Dr
.N
iha
lG
ab
r
Topic 8
Animal Transport
Dr. Nihal Gabr
22/11
Dr
.N
iha
lG
ab
r
Part 1 animal transport
Dr. Nihal Gabr
Lichambersgm
-2
2
upper
pulmonary
Lower
centrioles
Atia
.
artery (aorta)
artery
4BLooduesseligmsemi.lu
.
(
value
tricuspid)
atrium
atrium
¥1
ue¥i
-
op
b
#
veins
vein (pulmonary
arteries
bein)
aorta
enacaua
Pulmonary
.cm?Ulmonayoein
amount
value
.
'B'""""
artery
gayg.yqenf.ge?tttkBmcf..n
iha
atrioventricular
R
&
Dr
.N
Cava
t
.
lG
value
(vena bein
Semilunar value
.
ab
r
nar
-
septum
-
trio ventricular value
arteries
semilunar values
.
-
*
LORD
left oxygenated
In
vein
•
Away
Artery
⑨
right deoxygenated
.
Atrium
@
ventricle
a
.
artery
arley
Rd
vein
value
•
RA
-
atrioventricular
value
=
Right ventricle
-
-
Ru
Dr
.N
tricuspid
LA
f
tu
iha
.
win
•
lG
Right atrium
'
.
sea
.
R
value
Eo
ab
r
Semilunar
semilunar
-
left atrium
left atrioventricular value
left ventricle
-
Bicuspid
.
.
lG
iha
Dr
.N
RA
LA
AU
lo
ab
r
lG
iha
Dr
.N
ab
r
In → vein → Atrium
Aways Arley
→
ventriculi
→
.
Vena
s
Cava
*
14
potent
A
@
*
iha
Dr
.N
@
Ru
.
o
-
lG
ra
.
pulmonary
vein
ab
r
I.A
itnouenticukr
Uuluectncuspid )
aorta
"
KEEL:*
LU
m
>
€÷÷:::::...÷g
T
Aorta
artery
02
Oz
L
02
: ÷. ÷f÷÷÷÷÷nfige.ba?shepahcarleyuTMgexcgsoaqeucoaeqgen
vein >
y
ft
R
Oz
lG
:
o
iha
:*
r
'
N
liver
.
-
Dr
.N
se
Coz
kenqsjmpuimf.FM
Oz
ab
r
T
septum
7
259140k
Systemic
Souci
circulation
excess amino acids
→
deamination
3.out
.
i
n
#staexa:
s
o:
:
m
:
n
algtmi i iei i smu
.
excess
<
Renal
.
Renaja¥_
kidney
:
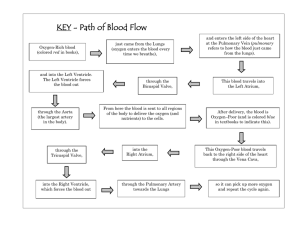
Flow of blood in the heart
Explain how the blood coming from the body reaches the lungs
Uenacaua
>
venacauu
②
g. A
Pulmonary
artery
⑦
-
8)
LA
Ru
LU
,
s
Aorta
3
.
RE
,
ab
r
artery
Right A.v
④
.
RA
pulmonary
vein
⑥
lG
-
L
#
#Tricuspid
P
R
Blood coming from the body , enter the heart through the vena cava into the right atrium
& The right atrium will contract, pressure of blood in right atrium increase.
Atrioventricular valve( tricuspid) open.
iha
: Blood is forced from right atrium into the right ventricle.
6
Dr
.N
⑤ Right ventricle contract, right atrium relax, and pressure of blood in ventricle increase, (volume of
Atrioventricular valve will close to prevent back flow of blood.,semilunar valve open
⑦ Blood is forced out of the heart through pulmonary artery to lungs
(left)
.
lungs
vein
The left atrium will contract, pressure of blood in left atrium increase.
Atrioventricular valve( bicuspid) open.
Id
Bicuspid
1. U
.
atrium
pulmonary
s
decreased
Blood coming from the lungd , enter the heart through the pulmonary vein, into the left
to
I. A
ventricle
To
>
Aorta
Blood is forced from left atrium into the left ventricle.
'
( semilunar
Vale
.
.
↳ to
body
.
Left ventricle contract, left atrium relax, and pressure of blood in ventricle increase,
Atrioventricular valve will close to prevent back flow of blood.,semilunar valve open
Blood is forced out of the heart through aorta to body.
26/11
Dr
.N
iha
lG
ab
r
Animal transport part 2
Dr. Nihal Gabr
Double circulatory system
Heart
Systemic
and
→
Aorta
pulmonary
Heart
circulation
Pulmonary
Body
→
-
Pulmonary
of double
Heart
lungs
Heart
-
pulmonary
vein
.
.
lG
Meaning
.
venaCava
artery
•
circulation
ab
r
Systemic
circulatory
system}
Advantage
II.To
E-
prevent
Mixing
blood
of oxygenated
Dr
.N
•
iha
Blood enters the heart twice in one complete circulation
deoxygenated
and
↳ maintain sleep concentration gradient
For
gas exchange
21 To pump blood under
-
high pressure
to body
Lower pressure to
→
lungs
2
diff pressures
longer distance
→
to avoid
.
damage of lungs
.
DoubkCirculaHonJn
mm
→
Blood
enter the
heart twice in one
circulation
Heart
→
lungs
→
Heart
Body
→
Heart
D. artery
Heart
→
Aorta
meee
the
iha
Aduantaaesfm-twoaifa.me
ptossuuemrbwnoigdnisndsesuetonoay
'
longer
energy
demand
of
living
metabolic
-
2)
blood
-
(
lungs
to avoid
→
steep
.
gradient
gases
.
→
Csystemic
circulation)
of lungs
high
damage
rate
To prevent mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated
to
conc
Maintain
with
(Pulmonary
Circulation)
.
distance
b) lower pressure to
organisms
venaCava
Dr
.N
''
→
Ruein
lG
.
ab
r
•
'
.
C)
Single circulation
Like in fish
Disadvantages
omg
1. Rapid fall in velocity and pressure of blood.
2. Pressure too low for efficient kidney function.
iha
lG
-
ab
r
In sufficient / slower supply of oxygen and nutrients
Dr
.N
*
singkcirculataysyslemgmm.BE
loud enter the heart
circuit
inone
Disadu-ST.is Rapid
once
fall in velocity
and
with oxygen and nutrients
pressure
→
systole
→
is
.
too low
For
kidney
Dr
.N
Function
Diastole
lG
3)
body
iha
cells
ab
r
pressure of blood
2) insufficient supply to
Relay
contract
Remembering
fgdtgpESBG.gg#
has thicker wall than right ventricle
to pump blood under higher pressure
For lonuedistance
*
Cardiac cycle
One heartbeat
.
.
Diastole
systole
→
relaxation
Contraction
ab
r
(0.8 Sec)
o.US
OIS
o
-
ZS
venhicukrsystokwhh-tn.am
.
Diastolezm
AhiaesystoIe3mm
lG
→
ventricle
Semilunar value
.
contract
relax
relax
open
open
Dr
.N
Atrioventricular value
iha
relax
Close
Filing of theheart
relax
contract
close
topreuentbacrftowol
Blood
close
into
.
open
ensuring emptying
of the blood 'm
atria
.
empty,nyd
ventricles
thehecrt
.
o
Blood Forced
outolhecnttobudyl
.
-
Cardisc
ac
cycle
or
O
-
do
one heart
ab
r
beat
G. Used
relax
Atrium
A. uvula
semilunar
.
.
contract
relax
relax
contract
Open
open
close to
Close
close
relax
.
Analysts
Dr
.N
ventricle
oenhicularsystok.fm
mm
iha
Diastok3m
G. 3Rd
Cossey
lG
co .8sec)
Filing of
prevent backflow
of blood
.
The
ensuring emptying
the heart
ofatiumihtooenhick
.
-
to
atria
.
open
to allow blood
flow
out of the heart
to
to push blood out
of heat
.com.ar#estgrmsane..es supplying
heart muscle
and glucose For respiration
→
walls
-
+ narrower
elastic
obesity
highFat intake
high salt intake
.
atherosclerosis
lack of
.
Dr
.N
iha
-
stiff Inch
smoking
lG
✓
Risk Factors
.
ab
r
CHD
with OXYGEN
exercise
stress
.
Treatment
②
-
At risk
→
avoid excess
avoid
Drugs
② Taking
lifestyle
Improve their
Stop smoking
→
,
Fat and salt intake ,
stress,
exercise
.
→
ab
r
Statins: lower blood cholesterol level
Anti platelets: aspirin reduce risk of blood clotting.
③
surgery
-
lG
Antihypertensives: lower the blood pressure.
→
iha
←
Blocked
Dr
.N
Narrowedartery
Angioplasty
artery
↳Lent
.
1 Insert a cable with non inflated balloon and stent in
.
Narrowed artery.
2 Inflate the balloon with water...press on walls of the
.
artery to wide open.
-
3 Deflate the balloon and can leave a stent to hold on the
.
walls of artery.
bypass the blocked
area
teatment3m→
I
At risk
.
Improve
→
his
Stating
Taking drugs
2.
→
→
life style
exercising ,
→
reduce Fat
intake
lower blood Cholesterol level
.
ab
r
of
reduce
Antipketektbmh aspirinclotting
ANHhyperlensiueswmme.to blood pressure
risk
Angioplasty
narrowed
1)
insert
2)
.
arteries
cable with
and stent
→
iha
a)
Surgery
c##××
Dr
.N
3.
lG
→
.
we
b)
.
Bypass
→
non
-
inflated balloon
into the narrowed
artery
then in flat balloon with water
press on the walls of artery to keep them open
3) Deflate balloon and can leave the stent to hold walls
artery
.
of
to
bypass the
blocked
area
.
29/11
Animal transport part 3
Dr
.N
iha
lG
ab
r
Pacemaker and blood vessels adaptation
Dr.Nihal Gabr
Heart muscle
jm
Involuntary muscle
With no need to receive electrical impulses from the brain to keep contracting
Pace maker: is a bundle of nerves found in the right atrium
1. Regulate rate of heart beats according to body demands.
2. Ensure atria contract before ventricles for emptying atria into ventricles
ab
r
What if pacemaker stops:
1. Use artifical pacemaker replaced in person’s heart.
Old: regular heart beats.
lG
New : can sense changes in breathing , movement and body temp so can adjust reate of heart beats.
mime
Dr
.N
iha
How to monitor the activity of heart in hospitals:
→
Heart sound
worm
Dr
.N
iha
lG
ab
r
Measuring heart rate /pulse rate
Emmy
CK
.
4
3/12
Dr
.N
iha
lG
ab
r
Blood vessels , blood components and lymphatic system
Dr.Nihal Gabr
tmrw
Structure of blood vessels:
( IL
→
-
thin
.de/gego7yIgeInwjal sheny*enwawofauenres
Arteries
bi smooth muscles
-
mhg.faneiemaaaaaanf.am?n-neai.%cFbres
Flow
.
under
pressure
.
from the
blood
.
lG
Carry
.
Stretch
recoil
away
heart
under
high pressure
all arteries
Cary oxygenated
blood except
pulmonary artery
-
E
-
AI
R
Blood flow
.
Dr
.N
Q
-
Thinner wall
.
→
→
12hPa
Tty
*
semilunar values
→
flow
no
.
7- sketch (expand)
6hPa recoil
( narrower)
.
flowing
.
resistance
under low pressure
preventing back flow of
Tunaimsmtanensnore:* .ca#a.biggabpagssiun7Iood
all veins
carry deoxygenated blood except
For Pulmonary vein
.
pressure
-
under low pressure
offer
Charrower)
high
under
.
as blood is
wide lumen →
to blood
( expand)
to maintain blood flow
.
(2) being
.
high
>
Trichroism
bursting
tfoad.tyfetneugygnyepoew.b.io
-
iha
•
-
from
od transported
.
ab
r
pulmonary artery in heart
prevent it
Contract Cuasoconshiction) and relax Coasodilutron)
→
blood
to maintain
and
→
Next slide
.
EE÷hj÷÷
veins have blood
→ so
blood has already
lost
its
pressure
+
.
wide lumen
Veins are found embedded between
lG
ab
r
How blood flows in veins?
In addition to presence of semilunar
muscles......when muscles contract ......squeeze
iha
valves prevent back flow of blood.
on blood in veins .....push blood up in veins
Capillary's
Function
exchangeofof substances
Dr
.N
(3)
→
By Diffusion
reabsorption of
Adaptors
wall
is
gases Cosas exchange)
.
useful
substances into
22
pores
8in their walls
to allow
small molecules
4
lumen almost
Same size as that of
RBC
BBC
can move
to allow
efficient
→
slowly
so
gas
exchange
→
Faster
.
to reach to
every
-
cell
.
diffusion
filtration of
From blood
large number of branching capillaries
to provide large surface area to allow blood
3
blood ex glucose
thin wall
one cell thick I
For Shorter diffusion distance
BBC
between blood and cells lakeoli
~
a
-
o
I
Arterials
•
Allow exchange of substances
Carry blood away from the
between blood and cells/alveoli
heart under high pressure.
Transport/ carry blood to the
heart under low pressure
All veins carry deoxygenated
ab
r
All carry oxygenated blood
blood except for pulmonary
except for pulmonary artery.
lG
vein
1. Wall is one cell thick ...shorter
withstand high pressure
diffusion distance.
1. Collagen to protect the walls from
2. They have pores to allow the
1.Thin outer wall and wide
iha
Have thick outer wall.....to
lumen to offer no resistance to
(vasoconstriction) and relax
3. Lumen almost same size as that
muscles to squeeze on blood-
(vasodilation)...changing volume of
of RBCs, so they can move slowly
blood transported to different body
to allow efficient gas exchange .
parts /organs.
4. Large number of branching
bursting due to high pressure.
filtration of small molecules from
2. Smooth muscles which contract
blood.
Dr
.N
a)
.
3. Elastic fibres that stretch
capillaries to provide large surface
(expand) and recoil ( narrower) to
area to reach to all body cells.
maintain blood flow under high
pressure
b)
narrow
lumen
.
No values [except Parley 8 Aorta)
.
blood flow.
2. They are embedded between
pushing it up towards the heart.
3. Semilunar valve to prevent
back flow of blood.
Blood
omg
omg
Plasma 55%.
45% blood cells
←
.
RBCsjmwB.GS
ab
r
n
in topic
Urea, lactic acid, carbondioxide
hormones , '
lG
b) Plasma proteins : fibrinogen , some
Enzymes, antibodies.
iha
water
10%
a) Dissolved substance
Glucose, amino acids, vitamins V
Dr
.N
90%
prig
cells
needed
inidmmunity
Erclottiny
Platelets when they touch the damaged
tissue......they become
①
activated .....becoming more
sticky....and
mum
②
some break and release thrombin enzyme.
elk
mum
EVI
catalyse
the
conversionof
Soluble
into
Fibrinogen
in
-
Soluble hr-br.is
mm
C.plasma protein
Formed in liver)
I
.
.
Forming
which
-
rmaclot
which will then
preventing entry
of pathogen and
dy
out and Form
Scab
←
blood lose
.
.
'
a mesh
tap blood cells
Bloodworm IEEE.BY#eietsPEYFYoutTssueTuidhSt
-
+
Plasma proteins
.
through
pores
plasma + some
typeset WBC,
.
but
§
allow
of
BBG ,no platelets
no plasma proteins
substances
between blood
and cells
no
.
.
Wp
ab
r
L
exchange
-
Og
o
O 0
&
lG
Tissue Fluid .ch cop)
-
I
Artery
B
D
Dr
.N
Bueso
e
iha
g
Carrying blood under high
pressure away from the heart.
To
nyeotuimo.is
Lymph
.
capillary by osmosis
-
y
2. Blood plasma filter out under high pressure through capillary pores
(.... except for RBCs, platelets and plasma proteins ( as they are
large).......forming tissue fluid.........which is an immmediate environment
around every cell to allow exchange of substances between blood and
cells. example. Glucose diffuse from blood to cell across tissue fluid)
through capillary pores
.
3 Tissue fluid return at
the other end of
=
E.
vein
.
°④
Lymphvessel
Drainexcess
tissue
Fluid to
juinlympnutc
system
.
TssueAuidwm
.BE/oodjm-sPkesmce+BBCs- Platelets
+
*
WBG
pores
lG
"
iha
signpost
Tissue fluid .ro
exchange
of substances
between
bloodand
.
proteins
Cells
Young
.
.
vein
.
low pressure
.
,
lymph
B.
Dr
.N
Carrying blood under high pressure
↳ allow
⑨wp-containpw.mu
( h.w.pl
O
Artery
RBCs ,
platelets and
no plasma
proteins
ab
r
o
away from the heart.
no
.
°
.
but no
through capillary
O
high pressure
-
plasma
Plasmaproteins
Blood
plasma , WBG
Filtration of Blood
.
2. Blood plasma filter out under high pressure through
3. Tissue fluid
return at the other
end of capillary by
↳
osmosis
capillary pores ( example. Glucose diffuse from blood to cell
across tissue fluid) through capillary pores.... except for
RBCs, platelets and plasma proteins ( as they are
large).......forming tissue fluid.........which is an immmediate
environment around every cell to allow exchange of
substances between blood and cells.
mm
vessel
Imf
*
Tissue fluid
End
→
How
tissuefluid is
Formed
11.immediate environment around every cell ( tissuefluid)
.
2 Formed due to high pressure of blood coming in arteries away from the heart.
.
3 Where blood plasma will be filtered out through capillary pores ( without RBCs, platelets , plasma
.
impf
→
ab
r
proteins).
Allows exchange of substances between blood in capillaries and cells
Example( diffusion of amino acid from blood in capillaries into the cells across tissue fluid,.....urea
lG
from cells to the blood in capillaries across tissue fluid)
-#
How tissue fluid returns at the other end of capillary ( nearer to veins)?
By osmosis.
Dr
.N
Importance of lymph vessels:
Enmity
*
I
\
iha
*
lymph vessel
T
#
lyfmmsymphatcsystem.SI
lymph
nudes
.
Drain excess tissue fluid to be transported to the lymphatic system to rejoin the circulation thus
preventing oedema
to
*
tyaphno@roducefiaueusurroundceustopaentedema.T
Fathi
2.
Drain
3. Transport
•
°
°
w Bcs
Transport Fatty
6.
?
lymphatic sy
excess tissue
.
ileum ( lacteal)
→
fluid
acid, from the
.
1. contain
Team.FI:5?::::j,:nmY:inesT
-
.
I.
Foreign
substances
.
insoluble in blood so it turns it into soluble Form
.
•
•
Blooding
Timpani
-
Plasma-112134
.
-
Plasma WBC
.
lympts.mg
Plasma + WBC
.
WBC, platelets
Found
in
capillaries
•
Immediate
ab
r
•
.
lymph vessels
.
environment around
by high pressure
ol Blood
causing hitting
of plasma out through Capillary
.
-
.
Formed
Drainage of
.
iha
.
lG
cells
excess
Dr
.N
→
pores
•
Transport molecules
tube exchanged
with cells
•
tissue fluid
vessels
medium Er exchange
-
cells
① Pass
.
nodes
.
join lymphatic
of substances between ① system
Blood and
lymph
into
.
by
→
lymphocytes
lymph
release
→
Antibodies
clean blood
.
Blood
es
Tissue fluid
es
Plasma + RBCs +
Plasma + WBCs
WBCs + platelets
Lymph
es
Plasma + WBCs
+ plasma proteins
ab
r
Immediate environmrnt
In lymph vessels
around cekls
lG
Found in blood capillaries
Drainage of excess
plasma filter out through
lymph vessels
Formed by high blood pressure
iha
coming from arteries, then
tissue fluid into
Transport
substances to be
exchanged with cells
Dr
.N
capillary pores
Allow exchange of
substances between
blood in capillaries and
cells.
Join the lymphatic
system ...to pass by
Lymphnodes thatproduce
lymphocytes that release
antibodies to clean the
lymph from any foreign
substances and to kill
bacteria
Rokoflympnwhicsyslemgmms.IO
nodes →
For the production of lymphocytes
lymph
Contain
needed
antibodies
produce
② Drain
excess
lG
edema
.
→
ab
r
to
→
tissue
⑥Transport
lacteal
Dr
.N
through
iha
③Transport fatty acids
WBC,
.
⑤ Return tissue fluid
back to blood
so
they
Soluble
.
b)
-
.
fluid, preventing
From villi in ileum
are water
insoluble
need to be turned into water
circulation
betting Joining
Fatty acid,
through walls
pathogens
→
fatty acids
a)
kill
are
large
al capillaries
.
so
cant
.
diffuse
o reduce risk
-
of plague Formation on wall , d- arteries
.
o.Expkemhowlymphmaesinlympnoessels7.mn
lymph vessel
Lymph)
nearby
muscles
→
Lymph
→
semilunar value
→
prevent back flow
lG
of Lymph
move
squeeze on
Forward
→
ab
r
1-
contract
.
iha
.
Dr
.N
I
×
,
=
'
Contract
-
y
relax
Biology IGCSE 0610
Page 7
October/November2010
Syllabus-0610
TRANSPORT IN HUMANS
Paper 31
DrDr
.N. N
ihaih
l Gal
abGa
r br
9
Paper 3
Dr.Nihal Gabr
267
Paper 3
TRANSPORT IN HUMANS
DrDr
.N. N
ihaih
l Gal
abGa
r br
Biology IGCSE 0610
Dr.Nihal Gabr
268
Biology IGCSE 0610
17
Page 4
Paper 3
October/November 2013
TRANSPORT IN HUMANS
Syllabus-0610
Paper 33
Page 7
October/November 2014
Dr
18
Dr. N
.N ih
ihaal
l GG
ababr
r
1-
Dr.Nihal Gabr
280
Syllabus-0610
Paper 32
Paper 3
TRANSPORT IN HUMANS
DrDr
.N. N
ihaih
l Gal
abGa
r br
Biology IGCSE 0610
Dr.Nihal Gabr
281
5
2
(a) Fig. 2.1 shows the transfer of materials between blood and tissues.
lymphatic
vessel
fluid A
fluid B
arteriole
venule
Key:
flow of blood
transfer of materials
(i)
Complete Table 2.1 by:
•
•
lG
ab
r
Fig. 2.1
stating the names of the fluids
writing yes if the fluid contains red blood cells or no if the fluid does not contain
red blood cells.
iha
Table 2.1
letter on
Fig. 2.1
lymph
Dr
.N
A
name of the fluid
B
(ii)
tissue fluid
contains red
blood cells
no
no
[2]
State the name of the process by which oxygen is transferred from fluid B to the cells.
Diffusion
..................................................................................................................................... [1]
(iii)
.
Explain why cells need oxygen.
Respiration
For aerobic
...........................................................................................................................................
to
...........................................................................................................................................
release
energy
( protein synthesis)
For cell metabolic reaction
...........................................................................................................................................
.
...........................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
[2]
plasma
Fibrinogen
proteins
→
© UCLES 2020
enzymes
antibodies
and
some hormones (insulin
0610/42/F/M/20
[Turn over
glucagon )
.
.
6
(b) Describe the functions of arterioles in the skin.
-
by helping maintaining
a role in homeostasis
...................................................................................................................................................
plays
body temp
Constant
...................................................................................................................................................
.
relaxation
By
of
smooth
contraction and
...................................................................................................................................................
.
vasoconstriction
muscles in a Knoles →
...................................................................................................................................................
Causing
-
vasodilation
of
changing
volume
→ thus
or
...................................................................................................................................................
flowing
surface
blood
in
near skin
...................................................................................................................................................
capillaries
............................................................................................................................................. [3]
(c) Describe the functions of lymph nodes in the lymphatic system.
lymphocytes
produce AB
Contain
...................................................................................................................................................
→
kill
.
lG
ab
r
'
pathogen
...................................................................................................................................................
Cleaning
.
lymph
before
returning
the
...................................................................................................................................................
.
Circulation
it back to blood
...................................................................................................................................................
.
.
............................................................................................................................................. [2]
(i)
iha
(d) Lacteals are part of the lymphatic system.
State where in the body lacteals are found.
Dr
.N
Villi
.....................................................................................................................................
[1]
(ii)
Describe the role of lacteals.
=
Fatty
acids
absorb ( Transport
...........................................................................................................................................
.
...........................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................... [1]
[Total: 12]
© UCLES 2020
0610/42/F/M/20
.
lG
iha
Dr
.N
¥
#
ab
r
¥¥¥*¥
Checklist
1. Heart label
2. Importance of having a double circulatory system.
3. Disadvantages of having a single circulatory system.
pressures
-
6. Risk factors for CHD
-
Atrial
-
cent
preventing Mixing of oxy
and deoxy blood
supply
.
.
mm
a
Muscle
with oxygen
.
artery
Dr
.N
Narrowed
artery
V.Blocked
.
iha
-
velocity
lG
( drugs : statins, anti hypertensives, anti platelets )
( surgery ; angioplasty, by pass )
low
heart
-
mm
.
ow pressure
.
systole systole
different
.
.
Diastole
5. Coronary arteries function
7. Treatment
under 2
ab
r
4. Cardiac cycle
{
-
Pump blood
8. Cardiac muscle ; involuntary with no need to receive nerve impulses to contract .
9. Pacemaker ( found right atrium) its a bundle of nerves send electrical impulses across walls of atria / heart
muscle
A) .regulate rate of heart beats according to the body activity.
B) Ensure that the atria contract before the ventricles .
10. Replacement by artificial pace maker.
11. Heart rate= pulse rate (bpm)
12. Pulse in arteries ( how to measure)
13. How to hear heart sound ( stethoscope lub bud sound )
14. How to monitor heart beats at a hospital (ECG)
15. Structure and function of artery , vein and capillary
16. Role of tissue fluid
ab
r
17.role of lymphatic system
18, why fatty acids are transported through lacteal into lymphatic system
Dr
.N
iha
lG
19. How lymph moves in lymph vessels.