Innovation Strategies: Schumpeter, Platforms, and Customer Experience
advertisement

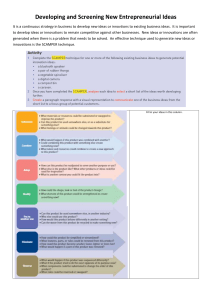
BLOCK 1. WHAT IS INNOVATION? INNOVATION: Drives into economic growth, achieve competitive advantage by creating new technologies and new ways of doing things. So, the INNOVATION is the introduction of new goods, methods of production, markets, sources of supply and the carrying out of a new organization of any industry. (SHUMPETER) JOSEPH SCHUMPETER SCHUMPETER (1934) is the entrepreneur who creates innovation. SCHUMPETER CAPITALIST ECONOMIES: In capitalist reality’s counts the competition from the new commodity, technology, source of supply and type of organization. The disruptions of entrepeneurial innovation occur at irregularly regular intervals Schumpeterian competition drives innovation, and begets imitators, leading a boom. When the original innovator’s profit advantage is eliminated, investment moves elsewhere, and the sector may even shrink, until the next disruptive innovation, which restarts the cycle INNOVATION AND CREATIVITY Creativity and innovation are connected, they are part of a process of creation. Creativity stage is the generation of the idea Innovation refers to the subsequent stage of implementing ideas toward better procedures, practices or products They can occur at different levels or more at one’s but will invariably result in identifiable benefits at one or more of these levels of analysis. Levels: Individual, work team, organization THE 12 SIDES OF INNOVATION Each benefit can become the pivotal element of an innovation strategy bringing to differentiation SERVITIZATION SERVITIZATION IS a Bussines Model change were we offer prod + serv in 1 It’s about offering an integrated bundle of products and services that require a different revenue/business model (solution). “EM3” is a farming service. Is the UBER of farm machinery, is an example of SERVITIZATION The oposite is SERVICE INFUSING, witch means adding complementary services to a product The pay 4 use is a mode to make a fix cost into a variable cost Google buyed “nest” because is good to save billions of dollars evicting a blackout by using the info of the energy consuming of the consumers and taking the capacity of monitoring and taking care of the energy to be sure it’s not a blackout PLATFORM FIRM PLATFORM: Set of subsystems that make a common structure which a company can produce a mount of other products (MODULARIZATION) SUPPLY CHAIN PLATFORM: Extension of the internal platform concept to the supply chain that supply intermediate products or components to the platform leader or the Final product assembler FIRM and SUPPLY CHAIN level create the preconditions for derivative offerings that can be developed faster and at minor costs COST SAVINGS Manufacturing efficiencies: • Continued focus on World Class Manufacturing • Emphasis on process and quality improvements trough digital manufacturing iniciatives Purchasing efficiencies • Higher volume of common components from increased architecture sharing • Focus on cost eduction processes as number of architectures is reduced MODULAR TOOLKIT Strategy: Is good to make lower the costs. They use the same body platform to all the cars for same mount of consumers, but also make MODULARIZATION, they make a visible costumization to can substain the differences between the cost of a Bugatti and e cost of a Clio INDUSTRY PLATFORM: INNOVATION: Platform serves as technological foundation upon which other firms develop complementary innovations (like AppStore) You can use blocks like lego to create a new thing and put it in a market place, so legos are innovation platform and the marketplace a transaction platform TRANSACTION : The platform serves as an intermediary for direct exchange or transactions, subject to network effects (Uber, Airbnb, amazon,…) HYBRID PLATFORMS: (Apple, google, Microsoft, valve, Salesforce, facebook, amazon) Typology of Industry Platform: Two-sided platform: Ther’s customers that publish their struggles and make a research of some solution, then at the platform the external innovators answer them to offer a solution and then they can make a contract. Product platform: There’s a company with a patent of some product or material and the external innovators can make new products with that material by paying a licence or smthng like that. Integrator platform: Like App Store. External innovators make a post at the platform to can get consumers. There’s no other solution. ONE STOP SHOP STRATEGY: A firm that offers a multitude of products or services to its customers, all under one roof, so to speak. Provides convenience and efficiency to clients, gaining loyalty as well as revenue. Saves the consumer a lot of time and effort. WHY ARE PLATFORM STTRATEGIES SO EFFECTIVE? BEACUSE THE ECONOMICAL/TECHNOLOGYCAL/PSYCOLOGICAL LOCK-IN Economical lock-in system: + use, + advantages Technological lock-in systems: complementary technologies that make harder to change the platform PSYCOLOGICAL lock-in systems: It’s easier 4 being where we are and harder changing of platform (like Microsoft vs apple) NETWORKING EFFECT it’s a PSYCOLOGICAL lock-in WHEN IT HAPPENS? • “Jump on the bandwagon” strategy. Simply use existing and “winning” platform • “Embrace-and-extend” strategy. Embrace existing winning platforms, as far as they go, but then extend them with proprietary features • Create new/alternative platforms strategy. Join forces if possible, • Avoid platforms (strategy or desperation?) Niche market solution SOLUTIONS Create integrated and customized offerings that solve end-to-end customer problems We offer lots of solutions to a problem. CUSTOMIZE CUSTOMERS A) Discover unmet customer needs JOB TO BE DONE THEORY discover the real needs of customers B) Identify new customer segment (to increase the potencial market) B.O.P = Bottom OF the Piramid If u segment d market u can observe if thers segments not being targeted and if its good or bad to target C) Innovate the market positioning (to meet + promising and profitable segments) 99% people use mental maps to make desitions (ike buying a new camera) Upselling and cross selling (Massimo dutty) Segmentation techniques: • DEMOGRAPHICS (Age, sex, marital status, income, education, culture…) • BEHAVIORAL (Benefits, usage rates…) • GEOGRAPHICS (Local, regional, national, international) • PSYCOGRAPHICS (Personality, values, attitudes, lifestyle…) CUSTOMER EXPERIENCE Revenue Model = RM Redesign customer interactions across all touch points and all moments of contact (ej. starbucks) VALUE CAPTURE Redefine how the company gets paid OR create (additional) innovative revenue streams RAZOR AND BLADES RM: A complete product is composed by a main item (low price) and a complimentary item (highly prices) which needs replacement after some uses FREEMIUM FM: pay to unlock all above 1 penny effect: the line that joins demand and price is straight and diagonal down. In this type of BM (freemium) that line turns different because of the 1 penny effect Is it possible to monetize FREE USERS? Not easy, but not impossible. How? • Up-selling, of course (unlock features) • TArget2Target: invite adversities to target your users • Sell intelligence about users behaviors to other players in the industry or outside • Build a community from the users and leverage the community to provide some services, like personalized support • Sell your platform logic to other players in the industry or outside • Donations PROCESS Redesign core operating processes to improve efficiency and effectiveness PRODUCTION PROCESSES Increase efficiency and reduce lead time. Reduce costs. Improve quality. KNOWLEDGE INTENSIVE PROCESSES 3D and multi-dimensional design. Simulation Software. AI based solutions. ORGANIZATION We cn reduce levels of management, and make the business more efficient, but it makes more difficult controlling. As that, we can reorganize all the company’s tat are merged on a same group. (Case of google, now is part of “ALPHABET”) SPECIALIZATION BASED MODEL: Firms develop global centers of excellence in different fields, which are globally responsible for the developement of a specific product/process/ technology INTEGRATION BASED MODEL: Different units around the world each contributes to the developement of technology projects SPECIALIZATION BM INTEGRATION BM SUPPLY CHAIN Think differently about sourcing and fulfillment. From a “captive” subcontractig system to a “fast-fashion” (from design to retailing in 3 weeks) PRESENCE Create new distribution channels or innovate points of presence (can overlap with experience) SHOP-IN-SHOP. Is an area that one retailer sublets within another retailer's premises. The majority of perfume sales are made through shop-in-shop points rather than standalone stores. SHOP-CORNER. Small shop, especially on a corner of a road, that sells foods and other things that are often needed. CONVENIENCE STORES. NETWORKING Create network-centric intelligent and integrated offerings Companies as “Network Orchestrator” or also “Empty companies” which main activity consists in orchestrating external info, data and logistics streams while the main resource is the network itself BRAND Leverage a brand into new domains INNOVATION TYPES INCREMENTAL INNOVATIONS Day-to-day changes. Marginal improvements in prod or optimizations in productions processes. They develop over solid basis (already existing prod to processes). RADICAL INNOVATIONS Represent a radical step change in a product process. Radically new prod are more frequent than radical changes in production processes. Radical process innovations generally take more time to spread because they involve assets and knowledge that will be applied to multiple products COMPONENT INNOVATION ARCHITECTURE INNOVATION Products composed by a multitude of components and sub components. The most common situation is Innovation processes at lower levels are constrained by innovation processes at the architecture level DISCONTINUOUS INNOVATIONS Technological innovation normally develop along predictable trajectories. DISCONTINOUS INNOVATIONS represent a rift un such trajectories that change the rules of the game for all the companies and can force incumbents to revise their business model to avoid competitive irrelevance. SOURCES OF DISCONTINUITY • NEW MARKET SEGMENTS. • NEW TECHNOLOGIES • NEW POLITICAL RULES / A SHIFT IN REGULATORY REGIMES • NEW CONSUMERS BEHAVIOURS • NEW BUSINESS MODELS IF YOU ARE IN SHORT TERM IN LONG TERM AN INCUMBENT A NEW COMER Adopt a wait and see behavior; limit the sailing ship effect with price tactics Gain as much mkt share as possible Shift to the winning technological trajectory Prepare for tough competition coming from converted incumbents DISRUPTIVE INNOVATION Process by which a product or service takes root initially in simple applications at the bottom of a market and then relentlessly moves up market, eventually displacing established competitors