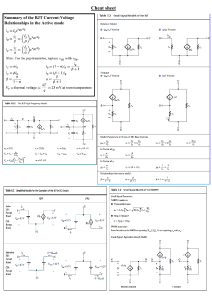
EET 150 Introduction to EET Lab Activity 5 Oscilloscope Introduction Required Parts, Software and Equipment Parts Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3 Component /Value Resistor 10 kΩ, ¼ Watt, 5% Tolerance Capacitor 1.0 F 25 V or above Resistor 22 kΩ, ¼ Watt, 5% Tolerance Quantity 1 1 1 Equipment Required On-Campus Students Solderless Experimenters' Board Hookup wire (22 AWG) Wire cutter/stripper Function Generator Oscilloscope 10x Scope Probe BNC-Alligator Leads cable Optional 2 Banana jack leads red/black On-Line Students Analog Discovery 2: Arbitrary Waveform Generator (AWG). Two channel oscilloscope Optional BNC adapter board for Analog Discovery 2 Digilent 410-263 available at: http://store.digilentinc.com/bnc-adapter-board-for-the-analog-discovery/ 1 BNC to alligator lead test cable 2 10x scope probes Digilent 460-004 or equivalent available at: http://store.digilentinc.com/bnc-oscilloscope-x1-x10-probes-pair/ 2 Banana jack leads red/black BNC-Alligator Leads cable Software On-Campus Students MS Word On-Line Students Waveforms 2015 for Analog Discovery 2 Available for download at : http://store.digilentinc.com/waveforms-2015-download-only/ Fall 2017 1 Lab5_ET150.docx MS Word Introduction Oscilloscopes are used to analyze and test electric circuits. They are capable of showing waveforms that vary in time and are present in an electrical or electronic circuit. Modern oscilloscopes, commonly known as scopes, have the ability to display and measure the electrical characteristics of signals. The measurement functions on the oscilloscope allow the user to see and measure peak voltage, frequency, phase shift, and much more. The user can visually measure the signals using the horizontal and vertical scaling factor or use the measurement functions of the scope to perform the operation automatically. When attempting to measure the signal of circuits manually, try to fit the waveform to the scope display. The larger the waveform is on the screen the greater the accuracy of the measurement. Adjust the vertical control knob if the wave form is too short or too tall to fit on vertical axis of the screen. This knob controls the volts per division (volts per box). To change the scaling on the horizontal axis, adjust the time base of the scope. Expand or compress the waveform time axis by changing the position of this control. This control changes the time per division. Common measurements made on an oscilloscope are signal frequency, peak voltage levels, and phase shift between to signals. Modern scopes take digital samples of signals and can perform a number of other measurements. They can also store waveform samples for later analysis using advanced mathematical functions that can display the frequency content of complex signals. Oscilloscopes can measure both AC and DC signals when the scope’s input mode is set to DC, which stands for direct coupling. Changing the input mode to AC will block any DC signal and allow only AC signals to pass. Use this mode when there are combined AC/DC levels on a signal. An example of this use is examining the AC ripple voltage on a DC power supply. Scopes should always be used with a proper set of probes. The probes should have the same frequency range as the rating of the scope for best performance. The 10x probe provides a 10 times range increase and also reduces the scopes loading effect on the circuit under test. Scope probes should be properly compensated before measurements are made. Review the video presentations that show how to make this adjustment. All scope measurements are made with respect to the ground reference. The scope will read incorrect values when place across components that have both leads connected to points other than ground. It will display correctly when one component lead is connect to ground. Fall 2017 2 Lab5_ET150.docx Objective The objective of this lab is to further the students’ knowledge in the use of oscilloscopes. The students will be able to measure the peak voltage and period of different signals and calculate their frequencies. Procedure 1. Construct the circuit shown in Figure 1 on the SEB. Figure 1. Test Circuit 1. 2. On-Campus Students: Inform the TA/Instructor that the circuit is constructed so they can set up the signal generator. They will set the signal source to 1000 Hz sine wave and 4.5 V peak. On-line Students: Review the tutorial videos that show how to set the output of the Arbitrary Waveform Generator (AWG) found in the Analog Discovery 2 (AD2). Set the AWG to output a 1000 Hz sine wave with a 4.5 V peak value and connect it between points A and ground. 3. On-Campus Students: Sketch and measure manually the waveform from points A to C and from B to C. Use the graph pages and tables in Appendix A end of this handout to document the measurements. Measure the peak-to-peak amplitude of the signal and its period. Compute the frequency from the measured period. Use the formula below to find the frequency. f= Where: Fall 2017 1 T T = period in seconds (S) f= frequency in Hertz (Hz) 3 Lab5_ET150.docx Enter these measurements and calculations in Table 1. Review presentation slides for the details of these measurements. On-line Students: Use the scope input of the AD2 and the WaveForms 2015 software to display the scope output. Display the signal from points A to C and from points B to C. Export the WaveForms display for both measurements to Appendix B of the Word document version of this lab for later submission. See the tutorial video on exporting the display for more details. Use the AD2 and WaveForms scope measurement functions to find the, peak-to-peak amplitude, the signal period and frequency. Enter these measurements and calculations in Table 1 in Appendix B. 4. Construct the circuit shown in Figure 2 on the SEB. C B R8 22k C4 1uF + R7 10k 1kHz Figure 2. Test Circuit 2. 5. On-Campus Students: Maintain the signal used in step 2 and connect it between points A and ground on Test Circuit 2. On-line Students: Maintain the signal used in step 2 and it between points A and ground. 6. On-Campus Students: Sketch and measure manually the waveform from points A to C and from B to C. Use the grids provided in Appendix A and record the horizontal and vertical scales. Measure the peak-to-peak amplitude of the signal and its period. Compute the frequency from the measured period. Enter these measurements and calculations in Table 2 in Appendix A. On-line Students: Use the scope input of the AD2 and the WaveForms 2015 software to display the scope output. Display the signal from points A to C and from points B to C. Export the WaveForms display for both measurements to Appendix B for later submission. Use the AD2 and WaveForms scope measurement functions to find the, Fall 2017 4 Lab5_ET150.docx peak-to-peak amplitude, the signal period and frequency. Enter these measurements and calculations in Table 2 in Appendix B. 7. Construct the circuit shown in Figure 3 on the SEB. AA C B R4 22k + 1kHz R3 10k C2 1uF Figure 3. Test Circuit 3. 8. On-Campus Students: Maintain the signal used in step 2 and connect it between points A and ground on Test Circuit 2. On-line Students: Maintain the signal used in step 2 and it between points A and ground. 9. On-Campus Students: Sketch and measure manually the waveform from points A to C and from B to C. Measure the peak-to-peak amplitude of the signal and its period. Compute the frequency from the measured period. Enter these measurements and calculations in Table 3 of Appendix A. On-line Students: Use the scope input of the AD2 and the WaveForms 2015 software to display the scope output. Display the signal from points A to C and from points B to C. Export the WaveForms display for both measurements to Appendix B for later submission. Use the AD2 and WaveForms scope measurement functions to find the, peak-to-peak amplitude, the signal period and frequency. Enter these measurements and calculations in Table 3 of Appendix B. Discussion Points What does the horizontal control knobs do? What does the vertical control knobs do? What is the trigger function used for? Why are there little boxes on the oscilloscope screen? What happened when you put the capacitor in the two circuits? Fall 2017 5 Lab5_ET150.docx Appendix A On-campus Student Measurements and Graphs Test Circuit 1 Measurement and Waveforms Table 1-Figure 1 Circuit Measurements Measurement A-C B-C Peak-to-Peak Volts Period (seconds) Frequency (Hz) Test Circuit 1 Voltage Measurement A-C Channel 1 Volts/div ______ Fall 2017 Channel 2 Volts/div _______ 6 Time/div __________ Lab5_ET150.docx Test Circuit 1 Measurement and Waveforms Test Circuit 1 Voltage Measurement B-C Channel 1 Volts/div ______ Fall 2017 Channel 2 Volts/div ________ 7 Time/div __________ Lab5_ET150.docx Test Circuit 2 Measurement and Waveforms Table 2-Figure 2 Circuit Measurements Measurement A-C B-C Peak-to-Peak Volts Period (seconds) Frequency (Hz) Test Circuit 2 Voltage Measurement A-C Channel 1 Volts/div ______ Fall 2017 Channel 2 Volts/div __________ 8 Time/div __________ Lab5_ET150.docx Test Circuit 2 Measurement and Waveforms Test Circuit 2 Voltage Measurement B-C Channel 1 Volts/div ______ Fall 2017 Channel 2 Volts/div _________ 9 Time/div __________ Lab5_ET150.docx Test Circuit 3 Measurement and Waveforms Table 3-Figure 3 Circuit Measurements Measurement A-C B-C Peak-to-Peak Volts Period (seconds) Frequency (Hz) Test Circuit 3 Voltage Measurement A-C Channel 1 Volts/div ______ Fall 2017 Channel 2 Volts/div _______ 10 Time/div __________ Lab5_ET150.docx Test Circuit 3 Measurement and Waveforms Test Circuit 3 Voltage Measurement B-C Channel 1 Volts/div ______ Fall 2017 Channel 2 Volts/div _____ 11 Time/div __________ Lab5_ET150.docx Appendix B On-Line Student Measurements and Graphs Test Circuit 1 Measurement and Waveforms Table 1-Figure 1 Circuit Measurements Measurement A-C B-C Peak-to-Peak Volts Period (seconds) Frequency (Hz) Test Circuit 1 Voltage Measurement A-C Remove this box and add the scope plot from Waveforms Fall 2017 12 Lab5_ET150.docx Test Circuit 1 Measurement and Waveforms Test Circuit 1 Voltage Measurement B-C Remove this box and add the scope plot from Waveforms Fall 2017 13 Lab5_ET150.docx Test Circuit 2 Measurement and Waveforms Table 2-Figure 2 Circuit Measurements Measurement A-C B-C Peak-to-Peak Volts Period (seconds) Frequency (Hz) Test Circuit 2 Voltage Measurement A-C Remove this box and add the scope plot from Waveforms Fall 2017 14 Lab5_ET150.docx Test Circuit 2 Measurement and Waveforms Test Circuit 2 Voltage Measurement B-C Remove this box and add the scope plot from Waveforms Fall 2017 15 Lab5_ET150.docx Test Circuit 3 Measurement and Waveforms Table 3-Figure 3 Circuit Measurements Measurement A-C B-C Peak-to-Peak Volts Period (seconds) Frequency (Hz) Test Circuit 3 Voltage Measurement A-C Remove this box and add the scope plot from Waveforms Fall 2017 16 Lab5_ET150.docx Test Circuit 3 Measurement and Waveforms Test Circuit 3 Voltage Measurement B-C Remove this box and add the scope plot from Waveforms Fall 2017 17 Lab5_ET150.docx