown themselves less able to mutate. 14 3. The following chart depicts the dose response curve of M. tuberculosis to an antibiotic drug. If a scientist knows that an intensity score of 20 or less is considered acceptable (the remaining bacteria can be eradicated by the host's immune response), click on the dose of antibiotic that the scientist should recommend for patients. (For this drill, mark the dose with an X.) 4. When a cell undergoes mitosis, it duplicates into two genetically exact replicas of itself, so that the cells have exactly the same number of chromosomes as did the original chromosomes. Meiosis, unlike mitosis, take place in two rounds. scientists conduct an Experiment on three different cells, and track the number of resulting cells and chromosomes after each cell undergoes either meiosis or mitosis, according to the cell type. The results are shown below. 15 Trial Number of Initial Chromosome Number of final Chromosomes in Each Resulting Cell 1 6 6 2 2 4 2 4 3 46 x 4 Number of Final Cells In trial 3, the cell undergoes ________________________(meiosis/mitosis) and each resulting cell has ____ (23/46) chromosomes. 5. Most animals have internal or external skeletons for structure and support. Which of the following parts provide a similar function in plant cell? A. Cytoplasm B. Chloroplasts C. Cell Membranes D. Cell walls Question 6 - 7 refer to the following information. The Cell and Heredity Each cell in a living organism consists of a membrane surrounding a cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is like jelly and has a nucleus in its center. Chromosomes are part of the nucleus. They are important because they store DNA. DNA stores the genetic code that is the basis of heredity. 16 6. What determines what traits you inherit from your parents? A. The cell B. The atom C. The nucleus D. The neutron E. DNA 7. What part of the chromosome carries the genetic code? A. Membrane B. Cytoplasm C. Nucleus D. Atom E. DNA Question 8 - 10 refer to the following passage. Cells are the basic units of all living organisms. The following summarizes some of the important differences between prokaryotic (bacteria) and eukaryotic (plant and animal) cells. The major distinction is that eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria, chloroplasts, lysosomes, and the nucleus. Each of these organelles carries out specialized functions. Another difference between the various cell types is the presence or absence of a cell wall. In bacteria, the cell wall provides structure to the cell, preventing if from being crushed due to mechanical street or lysing due to osmotic stress. Osmotic stress occurs because water tends to be drawn in to the cells since they typically contain more ions than their surroundings. The rigid bacterial cell wall physically prevents this increase in water from causing the cell to rupture. 17 Animal cells face the same challenges but deal with them in different ways. The cytoskeleton gives the cell structure and protects against mechanical stress. Animal cells do not have a cell wall to protect against lysis so they must constantly pump ions out of the cell. This decreases the tendency of water to enter the cell and protects against rupture. 8. In eukaryotes, which organelle contains the vast majority of the genetic material? A. Ribosome B. Rough endoplasmic reticulum C. Nucleolus D. Nucleus 9. Antibiotics are drugs that are used to treat bacterial infections. They are effective because that can specifically target bacteria without harming the human host. Based on this information, which cellular structure would be a good target for antibiotics. A. Mitochondria B. Cell membrane C. Cell wall D. Lysosome 10. Which of the following is a difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell? A. Prokaryotic DNA is store in the nucleus while eukaryotic DNA is not. B. Eukaryotes are always motile while prokaryotes are seldom motile. C. Prokaryotes actively pump ions across their membranes while eukaryotes pump ions within the cell. D. Eukaryotes use membranes to delineate specialized organelles while prokaryotes do not. 18 11. Most of the cells types in the body reproduce by mitosis except the gametes which reproduce using meiosis. Which of the following is a difference between mitosis and meiosis? A. DNA must be replicated before meiosis but not mitosis. B. In meiosis, there are two rounds of cell division but in mitosis there is only one. C. At the end of mitosis, the daughter cells have half the normal amount of genomic DNA. D. Meiosis uses prophase, metaphase, and telophase, but mitosis doesn’t.