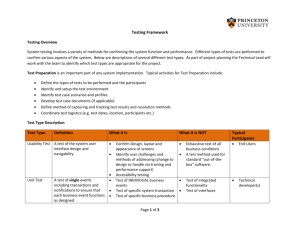
1. High-fidelity vs. Low-fidelity Prototypes:* High-fidelity prototypes are detailed and closely resemble the final product in terms of design and functionality. They are suitable for user testing to evaluate the realistic experience. Tools for high-fidelity prototyping include Adobe XD and Figma. Low-fidelity prototypes are basic representations that focus on functionality rather than appearance. They are quick to create and useful in the early stages of design. Tools like Balsamiq and Sketch are often used for low-fidelity prototyping. *2. Usability Heuristics and Nelson 10 Principles:* Usability heuristics are broad usability guidelines to evaluate user interfaces. The Nelson 10 Principles of Usability Heuristics include concepts like visibility of system status, match between system and the real world, and user control and freedom, emphasizing user-centered design principles for optimal usability. *3. History of UI Development:* The history of UI development dates back to early computer systems like ENIAC. Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs) gained popularity in the 1980s with the introduction of the Apple Macintosh. Early developments include command-line interfaces (CLI) and punch cards. *4. User Control vs. Custom Control:* User control refers to interfaces where users have control over system actions. Custom control involves interfaces where users can customize elements to suit their preferences. The distinction lies in the level of adaptability and personalization. *5. Principles for Visual Design in UI & UX:* Principles for Visual Design include clarity, contrast, consistency, hierarchy, and simplicity. These principles aim to enhance user experience by creating visually appealing and user-friendly interfaces. *6. User Personas in User Testing:* User personas are fictional characters representing different user types. They help in understanding user needs, behaviors, and goals. Developing personas involves research, interviews, and analysis to create a comprehensive representation for effective user testing. *7. Similarities and Differences between API and GUI:* APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) and GUIs (Graphical User Interfaces) serve different purposes. APIs enable software communication, often with a command-line interface, while GUIs provide visual interfaces for user interaction. Both facilitate interaction but through distinct methods. *8. Components of Screen-Based Interface Design:* Components of screen-based interface design include layout, navigation, input controls, informational elements, and feedback mechanisms. These elements collectively contribute to creating a functional and user-friendly interface. ANSWER 8. User Testing in UI & UX: User testing plays a crucial role in UI (User Interface) and UX (User Experience) design. It involves evaluating a product or service by testing it with representative users. The primary goals are to identify usability issues, gather qualitative and quantitative data, and ensure that the design meets user expectations. User testing typically involves tasks such as navigation, interaction, and feedback collection. 8. A/B Testing in UX Design: A/B testing, also known as split testing, is a method used in UX design to compare two versions of a webpage or application to determine which one performs better. It involves presenting two variations (A and B) to users and analyzing their responses to identify the more effective design. A/B testing can be used to optimize various elements, such as button placement, color schemes, or navigation menus, based on user preferences and behavior. 9. Interaction Styles: Different interaction styles include: Command Line Interface (CLI): Requires users to input commands in text form. It is efficient for experienced users who prefer keyboard shortcuts and have specific commands in mind. Graphical User Interface (GUI): Relies on visual elements such as buttons, icons, and menus, making it more intuitive for users who are not familiar with command syntax. GUIs are generally user-friendly and are suitable for a broad audience. Comparison: CLI: More efficient for power users and experienced individuals who are comfortable with commands. GUI: More user-friendly for the general population, as it provides a visual representation of actions and options. 10. Microsoft Word Interface Golden Rules: While Microsoft Word's interface may evolve with updates, as of my last knowledge update in January 2022, some general design principles or "golden rules" may include: Consistency: Elements like toolbar placement, menu structures, and icons should remain consistent throughout the application for a predictable user experience. Feedback: Provide clear feedback for user actions, such as highlighting selected text, changing cursor shapes, or displaying status messages. This helps users understand the system's response to their inputs. Efficiency: Design features and workflows to be efficient, allowing users to accomplish tasks with minimal clicks or steps. This includes providing keyboard shortcuts for power users. It's worth noting that interface design can change with updates, so it's a good idea to refer to the latest Microsoft Word documentation or guidelines for the most accurate and up-to-date information.