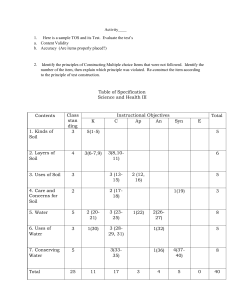
Soil Properties: Parent Material, Climate, Topography, Organisms, Time
advertisement

Five Properties Affecting Soil Parent Material y h p a r Clima Topog te Organisms Time Properties Affecting Soil – 1. Parent Material • Either from an igneous (cooled lava), sedimentary (weathered and eroded igneous), or metamorphic (changed due to heat and pressure) • Determines what chemical properties and minerals the soil will have • Ex. Quartz • Nutrient-poor (Atlantic coast) • Ex. Calcium carbonate (limestone) • high calcium, high pH, high agricultural productivity Properties Affecting Soil – 2. Climate • Temperature and precipitation were the two factors that most affected biomes, and they also have a high impact on weathering and erosion • Too cold: Much undecomposed organic material • Humid tropics: Rapid weathering, leaching of nutrients, decomposition of organic detritus Leaching: • The loss of minerals through from the top layer of soil by percolating precipitation. • The materials lost are carried downward and are generally redeposited in a lower layer. Properties Affecting Soil – 3. Topography • The steeper the landscape: • The higher the erosion • The less “deep” the soil • The less saturated soil will become during precipitation Properties Affecting Soil – 4. Organisms • Soil organisms provide ecosystem services themselves • Examples • Decaying organic material • Breaking down toxic materials • Cleansing water • Soil aeration (especially done by earthworms) • Nitrogen-fixing bacteria for the nitrogen cycle • Large grazing herbivores can also have large impacts on the soil Rhizobium • Nitrogen Fixing Bacteria Mycorrhizal • Fungi, plant support Properties Affecting Soil – 5. Time • Young soil: no horizons, no organic matter • Moderately old (mature) soil: more O layer and many nutrients • Oldest soil: may be nutrient-poor due to climax community leaching nutrients (ex. rainforest)