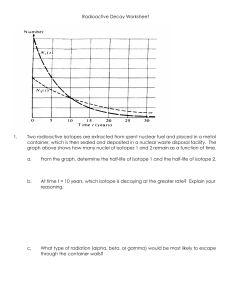
1 1 Only one isotope of gold occurs naturally on Earth. There are several artificially produced isotopes of gold. Gold-198 is an artificial isotope which is used in medicine and in scientific research. A sample of gold-198 is placed near to a radiation detector in a research laboratory. The count rate is recorded at the same time every day for 32 days. The results are used to plot the graph. 400 count rate counts / min 300 200 100 0 0 4 8 12 16 20 24 28 time / days (a) Using the graph, determine the background count rate in the research laboratory. count rate = ...................................................... [1] (b) Using the graph, determine the half-life of gold-198. half-life = ...................................................... [4] [Total: 5] 32 2 2 The diagram shows the paths of three α-particles moving towards a thin gold foil. Four gold nuclei are shown. gold nuclei paths of a-particles (not to scale) On the diagram, complete the paths of the three α-particles. [3] [Total: 3] 3 In a nuclear fusion reactor, a nucleus of hydrogen-2 fuses with a nucleus of hydrogen-3 at an extremely high temperature. This fusion reaction produces an isotope of element X and releases a neutron. Using nuclide notation, complete the equation for this reaction. + → [2] [Total: 2] 4 The diagram shows a β-particle moving in the direction of the arrow between two poles. S b-particle N direction of travel of b-particle when in the position shown On the diagram, draw an arrow to show the direction of the force on the β-particle due to the magnetic field. [2] [Total: 2] 3 5 (a) Write down the nuclide equation for this decay of protactinium-234. [3] [Total: 3] 6 In a nuclear fusion reactor, a nucleus of hydrogen-2 fuses with a nucleus of hydrogen-3 at an extremely high temperature. This fusion reaction produces an isotope of element X and releases a neutron. Explain why an extremely high temperature is needed when forcing these two nuclei together. .................................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................................. [3] [Total: 3] 4 7 A student places a sample of an isotope of protactinium (Pa-234) near a radiation detector. The readings on the detector, taken every 20 s, are recorded in the table. count rate counts / min time / s 0 101 20 88 40 76 60 66 80 58 100 51 120 46 140 42 160 38 180 35 The graph shows the count rate due to this sample against time. count rate counts / min 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 time / s Explain why the readings in the table are not the same as those plotted on the graph. .................................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................................. [2] 5 [Total: 2] 8 The diagram shows a simple diagram of a smoke detector. The smoke detector contains a small sample of americium-241. This isotope emits alpha particles and ionises the air between the metal plates in the detector. detector circuit radioactive source metal plates air flow Suggest and explain two reasons why smoke detectors use an isotope that emits α-particles rather than an isotope that emits γ-radiation. 1. .............................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................................. 2. .............................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................................. [2] [Total: 2] 6 9 The diagram below is a simple diagram of a smoke detector. The smoke detector contains a small sample of americium-241. Americium-241 decays by an α-emission to an isotope of neptunium (Np). This isotope ionises the air between the metal plates in the detector. detector circuit radioactive source metal plates air flow Describe how the americium-241 ionises air. .................................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................................. [3] [Total: 3] 10 The isotope americium-241 is represented by This isotope decays by an α-emission to an isotope of neptunium (Np). Complete the nuclide equation for this decay. [3] [Total: 3] 7 11 A nucleus of strontium-90 consists of 38 protons and 52 neutrons. Strontium-90 is radioactive and decays by β-emission to an isotope of yttrium. The symbol for strontium is Sr and the symbol for yttrium is Y. Write down the nuclide equation of this decay. [3] [Total: 3] 12 Radioactive nuclides can be used in medicine as radioactive tracers. State another use of radioactive nuclides in medicine. .................................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................................. [1] [Total: 1] 13 State two differences between nuclear fission and nuclear fusion. 1 ............................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................................. 2 ............................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................................. [2] [Total: 2] 8 14 The diagram shows a beam of α-particles, β-particles and γ-rays directed between two metal plates P and Q. The metal plates are parallel and there is a large potential difference (p.d.) between them. Plate P is positive and plate Q is negative. On the diagram, draw the paths of each of the radiations between the plates and after leaving the plates. Label the paths α, β and γ. [5] [Total: 5] 15 Radioactive tracers emitting γ-rays can be used in medicine. The half-life of the source of these γ-rays is 6 hours. Explain why a source of γ-rays used in this way should not have a half-life shorter or longer than about 6 hours. .................................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................................. [2] [Total: 2] 9 16 A beam consists of α-particles, β-particles and γ-rays. Explain how a uniform magnetic field may be used to separate the α-particles, the β-particles and the γ-rays .................................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................................. [3] [Total: 3] 17 With no radioactive sample present, a scientist records a background radiation count of 40 counts / minute. The scientist brings a radioactive sample close to the detector. The count rate increases to 200 counts / minute. After 24 days the count rate is 50 counts / minute. Calculate the half-life of the radioactive sample. half-life = .............................................. [4] [Total: 4] 18 Thorium-234 ( (Pa). ) is radioactive. It decays by β-emission to form an isotope of protactinium (a) A pure sample of thorium-234 emits β-particles at a count rate of 2480 counts/second. The half-life of thorium-234 is 24 days. Calculate the count rate for the emission of β-particles from the thorium in the sample after 72 days have passed. count rate .............................................. [3] 10 (b) The isotope of protactinium produced by the decay of Thorium-234 is also radioactive. It decays by β-emission and has a half-life of 70 seconds. State and explain how this would affect the observed count rate for the sample in (a) after 72 days. ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... [3] [Total: 6] 19 The isotope radon-220 is radioactive. The half-life of radon-220 is 56 s. 6 A sample of this isotope contains 7.2 × 10 atoms. Predict the number of α-particles that the radon-220 in the sample emits in the next 168 s. number of α-particles emitted = .............................................. [3] [Total: 3]