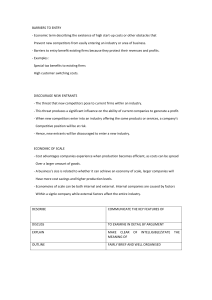
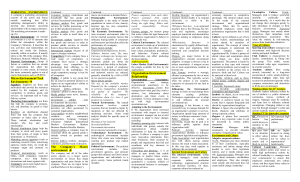
Chapter 1 Business and Its Environment What is business? Kinds of Business Objectives of Business The Environment of Business Forms Matching the Organization with the Environment Survival Strategies in Uncertain Environments Coping Strategies Environmental Controlling What is Business? ◉Business forms and the Government are expected to provide goods and services to the society. The major part of this job, however, is assigned to the private business firms. ◉Under this system, firms are free to compete with each other and competition leads to offering new and improves products and services to the society. ◉The standard of living is raised or lowered depending to a large extent on the performance of business firms. What is Business? ◉Business may be defined as all profit-seeking activities and enterprise that provide goods and services to an economic system ◉Profit refer to the rewards for businesspersons who take the risk involves in producing and marketing goods and services. Kinds of Business 1. Commerce Business firms, which are engaged in buying and selling of goods and services are classified as commerce. Also included in this category are trading, merchandizing, and marketing. 2. Industry Industries are those that are mainly engaged in the production. Goods produced, which are intended for ultimate consumption are called consumer goods, while goods intended for use of business and industry are called producer’s goods. Industry business may be further classified into: a.Genetic industries are those involved in agriculture, forestry and fish culture. b.Extractive Industries are those involved in the extraction of goods from natural resources, which include mining, lumbering, hunting, and fishing c.Manufacturing Industries convert raw materials into finished products. Examples are firms engaged in the manufacturing of drugs, plastics, food, liquor, footwear, motorcars, tools, office supplies, etc. d.Construction Industries are those engaged in building infrastructures like airports, seaports, dams, and highways and dwelling units. Kinds of Business 3. Services A service business is one, which sells service to the buyer. Service firms may be classified as: a. Recreation – movie houses, television and radio stations, theatres for drama and stage presentations, resorts and the like b. Personal – restaurants, barber shops, transportation, hotels, tailoring shops, slimming salons, and the like and; c. Finance – banks, insurance companies, investment houses, financing institutions, credit unions, savings and loans associations and the like. Objectives of Business Profit - Making profit is the primary goal of any business enterprise. Objectives of Business Growth - Business should grow in all directions over a period of time. Objectives of Business Power - Business houses have vast resources at its command. These resources confer enormous economic and political power. Objectives of Business Employee satisfaction and development - Business is people. Caring for employee satisfaction and providing for their development has been one of the objectives of enlightened business enterprises. Objectives of Business Quality Products and Services Persistent quality of products earns brand loyalty, a vital ingredient of success. Objectives of Business Market Leadership - To earn a niche for oneself in the market, innovation is the key factor. Objectives of Business Challenge - Business offers vast scope and poses formidable challenges. Objectives of Business Service to society - Business is a part of society and has several obligations towards it. The Environment of Business Firms Business Environment Business Environment means all of the internal and external factors that affect how the company functions including employees, customers, management, supply and demand and business regulations. The External Environment The term external environment are factors and institutions that are beyond the control of the business and they affect the function of the enterprise. The external environment consists of elements outside an organization that are relevant to business operations. Types of Elements in the External Environment 1. Direct Action Elements 2. Indirect Action Elements - The Main Function of Business Firm Direct Action Elements • Consumers • Competitors • Labor Unions • Suppliers • Financial Institutions • Government Agencies Indirect Action Elements • Technological Variables • Economic Variables • Political-Legal Variables • International Variables Direct Action Components 1. Customers ◉Customer patronage is very vital to the existence of the business firm. ◉The manager must continuously strive to keep old customers and attract new ones. 2. Suppliers ◉Business firms achieve their objectives through a combination of activities. First and foremost is the transformation of production inputs like raw materials, energy, services, equipment and labor into usable products or services. ◉ Suppliers provide these inputs. Note: Business firms must maintain good relationship with suppliers if they want on-time deliveries of inputs. 3. Competitors ◉The target market share can be successfully achieved through careful analysis of competitors. ◉In determining the appropriate marketing strategy, the manager will have to consider not only the target customers but also the competitors. 3. Competitors ◉ competitors are either Direct or Indirect Example ◉Nescafe and Kopiko – Direct Competitors ◉ Pepsi and Coke – Direct Competitors ◉Pepsi and Nescafe – Indirect Competitors 4. Labor Supply ◉The services of managers and employees are indispensable requirements of business operations. ◉These services are in a way procured through recruitment and hiring by the human resource specialist of the business firms. 5. Financial Institutions ◉Business Firms are concerned with maintaining and expanding their operations. In either case , the company will need funds. ◉As such a company planning to expand its business must be well regarded by financial institutions such as commercial banks, development banks and other lending institutions. 6. Government Agencies ◉In many ways business organizations are affected by change in government policies. ◉From enactment of laws to the granting of business permits, the viability of business firms could be enhanced or limited by actions of government. The Indirect Action Elements 1. Technological Variables ◉Technology has become widely recognized as an important ingredient in the success of business firms and manager who does not consider the technological variable in his strategy faces the risk of losing out to competitors. ◉Technology refers to the tools and ideas that may be used by an organization to pursue its goals. 2. Economic Variable ◉This concern will touch the health of the economy in terms of inflation, income levels, gross domestic product, employment and job outlook. ◉Because of the importance of economic variables, business managers are required to devote time and resources to forecasting the economy and to anticipate changes in important concerns like prices. 3. Socio-Cultural Variables ◉Business Organization can only flourish if they consider society's customs and values in the planning and implementation of their activities. 4. Political-Legal Variables ◉These consist of laws and regulations promulgated and implemented at the local , national, and international levels. ◉Also included in the element are individuals and organizations that attempt to influence the political-legal environment. 5. International Variables ◉This elements includes changes occurring in various parts of the world, which may affect business organizations in various ways and degrees. Type of Business Environment 1. Static ◉Few forces in the environment are changing to affect the business. Among the notable features of static environments are no new technological breakthroughs by current competitors , and little activity by public pressure group to influence the organization. 2. Dynamic ◉When significant number of environmental forces that affect the business are changing. Among the features of a dynamic environment are rapidly changing government regulations affecting business, new competitors, difficulties in acquiring raw materials, and continuously changing sociocultural aspects of the population. Environmental Uncertainty This may be defined as a lack of complete information regarding what exists and what developments may occur in the environment. The uncertainty makes it difficult for managers to perform the following: 1. Analyse constituencies and their needs 2. Predict future state of affairs and 3. Understand their potential implications for the organizations Dimensions of Environmental Uncertainty 1. Complexity – This refers to the number of different factors in the environment such as information, capital, material, people, and other organizations. 2. Rate of Change in these Factors – These are the factors in the external environment change from time to time. For instance, income levels and the number of qualified teachers may increase or decrease after a few years. Environmental uncertainty rises as the rate of changes increases. Designs of Business Organizations 1. Mechanistic Design ◉An organization with mechanistic design is deemed appropriate for a task that is routine and unchanging. This design is characterized by a vertical structure that typically operates with: a. more centralized authority b. many rules and procedures c. a precise division of labor d. narrow spans of control and e. formal means of coordination 2. Organic Design ◉An organization with an organic design is appropriate that is non-routine and changing. ◉It is characterized by the following: a. decentralized authority b. fewer rules and procedures c. less precise division of labor d. wider spans of control e. more personal means of coordination 2. Organic Design ◉Task in organic organizations are completed through group efforts and are adjusted and redefined to cope with demands made by the changing environment. ◉Those close to the task are vested with authority to make decisions since they have a more immediate understanding of problems. Organization members exchange information about adjustments in tasks and changes that have occurred in the environment making communication as primarily horizontal. Survival Strategies in Uncertain Environments 1. Application of Coping Strategies ◉Coping Strategies refers to the transformation of a part or all of the organization to make its activities more compatible with existing environmental conditions. 2. Adaptation of Environmental Control Measures ◉ Environmental control refers to management actions to identify and influence environmental factors to obtain more positive effects on organizational activities. Coping Strategies Coping Strategies are those used to protect internal operations from the harmful effects of changes in the environment 1. Buffering ◉This refers to setting up buffers for both input and output sides of organizational activities in order to absorb and cope with environmental uncertainty. ◉Programs or practices are instituted to prevent environmental factors from upsetting the production process. 1. Buffering ◉E.g. Input buffer is the stock file of fuel by a shipping company to provide some assurance of unhampered operation for a certain period. ◉When the production outputs of finished goods are not disposed as fast as they are produced, it may cause disruption in the production activities of the firm. If such disruption will jeopardize operations, management may choose to sell their product at low prices, sometimes even lower than production costs. This action is referred to as buffering on the output side. 2. Smoothing ◉ Irregular demand is always a problem for many business firms. This is so because of the difficulty in making adjustments concerning manpower and equipment. ◉ This is remedied by smoothing which refers to efforts involved in reducing changes in the environment. ◉ E.g. Offering of discounts during slack seasons like selling raincoats at big discounts during summer. 3. Forecasting ◉ This refers to making predictions, projections or estimates of future events or conditions in the environment in which the organization operates. If forecasting is effective, the business firm will be able to make the necessary adjustments in its operations to meet changes in the environment 4. Rationing ◉ This happens when the organization ignores some operations and emphasizes others in order to preserve the most critical functions of the technical core. ◉ E.g. University, which temporarily deploys its research personnel to assist in enrolment activities. After the enrolment period, the reassigned employees go back to their permanent units. 5. Boundary Spanning ◉ This is the process of creating jobs or roles in which individual employees are required to “have a strong communication links within their department, with people in other units, and often with the external community.” ◉ The individuals, called boundary spanners, gather and collect critical information, which can be used for planning in the technical core. The information gathered can also be used to reduce uncertainty in some areas of operation. 6. Structural Complexity ◉ This is when the business adapts to the environment by setting up departments or subsystems that will respond to specific groupings of environmental factors. ◉ E.g. The production of a book publishing company may create another unit that will deal with author’s concerns. Another example is the creation of senior citizens lanes in various government offices and large retail establishments. 7. Executive Succession ◉ One way of adapting to uncertainty in the environment is the adoption of an effective executive succession. The replacement of a top manager by another manager is referred to as executive succession. ◉ The following advantage may be derived from an effective executive succession: a. enable the organization to hire executives with the new energy and vitality; b. Provide organization with a way to bring in specific skills needed to analyze and respond to the environment; c. Provide a coordinated means of replacing retiring executives. Environmental Controlling 1. Creating Favorable Linkages a. Mergers ◉From a legal point of view, a merger is a legal consolidation of two entities into one entity. b. Joint Ventures ◉A joint venture (JV) is a business arrangement in which two or more parties agree to pool their resources for the purpose of accomplishing a specific task. This task can be a new project or any other business activity. c. Interlocking Directorates ◉When some members of the board of directors of one company are also members of another company’s board of directors, such arrangement are called interlocking directorates. d. Executive Recruitment ◉When companies hire executives who have prior experience in the industry, it is called Executive Recruitment Wilma Valle Galvante is the current head of TV5's entertainment division and former GMA Network's senior vice president for entertainment e. Institutional Advertising ◉This type of advertising is designed to build goodwill for a company among stockholders, employee, distributors, the public , and the government. f. Resource Flows ◉This refers to the pattern of resource exchanges between the organization in the environment ◉In the attempt to control the environment , the manager can make important decisions on the pattern of exchanges. His options fall under any of the following: a. FREQUENCY OF EXCHANGES b. QUANTITY INVOLVED IN THE EXCHANGES 2. Manipulating the Environment a. Changing Elements b. Lobbying ◉This term refers to the act of attempting to influence business and government to create legislation or conduct an activity that will help a particular organization. c. Forming Trade Associations ◉Members of the trade associations pool their resources to influence government policies affecting their business. THANK YOU!!!