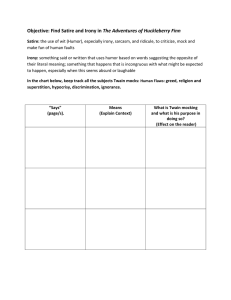
SATIRE Points to Remember Regarding Satire • A literary work that ridicules its subject in order to make a comment or criticism about it. • Although satire is usually witty, and often very funny, the purpose of satire is to criticize in order to shame someone or something into reform. • Satire usually has a definite target, which may be a person or group of people, an idea or attitude, an institution, or a social practice. Irony as a Strategy • Verbal Irony: the use of words that mean the opposite of what you really think especially in order to be funny • Situational Irony: a situation that is strange or funny because things happen in a way that seems to be the opposite of what you expected • Dramatic Irony: when the audience or reader knows something the character/speaker does not Other Strategies Used within Satire • Sarcasm: a sharp and often satirical or ironic utterance designed to cut or give pain EX. "I didn't attend the funeral, but I sent a nice letter saying I approved of it." - Mark Twain • Hyperbole: language that describes something as better or worse than it really is (over-exaggeration) EX. From Joseph Conrad’s novel The Heart of Darkness: “I had to wait in the station for ten days - an eternity.” • Understatement: to say that (something) is smaller, less important, etc., than it really is EX. In J.D. Salinger’s Catcher in the Rye, Holden Caulfield says: “I have to have this operation. It isn’t very serious. I have this tiny little tumor on the brain.” Other Strategies Cont. • Incongruity: • Putting things together that normally wouldn’t go together • This can be used to make ordinary things seem ridiculous • Parody: • Imitating someone/something for comedic effect • Often includes the use of other techniques (hyperbole, irony, etc.) • Parody has entered our day-to-day life through hilarious parody movies that mimic famous blockbusters. Vampire Sucks parodies and pokes fun at Twilight. When analyzing satire, consider… • Subject: What is the main idea? • Occasion: What current event/trend is the author reacting to? • Audience: What person/group is the satire targeting? • Purpose: What is the “real” message behind the satire? • Speaker: How does the author create credibility? Why should we trust this person? • Tone: What is the author’s feeling towards the subject? How is the tone used to further their purpose? Film Clip Analysis of Satire • How does this text function? • What does the author of this text hope to accomplish? • Who is the target audience, and how do you know? • What is the larger message? • Is the piece effective, why or why not? • What do these texts have in common? What are their differences? How do you account for those differences? Videos • “Teaching Center” https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dkHqPFbxmOU • “Shrek: Merry Men” https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LoKYEF_q7Js • Obama’s Home Teleprompter Fails (Onion) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aXQTaWjMoFw&feature= youtu.be • Aussie Just Right Commercialc • What do you need to know to explain this cartoon? • The author’s subject • Purpose • How effective is he in getting across his meaning?