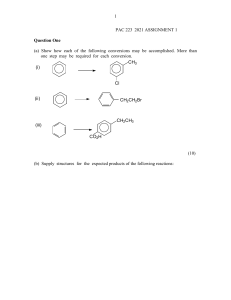
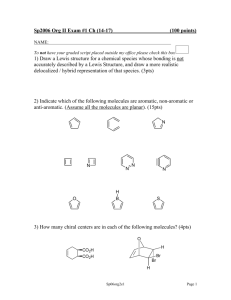
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL AS & A LEVEL CHEMISTRY: COURSEBOOK Exam-style questions and sample answers have been written by the authors. In examinations, the way marks are awarded may be different. Coursebook answers Chapter 25 Self-assessment questions 1 a d 6 b p (or 2p) orbitals c electrons that are free to move around the molecule in the π bonding system above and below the plane of the carbon atoms in the benzene ring d e Br Br In benzene the six electrons in the π bonding system are no longer associated with any particular carbon atoms in the molecule, whereas in hex3-ene the two electrons in the π bond in the centre of the molecule are only found above or below the central two carbon atoms. i CH3 Br 3 Br e The hydrogen atoms in the —CH3 side-chain would be all or partially replaced by Br atoms. f free-radical substitution a i C6H4(NO2)CH3 + H+ ii C6H4(NO2)CH3 + H2O iii 1-methyl-2-nitrobenzene and 1-methyl-4-nitrobenzene iv CH3 CH3 NO2 Br Br ii Cl O2N i ii 2 b i sulfur atom 2-methylphenol ii 1-bromo-2,3-dichlorobenzene C6H6 + SO3 → C6H5SO3H 4 C6H5CH2CH2CH3 + HCl Cl + Cl2 AlCl3 b + HCl H stage 1 Cl+ ⎯⎯→ i Cl stage 2 ⎯⎯⎯→ [AlCl4]– i ii c Cl + a ii electrophilic substitution c 1 1-methyl-2,4, 6-trinitrobenzene Cl a b NO2 NO2 1-methyl-2, 4-dinitrobenzene f NO2 O2N + HCl (+AlCl3) C6H5COCH2CH2CH2CH3 + HCl propylbenzene (aryl) ketone With hexylbenzene, the hexyl side chain would be oxidised to form an aryl carboxylic acid (and the purple potassium manganate(VII) solution would be decolourised), whereas no reaction would occur with hexane. Cambridge International AS & A Level Chemistry © Cambridge University Press 2020 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL AS & A LEVEL CHEMISTRY: COURSEBOOK d i ii 5 HCl, CH3COOH, C6H5OH, H2O, C3H7OH b Methanol is less acidic than phenol because methanol has an electrondonating methyl group attached to the oxygen atom in the methoxide ion that is formed on dissociation. This has the effect of concentrating more negative charge on this oxygen atom, which more readily accepts an H+ ion, re-forming undissociated methanol. On the other hand, the phenoxide ion, C6H5O−(aq), has its negative charge spread over the whole ion as the benzene ring draws in electrons from the oxygen atom, reducing the attraction of this ion for H+ ions. i ii i O−K+ A a c 6 c Heat / hydrogen / nickel or platinum catalyst Phenylamine, sodium nitrate(III) / sodium nitrite and dilute hydrochloric acid (water) ii O−Na+ iii OH OH Br or Br iv OH OH NO2 or NO2 ice / below 10 °C a C6H5OH, C6H5CH3, C6H6, C6H5COOH (remember —COOH is a deactivating group) b i OH OH Cl Cl + 3HCl + 3Cl2 Cl ii 2 A catalyst of AlCl3 would be needed. Cambridge International AS & A Level Chemistry © Cambridge University Press 2020