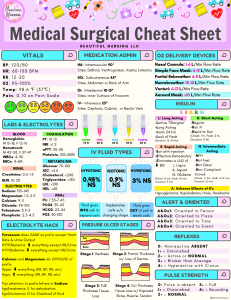
Clinical Judgment, Prioritization, & Delegation Chris Garrison, PhD, RN, CNE,CHSE Objectives Learners will be able to: Describe how clinical judgment impacts nursing practice Develop a framework for applying clinical judgment Apply frameworks for determining clinical prioritization when caring for individuals or groups of clients Apply the NCSBN “Five Rights of Delegation” to client scenarios Novice Nurse & Clinical Judgment Moves beyond rules Recognition of aspects of a clinical situation that are most relevant 65% of errors are due to poor clinical decision making (Caputi, 2019) NCSBN Clinical Judgment Definition The observed outcome of critical thinking and decision- making. It is an iterative process that uses nursing knowledge to observe and assess presenting situations, identify a prioritized client concern, and generate the best possible evidencebased solutions in order to deliver safe client care. (NCSBN, 2022) NextGen NCLEX Case Studies Each exam will include 3 clinical judgment case studies Client data presented in context 6 questions 6 Steps of CJMM Recognize Cues Which data are important? Analyze Cues What does the data mean? Prioritize Hypotheses What is the most likely problem based on the data? Generate Solutions What is my plan? Take Action How do I implement my plan? Evaluate Outcomes Was my plan effective? Failure to Rescue Failure to Rescue: “Clinician’s inability to save a hospitalized patient’s life when he experiences a complication (a condition not present on admission)” (Clarke & Aiken, 2003, p. 42-43) Most Codes are Preventable Successful Rescue Surveillance Ongoing interpretation and synthesis Recognize emerging complications Rescue Mobilize resources SBAR Anticipate what is needed Rapid Response Team Examples of Complications Pneumonia Shock Cardiac Arrest GI Bleed DVT/PE Respiratory Failure Seizures Acute Renal Failure Indicators of Emerging Complications Change in LOC Pain Dyspnea Change in Vitals Change in Labs Urine Output Questions to ask What is my patient at risk for? How would I detect it? What assessment data should I collect? Identify relevant signs and symptoms What would I do about it? Put the picture together What data are relevant? Case Study A 73 year old female with a history of HTN, Type 2 DM, and Renal Insufficiency was admitted for a Sigmoid Resection and Colostomy What is she at risk for? What would you assess? Prioritization Essential aspect of clinical judgment Frameworks: ABCs Maslow Assess before Intervening Systemic before local (“life Acute before Chronic before limb”) Actual before Potential Unexpected before Expected Frameworks are guidelines not black and white Maslow NCLEX Question The nurse receives report on a group of patients. Which of the following patients should the nurse assess first? A. A diabetic patient being treated for a COPD exacerbation with a blood glucose of 290 mg/dL B. A patient who is post-op day one after a total hip replacement with a pain rating of “8” C. A patient recently diagnosed with stage 4 lung cancer who is crying D. A patient who is post-op day 2 after a tracheostomy with an SpO2 of 88% NCLEX Question The nurse receives laboratory results on 4 patients. Which result should the nurse address first? A. A patient being treated for heart failure with a potassium of 2.6 mEq/L B. A patient who is 24 hours S/P Total Knee Replacement with a hemoglobin of 9.1 mg/dL C. A patient on Warfarin for atrial fibrillation with an INR of 3.3 D. A dialysis patient with a creatinine of 5.7 mg/dL NCLEX Question The nurse is preparing to administer medications to a group of patients. Which medication should the nurse give first? A. A PRN dose of lorazepam for a patient experiencing anxiety B. An IV bolus of diltiazem for a patient in atrial fibrillation with a heart rate of 150 C. A dose of lisinopril for a patient with hypertension and a BP of 168/94 mmHg D. A dose of sliding scale insulin aspart for a diabetic patient with a blood glucose of 310 mg/dL NCLEX Question The nurse is planning care for a patient with chronic COPD who is admitted for an acute myocardial infarction. Which nursing diagnosis would have the highest priority? A. Risk for ineffective airway clearance R/T excessive pulmonary secretions AEB productive cough B. Ineffective individual coping R/T acute illness AEB patient statement of distress C. Ineffective myocardial tissue perfusion R/T coronary occlusion AEB elevated troponin D. Risk for fall R/T nitroglycerin drip NCLEX Question The nurse is caring for a patient with heart failure. The patient reports worsened shortness of breath. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first? A. Increase the flow rate of the O2 B. Check the SpO2 and auscultate the lungs C. Request an order for a stat dose of IV furosemide D. Encourage the patient to use pursed lip breathing Delegation Delegation: “Transferring the authority to perform a selected nursing task in a selected situation to another team member while maintaining accountability” Assignment: “Transferring the authority, accountability, and responsibility to another member of the health care team” (ATI, 2013, p. 13) The NCSBN 5 Rights of Delegation Right Task Right Circumstances Specific instructions Right Supervision Consider skills and abilities of individual Right Communication Consider patient’s condition and degree of supervision required Right Person Consider credentials, nurse practice act, agency policy Monitoring and evaluation of patient and staff member performance (National Council of State Boards of Nursing, 1997) Scope of Practice Issues (Right Task) NCLEX will address national norms RN: Care of complex or unstable patients or care with uncertain outcomes Initiate the Nursing process Client education Blood products IV Push Scope of Practice Issues LPN: Care of stable client Gather data Contribute to care plan Reinforce teaching Perform skills with predictable outcomes Administer medications (no IVP, chemo, blood products, TPN) Scope of Practice Issues Unlicensed Assistive Personnel (UAP) Stable client Obtain vital signs Record I & O Hygiene care Positioning and Ambulation Feeding Delegation The RN cannot delegate “what you can EAT” Evaluation Assessment Teaching Right Communication The RN is caring for a patient with endocarditis. The nurse is concerned about the patient’s risk of developing sepsis and asks an experienced UAP to take vital signs Example A: Take vitals signs on Mrs. Jones Example B: Take vital signs on Mrs. Jones every two hours. Notify me immediately if temp is > 38, pulse > 90, or SBP < 90 NCLEX Question The charge nurse is planning client care for a patients on a cardiac unit. Which patient is most appropriate for the LPN to care for? A. A patient scheduled for cardiac catheterization today B. A patient with coronary artery disease who had an episode of chest pain last night C. A patient being discharged today after successful insertion of a pacemaker two days ago D. A patient with heart failure being treated with PO furosemide and digoxin NCLEX Question The nurse is planning care for a patient who is post-op day 1 after an Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA) repair. Which of the following activities is appropriate to delegate to the unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) A. Record vital signs B. Monitor hourly urine output C. Change the surgical dressing D. Teach the patient how to use the incentive spirometer NCLEX Question The nurse is planning care for a patient who is post-op day 2 after a laryngectomy. Which of the following activities is appropriate to delegate to the LPN? A. Observe the patient’s ability to swallow B. Evaluate the patient’s Spo2 C. Suction the laryngectomy tube D. Interpret the patient’s CBC NCLEX Question The nurse is planning care for a patient with neutropenia. Which of the following can be appropriately delegated to the unlicensed assistive personnel? (Select All that Apply) A. Take vital signs B. Report temperature above 38 degrees Celsius C. Assess for signs or symptoms of infection D. Instruct the family on reverse isolation procedure E. Place Isolation supplies outside the room NCLEX Question The nurse is planning care for a patient who is post-op day one after a thoracotomy for lung cancer. Which intervention can be delegated to the unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP)? A. Assist the patient to sit in an upright position B. Instruct the patient to cough effectively C. Teach the patient to use the incentive spirometer D. Monitor chest tube output NCLEX Question The nurse is planning care for a patient who is 12 hours post-op after a thoracotomy. Which of the following actions can be delegated to the LPN? A. Assess the patient’s pain B. Auscultate breath sounds C. Review CBC for signs of post-op hemorrhage D. Evaluate the functioning of the chest tube References ATI (2013). The comprehensive NCLEX-RN Review. Leawood Kansas: Assessment Technologies Incorporated. Caputi, L. (2019). Teaching Clinical Judgment. Workshop, Altoona, PA. Clarke, S. P. & Aiken, L. H. (2003). Failure to rescue: Needless deaths are prime examples of the need for more nurses at the bedside. American Journal of Nursing, 103(1), 42-47. National Council of State Boards of Nursing (1997). The five rights of delegation. https://www.ncsbn.org/fiverights.pdf National Council of State Boards of Nursing (2022). The NCSBN Annual Meeting. Tanner, C. A. (2006). Thinking like a nurse: A research-based model of clinical judgment in nursing. Journal of Nursing Education, 45(6), 204-211