Presentation for ICCS2023:DPS-CR: A Task Scheduling Algorithm Based on Computation Reuse in Vehicular Edge Computing
advertisement
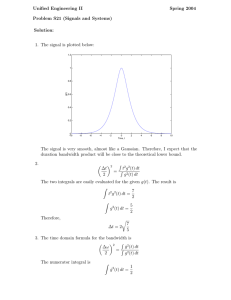
DPS-CR: A Task Scheduling Algorithm Based on Computation Reuse in Vehicular Edge Computing Authors: Zhipeng Li,Shihong Hu,Bin Tang Institute: Hohai University Speaker: Zhipeng Li Directory ▶01 Background and Significance ▶04 Solution ▶02 Data set ▶05 Performance Evaluation ▶03 Problem ▶06 Conclusion 1 Background and Significance • The rapid development of mobile communication and computing technology • Limitation of the computational capability of mobile devices • Cloud computing and vehicular edge computing(VEC) 2 Data set We simulate two different traffic models: 1.congested scenario 2.uncongested scenario Uncongested scenario Congested scenario Intervals t=1~2500 t=1~2500 Traffic model parameters λ=1 λ=2 3 Problem 1.How to improve computational reusability by mining data similarity. 2.The tasks generated by vehicles typically have bandwidth limitations. 4 Solution For tasks with spatiotemporal attributes, the inputs of tasks with similar attributes tend to produce similar outputs. Task reusability assessment: 1. same vehicle position coordinates 2. same task attributes (bandwidth, workload, task size) Our goal is to make full use of bandwidth resources to reduce system cost as much as possible. Thus, we can conclude that this is a 0-1 knapsack problem and is NP-hard. Allocable bandwidth resource → backpack capacity Bandwidth that needs to be allocated for task → volume of the item System cost generated by the completion of the task → value 𝑑𝑝[𝑝][𝑞] = 𝑚𝑖𝑛(𝑑𝑝[𝑝 − 1][𝑞] + 𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒[𝑖0], 𝑑𝑝[𝑝 − 1][𝑞 − 𝑛, 𝑖] + 𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒[𝑖𝑚]) Combining Task Reusability Assessment and Dynamic Programming to form our DPS-CR algorithm. 5 Performance Evaluation 6 Conclusions •Multi-Base Station Environment •Bandwidth-Constrained Tasks •Optimizing BS Storage Capacity and Spatiotemporal Task Reusability THANKS FOR YOUR ATTENTIONS