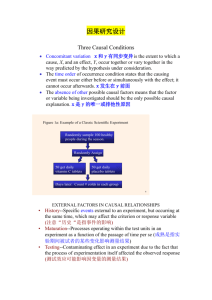
9 Research I Quarter 3 – Module 1: Research Design DIVISION OF ANGELES CITY Research I – Grade 9 Alternative Delivery Mode Quarter 3 – Module 1: Research Design First Edition, 2021 Republic Act 8293, section 176 states that: No copyright shall subsist in any work of the Government of the Philippines. However, prior approval of the government agency or office wherein the work is created shall be necessary to exploit such work for a profit. Such agency or office may, among other things, impose as a condition the payment of royalties. Borrowed materials (i.e., songs, stories, poems, pictures, photos, brand names, trademarks, etc.) included in this module are owned by their respective copyright holders. Every effort has been exerted to locate and seek permission to use these materials from their respective copyright owners. The publisher and authors do not represent nor claim ownership over them. Published by the Department of Education Regional Director : May B. Eclar PhD, CESO V OIC Asst. Regional Director : Rhoda T. Razon EdD, CESO V Development Team of the Module Writer: Lolita G. Bautista Editors: Cazarina L. David, Mary Ann Manlapaz, Jennilyn C. David Reviewers: Gemima A. Estrabillo, Emily F. Sarmiento, Hermes P. Vargas, Adrian P. Tamayo, Krislene Ida N. Mercado, Noel S. Reganit, Wajavina N. Catacutan, Billy Ray B. Manuel, Marvin R. Leano, Gemmarie G. Rivas Illustrator: Norween T. Malonzo Layout Artist: Norween T. Malonzo Management Team: May B. Eclar PhD, CESO V Rhoda T. Razon EdD, CESO V Ma. Irelyn P. Tamayo PhD, CESE Fernandina P. Otchengco PhD, CESE Librada M. Rubio PhD Ma. Editha R. Caparas EdD Emily F. Sarmiento, PhD Gemima A. Estrabillo, PhD Rochella C. David Printed in the Philippines by ________________________ Department of Education – Region III – Schools Division of Angeles City Office Address: Jesus St., Pulungbulu, Angeles City Telephone: (045) 322-5722; 322-4702; 888-0582; 887-6099 E-mail Address: angeles.city@deped.gov.ph 9 Research I Quarter 3 – Module 1: Research Design Introductory Message This Self-Learning Module (SLM) is prepared so that you, our dear learners, can continue your studies and learn while at home. Activities, questions, directions, exercises, and discussions are carefully stated for you to understand each lesson. Each SLM is composed of different parts. Each part shall guide you step-bystep as you discover and understand the lesson prepared for you. Pre-tests are provided to measure your prior knowledge of lessons in each SLM. It will tell you if you need to complete this module or if you need to ask your facilitator or your teacher's assistance for a better understanding of the lesson. At the end of each module, you need to answer the post-test to self-check what you are learning. Answer keys are provided for each activity and test. We trust that you will be honest in using these. In addition to the material in the main text, notes to the Teacher are also provided to our facilitators and parents for strategies and reminders on how they can best help you with your home-based learning. Please use this module with care. Do not put unnecessary marks on any part of this SLM. Use a separate sheet of paper in answering the exercises and tests. And read the instructions carefully before performing each task. If you have any questions using this SLM or any difficulty in answering the tasks in this module, do not hesitate to consult your teacher or facilitator. Thank you. 1 What I Need to Know This module was designed and written with you in mind. It is here to help you master the principles of research design. Once the principles of research design have been learned, students are now ready to write the research proposal or any other application on the principles of research design. The language used recognizes the diverse vocabulary level of students. The activities are arranged to follow the standard sequence of the course. But the order in which you read them can be changed to correspond with the textbook you are now using. The module contains: Lesson 1 – Principles of Research Design (Apply Principles of Research Design – MELC Q3W1) After going through this module, you are expected to: identify the variables, recognize the basic research principles, and apply the research design structures. 2 What I Know Directions: Read each question carefully. Choose the letter of the correct answer. 1. Which of the following best describes a research design? a. It serves as a framework for the literature review and answering the research questions. b. It is the overall strategy that you choose to integrate while planning the research proposal. c. It makes the conclusion valid because it takes into consideration all the assumptions that went into deriving the various inferences. d. It ensures that appropriate data will be obtained that permits an objective analysis, leading to valid inferences about the stated problem. 2. How many tests do homogeneous experimental units be subjected to the same treatment under similar conditions? a. at least one replicate c. minimum of three replicates b. minimum of two replicates d. multiple times 3. Anna thinks that if people are exposed to ultraviolet light then they are more likely to get skin cancer. She designs an experiment wherein sample A consisted of people who were exposed to ultraviolet light and sample B was not. Which is the independent variable in the problem? a. skin cancer c. exposure to ultraviolet rays b. samples A and B d. people who are exposed to ultraviolet light 4. A researcher plants three plots of flower seeds. He weeds and waters the first plot every day. He weeds and waters the second plot every other day. He leaves the third plot alone. After 12 weeks, the researcher measures the height of each flower. What is the role of the plots of flowers in the experiment? a. control group c. dependent variable b. experimental units d. independent variables 5. Justin B. believes that the temperature lowering during the fall months is what causes the color of the leaves to change. He set up an experiment wherein he placed some plants in 80 degrees rooms and some in 60-degree rooms. He then observed the color of the leaves for a total of 1 month. At the end of the month, Justin observed that ¾ of the plants in the 60-degree temperature had been to change colors and only ¼ of the plants in the 80degree temperature began to change colors. What is the dependent variable in the problem? a. the changing colors of the leaves b. temperature lowering during the fall months 3 c. ¾ of the plants placed in the 60-degrees temperature d. ¼ of the plants placed in the 80-degrees temperature 6. The boss in a company wants to experiment if workers will complete the 2 months of stress management training will lessen their number of sick days in a year. How should the control group in this experiment be treated? a. no participation in the stress training program b. complete the stress training program for 2 months c. participate in different training programs in 2 months d. participate in the stress training program at different number of days For questions 7-10, refer to the given situation. Situation: A farmer wants to study whether organic fertilizer will increase the growth of the lettuce plants at a fast rate. He used 20 lettuce plants for this experiment. He randomly chose 10 lettuce samples treated with organic fertilizer while the remaining 10 samples are to be treated with commercial fertilizer. The amount of water and sunlight are kept the same for all the sample plants. 7. What type of experiment design is used in the given situation? a. complete block design b. completely randomized design c. randomized complete block design d. both b and c 8. Which are the experimental units? a. 10 lettuce plants without fertilizer b. 10 lettuce plants with organic fertilizer c. 20 lettuce plants used in the experiment d. 40 lettuce plants used in the experiment 9. What is the purpose of keeping the same amount of water and sunlight for all lettuce plants? a. serve as extraneous variables b. to focus on the experimental treatment c. to know other variables that may contribute to the growth of the lettuce plants d. both a and b 10. What is the primary purpose of having a group of 10 lettuce plants treated with commercial fertilizer? a. control b. extraneous c. experimental d. study subject 4 Lesson 1 Research Design A. Definition: The research design serves as a framework for research planning and answering your research questions. Formulating your research design means determining the following (McCombes 2020): What type of data do you need? Who are the sources or the participants of your study? Which variables and or hypotheses (if relevant) will you investigate? How will you collect and analyze your needed data? B. Significance: It serves as a guide for direction during the actual experimentation. It allows a gain of maximum information relevant to the problem at a minimum cost. It makes the statistical test of significance valid because it takes into consideration all the assumptions that went into deriving the various statistics. 5 What's In In our previous lesson, you were introduced to a scientific method. Let us recall by exploring the processes involved. Directions: Label each arrow with the correct step in the scientific method. First 1. A question that needs to be answered 2. A process skill that uses the senses to gather information 3. An educated guess 4. A procedure to test the hypothesis 5. Collect, record, and examine the data Compare the hypothesis result in the experiment 6. Hypothesis supported Hypothesis not supported Share results 7. Figure 1: Scientific Method 6 What's New The research design refers to the complete sequence of steps that will be undertaken in a project. The design should ensure that appropriate data will be obtained in a way that permits an objective analysis, leading to valid inferences concerning the stated problem. Preparation of the research design is a step in problem-solving, consisting of a detailed plan to be followed to obtain the needed data. One of the basic elements that you must consider when planning the sequence of steps that will embody the research design is the identification of variables. In research, variables are any characteristics that can take on different values, such as height, age, species, or exam score. In scientific research, we often want to study the effect of one variable on another one. Classification of Variables There are different ways of classifying variables. The method of classification will depend on what stage of the research process you are in. When formulating the experimental design, you classify the variables based on cause and effect because you need to define the relationships that exist between your variables. Classes of Variables Based on Cause and Effect: Independent or Manipulated Dependent or Responding Extraneous or Constant Variables in the Research Design When you design your experiment, you need to make sure that you have covered all your bases in terms of the different types of variables used, the values for the identified variables, and the time that each variable takes on a value. Here are guide questions that you may use to determine if you have covered all the bases: Independent Variables - What variables will you manipulate or vary? Extraneous Variables - What will you keep constant during experimentation or data gathering? Dependent Variables - What will you observe during and/or after experimentation/testing? 7 Here is the example showing the application of the three variables: Type of variable Definition Example (fertilizer added to plants experiment) Independent variables Variables you manipulate The amount of fertilizer added to affect the outcome of an to each plant’s water. experiment. Dependent variables Variables that represent the outcome of the experiment. Any measurement of plant health and growth: in this case, plant height. Extraneous variables Variables that are held constant throughout the experiment. The temperature and light in the room the plants are kept in, and the volume of water given to each plant. Table 1: Independent vs dependent vs extraneous variables Groups in Experiment Design An experimental group is a test sample or the group that receives an experimental procedure. This group is exposed to changes in the independent variable being tested. A control group is a group separated from the rest of the experiment such that the independent variable being tested cannot influence the results. While all experiments have an experimental group, not all experiments require a control group. Controls are extremely useful where the experimental conditions are complex and difficult to isolate. Experiments that use control groups are called controlled experiments. Let us Check our New Learning on Variables! SPOT THE VARIABLES Directions: Read the following experiments and fill in the blanks that follow. Hint: One problem does not contain a control group 1. A study was conducted to test the effects of jazz on people's sleeping patterns. The experiment hypothesized that if people listened to jazz music as they fell asleep, they would sleep for more extended periods. For the experiment, two groups of people were created. One group was placed in a quiet room where they went to sleep, and they were timed on how long they slept. The other group was placed in a room where jazz music softly played as they began to sleep and 8 played throughout the night. As each group awoke, their sleep times were monitored. Independent Variable: __________________________________________________________________________________ Experimental Group: __________________________________________________________________________________ Control Group: __________________________________________________________________________________ Dependent Variable: __________________________________________________________________________________ Extraneous Variables: __________________________________________________________________________________ 2. A student wanted to test how the mass of a paper airplane affected the distance it would fly. Paper clips were added before each test flight. As each paper clip was added, the plane was tested to determine how far it would fly. Independent Variable: __________________________________________________________________________________ Experimental Group: __________________________________________________________________________________ Control Group: __________________________________________________________________________________ Dependent Variable: __________________________________________________________________________________ Extraneous Variables: __________________________________________________________________________________ Sources: Kathryn's experimental design examples – Course Hero VARIABLES WORKSHEET #2: MORE PRACTICE - pch.district70 What is It The research design refers to the overall strategy that you choose to integrate the different components of the study coherently and logically, thereby, ensuring you will effectively address the research problem; it constitutes the blueprint for the collection, measurement, and analysis of data. The following are the basic elements that you must consider when planning the sequence of steps that will embody the research design: 1. Identification of variables 2. Application of basic research principles 3. Consideration of the research design structure 9 I. Variables A variable is any entity that can take on different measurable or observable values. The use of variables is an intrinsic part of any investigative research. Variables are used as the point of comparison between two or more objects or experimental units, as a means for specifying the focus of the investigation, and as the basis for defining the scope of a project. (Detailed discussion of the classification of variables in this module - What's New) Variables in Engineering Projects Experimentation is not always apparent in engineering projects because in creating a new device, software, or system, there is already a design in mind that is based on known concepts and theories. What you need to remember, though, is that when a new product is created it needs to be tested in terms of functionality and efficiency. In an engineering project, the use of variables is applied mainly during the testing phase, when the product is being evaluated for its performance or effectiveness in providing a solution to the real-life problem. Testing a product follows the same process of identifying independent and extraneous variables, setting values for these variables, and then making observations to come up with values for the dependent variables. It is done only when it has been proclaimed by the researcher that the product is “finished.” This means that the prototype is built and that there are no more changes that will be made to its design or functional specifications. Example of an engineering project: A salt manufacturing device was designed to be able to produce mineral-rich salt via solar method at a faster rate than ordinary methods. To test the performance of the salt manufacturing device, the following variables are identified: Independent variable: method of salt production (two values are “using the created device” and “via traditional method.”) Extraneous variables: amount of saltwater used source of saltwater (thus the assumption that the salinity of the water is constant) I. exposure of the saltwater in the device to sunlight Basic time Principles of Research Design place of exposure Dependent variables: time for total evaporation to occur, in minutes amount of salt produced, in grams mineral content of the salt produced (list of minerals in grams per unit weight of salt) 10 Source: Variables - BSICR-Ch-4-Copy II. Basic Principles of Research Design For a Research Design to be considered sound, three basic principles are expected to be present: Local control refers to the balancing, grouping, and blocking of experimental units so that the units within each block are relatively homogeneous. In engineering projects where new products or systems are created, the product or system itself may be considered as the experimental unit. Examples are a prototype of a device or a computer program that is subjected to various treatments (test cases) to determine its correctness and consistency in performance. Replication refers to the conduct of an experiment or test using three or more homogeneous experimental units subjected to the same treatment under similar conditions. In the case of technical research where the product of design is the lone experimental unit, replication refers to the repetition of a test under controlled conditions. Replication makes the test of significance possible. Randomization refers to an unbiased method of assignment of experimental units (or subjects) to the treatment/s or vice versa. It assures the validity of the statistical tests of significance. The Experimental Units Before you start verifying if you have considered the three basic principles of research design in your project, make sure that you have correctly identified your experimental units first. An experimental unit also referred to as the experimental subject, is the focus of testing or experimentation. It is the organism, material, product, or device that is subjected to one or more treatments and is, therefore, the source of observation or data. It could be plants, animals, or inanimate objects. Examples are lettuce heads, bacterial culture set-ups, mice pieces of wood, and rabbit human testers. Checklist of Applied Principles After identifying your experimental unit, you may now check if the three basic principles of research design are evident in your project: 1. Local Control Do all experimental units that receive the same treatment bear the same characteristics? 2. Replication 11 For every treatment (experimental or control) or test, do you have a minimum of three replicates? 3. Randomization Is there a randomization method used to divide the experimental units in each block among the various treatments? Note that if randomization were done, it would not matter what treatment is assigned to an experimental unit. III. Basic Types of Research Design A good research design also considers the organizational structure of the experimental units. There are two basic types: completely randomized design and randomized complete block design. The other designs are variations of these two basic types. Completely Randomized Design (CRD) is used when the set of experimental units is homogeneous concerning the factors that may affect the results. Each experimental unit is simply assigned a treatment randomly. In the figure below, there are a total of nine experimental units, all of the same type. Any three experimental units may be assigned for each of the three treatments (T1, T2, T3). Figure 1: Experimental units assigned randomly in three treatments Source: Variables - BSICR-Ch-4-Copy Randomized Complete Block Design (RCBD) is used when the experimental units have varying characteristics that may affect the results of the experiment. When this happens, the units are divided into homogeneous groups or blocks. Within each block, the subjects are assigned treatment randomly. The result is that all treatments should be assigned to corresponding experimental units within each block. 12 Figure 2: Experimental units divided into three blocks and assigned treatment randomly Source: Variables - BSICR-Ch-4-Copy The sample illustration above shows three types of frogs, hence the division into three blocks. Within each homogeneous block, treatment is assigned to three frogs. Note that the number of replicates per treatment is still three. Because the frogs in Block 2 are different from those in Block 1, they are considered as different set-ups. Features of a Good Design A good research design should have a well-defined set of experimental units. Before execution of the project, it must be verified that the experimental units have homogeneous characteristics or have been classified accordingly into homogeneous groups. If the characterization and blocking of experimental units are done properly, it should be easy to verify if these basic principles (replication, local control, and randomization) are applied in the research design. Once the basic elements of the research design are set, then you are ready to write the research proposal. What's More Directions: Read the situation below and answer the guide questions for each of the activity that follows. Situation: A footwear company wants to test the effectiveness of its new insoles (soft insole and air-fill insole) designed to prevent shin splints resulting from running. They hire a group of physical trainers and a statistician, who recruits 100 healthy adult runners with the same age range to participate in a study. The statistician randomly assigns the 60 runners to follow the same weekly running schedule, wherein 30 runners will use new insoles and the remaining 30 will use the existing insoles the company already sells. After 10 weeks, the statistician records the number of runners from each group that has developed shin splints. They made sure that the results are valid that they have performed the testing three times for each treatment. Activity I: Identification of Variables Guide Questions: 1. Which is the independent variable? 13 ____________________________________________________________________________ 2. Which is the dependent variable? ____________________________________________________________________________ 3. What are the extraneous variables? ____________________________________________________________________________ Activity II: Recognition of Basic Research Principle Guide Questions: 1. What is the primary purpose of the 30 runners who used the new insole in the experiment? ___________________________________________________________________________ 2. What is the significance of the 30 runners who used the existing insole in the experiment? ___________________________________________________________________________ 3. How is replication applied to test the significance of the result? ___________________________________________________________________________ Activity III: Application of Research Design Structure Guide Questions: 1. What type of research design was used in the situation? Why? ___________________________________________________________________________ 2. Illustrate the type of research design used in the situation. Show how the samples were assigned to the treatments. What I Have Learned Directions: Fill in the blanks with the correct word/s. 1. ___________________ means planning a set of procedures to investigate a relationship between variables. 2. ___________________ is the variable you think is the cause, while a/an ___________________ is the effect. 3. An treatment group, also known as a/an ____________________, receives the treatment whose effect researchers wish to study. 14 4. The ________________________ refers to the balancing, grouping, and blocking of experimental units so that the units within each block are relatively homogeneous. 5. The ____________________ receives no treatment in the experiment. 6. In a/an _____________________________, every subject is assigned to a treatment group at random. 7. ______________________________ is used when the experimental units have varying characteristics that may affect the results of the experiment. 8. __________________ refers to the repetition of a test under controlled conditions. 9. In a controlled experiment, ______________________are held constant to focus on your experimental treatment. 10.In an engineering project, when the researcher says that the product is “finished,” it means that the _______________ is built and that there are no more changes that will be made to its design or functional specifications. What I Can Do Directions: Read the given situation, identify the variables, and illustrate a research design structure. Situation: A local pharmaceutical company introduced Moringa D, a new pill that has a good chance of helping people lower their blood sugar. Typically, the Hemoglobin A1C test is a way to measure the average blood sugar for the last three months. The company hopes that the pill lowers blood sugar as shown with lowered AIC. To experiment, 100 diabetic patients were randomly selected into two groups: patients who would take the New pill and patients who would take the popular Brand A pill in the market. Guide questions: 1. What is the role of Moringa D in the experiment? ____________________________________________________________________________ 2. What is the significance of having a lowered AIC in the experiment? ____________________________________________________________________________ 3. What are the extraneous variables? ____________________________________________________________________________ 4. Which is the experimental unit and what treatment is applied? ___________________________________________________________________________ 15 5. How should the control group in this experiment be treated? ___________________________________________________________________________ 6. Illustrate how the samples are assigned using a Randomized Complete Block Design. Show the repetition of tests in triplicate in each treatment. Assessment Directions: Read the situation carefully and answer the questions that follow. Choose the letter of the correct answer. Situation #1. Gym instructress Korina wants to determine if keto diet consumption affects blood pressure. She recruits 100 households and randomly assigns each household to either a keto-free diet or a keto-based diet. At the end of two months, she plans to record the original and final blood pressures for members of each household. 1. What a. b. c. d. is the cause variable? the households keto-diet consumption change in blood pressure members of each household 2. What a. b. c. d. is the response variable? the households keto-diet consumption change in blood pressure members of each household 3. Who/what are the experimental units and the treatment? a. households with keto-based diet b. households with changes in blood pressure c. members of each household with a keto-free diet d. members of each household with a keto-based diet 4. Who/what are the control groups? a. the household 16 b. members of each household c. households with a keto-free diet d. households with a keto-based diet 5. Which is the best way to assign samples using a completely randomized design? a. random select 75 households with keto-based and 25 with keto-free diets b. random select 75 households with keto-free and 25 with keto-based diets c. random select 50 households with keto-based diet and 50 households with keto-free diet d. random select 50 households with other diet and randomly select 25 with keto-based and 25 keto-free diets Additional Activities Directions: Read the given engineering project and answer the questions that follow. Situation: Graphene is proven in several studies to possess high energy storage. A local manufacturer designed a graphene-made battery that has a longer charge capacity. To test the performance of his invention, he compared the charge capacity of a graphene-made battery to a conventional battery in the market. Guide questions: 1. What is the independent variable? _________________________________________________________________________________ 2. What are the extraneous variables? _________________________________________________________________________________ 3. What is the dependent variable? _________________________________________________________________________________ 4. What is the experimental treatment applied? _________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Which is the control in the experiment? 17 _________________________________________________________________________________ 6. If you were the manufacturer, how will you test the performance of your invention? _________________________________________________________________________________ Answer Key 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. d b c b a a b b d a What’s In 1. Identify the problem 2. Observe 3.Formulate hypothesis 4. Conduct experiment 5. Gather and analyze data 6. Draw conclusion 7. Communicate results 18 What's New 1. Problem Independent Variable: jazz music played Control Group: No jazz music while sleeping Experimental Group: Listened to jazz music while sleeping Dependent Variable: Sleep length Extraneous Variables: same jazz music, activities of people time of sleeping Activity 3: 1. Completely Randomized Design because each experiment unit is simply assigned a treatment randomly. 2. To illustrate: -Two treatments: T1 as new insole, T2 as existing insole -Assign the 60 runners randomly into two groups: 30 runners using new insole and 30 runners with existing insole -Illustration What I Know Answer Key What I Have Learned 1. Research Design 2. Independent and Dependent Variables 3. Experimental group/units 4. Local control 5. Control group 6. Completely Randomized Design 7. Randomized Complete Block Design 8. Replication Problem 2: 9. Extraneous variables Independent 10. prototypevariable: Mass What’s New of the paper airplane Control group: no paper clip Experimental group: with paper clip added Dependent Variable: The distance the paper plane fly Extraneous variables: size of the paper plane, type of paper use, same weather condition Assessment 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. b c a c c What Can I Do 1. Independent variable 2. Dependent variable or the effect on the changes in independent variable 3. all are diabetic patients, range of sugar level in the blood, dosage of pills 4. patients who will take the Moringa D 5. patients who will take the What’s More popular Brand A pill Activity 1: 1. Independent Variable: new insoles 2. Dependent Variable: prevent shin splints Extraneous Variables: same age range and sports, same weekly running schedule Activity 2: 1. Experimental group: 30 runners with new insoles 2. Control group: 30 runners with existing insoles the Additional company sells Activities 3. The test was repeated three times for added each 1. graphene treatment. 2. ampere, charging time 3. longer charging capacity 4. graphene-made charger 5. conventional charger 6. Test the prototype sample charger and the conventional one. Observe the extraneous variables on both treatment. Repeat testing at least thrice on both treatment. 19 What Can I Do 2 Blocks (Male and Female), treatment is assigned to both blocks. Number of replicates per treatment is three. Block I Male Block 2 Female 25 25 25 25 25 25 T1 T1 T1 T2 T2 T2 25 25 25 25 25 25 T1 T1 T1 T2 T2 T2 References Bevans, Rebecca. 2020. “A Quick Guide to Experimental Design: 4 Steps & Examples.” Scribbr. 2020. https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/experimental-design/. Chupungco, Ana Maria A. 2013. “Variables.” Accessed January 17, 2021. BSICRCh-4-Copy. De Vaus, D. A. 2001. “Research Design in Social Research.” SAGE. 2001. https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/researchdesignsethods Knowledge Base. 2006. "Experimental Design Multiple Choice Test-Review Game Zone." Accessed December 30, 2020. http://bit.ly/3oxEm6e. “Introduction to experiment design.” Accessed January 19, 2021. https://www.khanacademy.org/math/ap-statistics/gathering-dataap/statistics-experiments/v/intro-experiment-design. “Kathryn's Experimental Design Examples Worksheet.” n.d. Course Hero. Accessed January 10, 2021. https://www.coursehero.com/file/45514515/Kathrynsexperimental-design-examples-worksheet/. McCombes, Shona. 2020. "Research Design: Types, Methods, and Examples." Scribbr. September 21, 2020. https://www.scribbr.com/researchprocess/research-design/. Schmied, John. 2020 "Experimental design version 4.3." https://www2.slideshare.net/jschmied/experimental-design-verision-3. Wichmanowski, Taylor. "Evaluating Existing Experimental Designs." Last modified July 29, 2014. https://betterlesson.com/lesson/619737/evaluating-existingexperimental-designs. 20 For inquiries or feedback, please write or call: Department of Education – Region III – Division of Angeles City Jesus St., Pulungbulu, Angeles City Telephone No.: (045) 322-5722; 322-4702; 888-0582; 887-6099 E-mail Address:angeles.city@deped.gov.ph