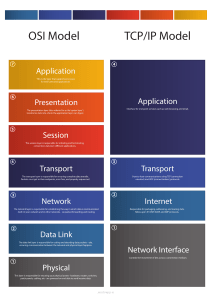
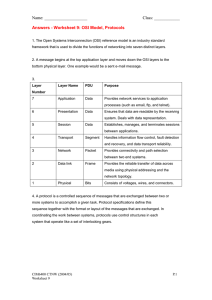
Module 1: Introduction to Network Security Emphasizing the critical importance of robust network security measures Highlighting prevalent security threats and vulnerabilities in the digital landscape Establishing a foundational understanding of the Open Systems Interconnection Model (OSI Model) Module 2: OSI Model and Protocols Delving into each layer of the OSI Model with a focus on security implications Exploring key security protocols at each layer to fortify the network defense Module 3: Network Infrastructure Security Securing network media types and understanding their characteristics Implementing security measures for various cable types, including Coaxial and Twisted Pair, and wireless technologies Addressing security concerns related to network topology and sizing considerations Distinguishing security aspects in circuit-switched and packet-switched networks Examining security considerations within Intranet, Extranet, and the Internet frameworks Module 4: Network Devices and Enhanced Security Analyzing the security roles of network devices and ensuring their secure configuration Implementing segmentation and subnets for enhanced network security Strengthening security at the Physical and Data Link layers Surveying diverse firewall types and their applications Integrating robust security practices into DHCP and Name Resolution processes Module 5: Wireless Networks and Advanced Security Measures Securing IEEE 802.11 networks and wireless signaling protocols Establishing secure associations to wireless networks Implementing advanced security measures, including encryption and authentication Exploring the security benefits of Multiple Input & Output (MIMO) technology Module 6: Advanced Protocols and Security Examining security considerations in Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) and Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Enhancing security through Network Address Translation (NAT) & Port Address Translation (PAT) Securing File Transfer Protocol (FTP) and Email Protocols Implementing secure communication with Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) Establishing Virtual Private Network (VPN) security using IPsec, L2TP, and Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) Module 7: Network Types and VoIP Security Fortifying Local Area Networks (LANs), Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs), and Wide Area Networks (WANs) against security threats Addressing security considerations in Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) and Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) Ensuring secure Voice Over Internet Protocol (VoIP) implementations Module 8: Network Security Threats and Countermeasures Understanding and mitigating various attack vectors Defending against Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) and Denial of Service (DoS) attacks Recognizing and countering Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) Implementing security measures for mobile devices, emphasizing cell phone security Module 9: Understanding Storage Vulnerabilities Overview of vulnerabilities in storage systems Encryption challenges in NAS and SAN devices Impact of cloud storage on security Risks associated with incomplete data destruction Importance of physical security in storage environments Module 10: Data Storage Security Principles Introduction to "CIA" principles – Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability Strategies for ensuring confidentiality Measures to maintain data integrity Ensuring data availability and mitigating risks Module 11: Data Security Best Practices Development and implementation of data storage security policies Role-based access control and multi-factor authentication Encryption practices for data in transit and at rest Deployment of Data Loss Prevention (DLP) solutions Integration of strong network security measures Module 12: Endpoint Security Importance of strong security measures on endpoints accessing stored data Implementation of security measures on PCs, smartphones, and other devices Role of firewalls, anti-malware protection, security gateways, and intrusion detection systems in network security Module 13: Redundancy and Availability Role of redundant storage and RAID technology in improving availability Mitigating security incidents through redundancy measures Module 14: Backup, Recovery, and Disaster Preparedness Significance of robust backup systems in mitigating malware and ransomware attacks Ensuring backup systems have the same level of data security as primary systems Disaster recovery planning and execution