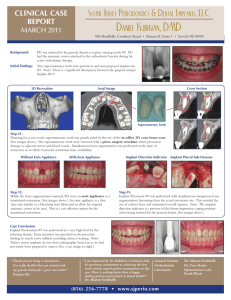
Abutment Selection for Fixed Dental Prostheses True Or False The Clinical Use Of Ceramic Abutments In Molar Sites Is Recommended Since Their Behavior In These Sites Has Been Sufficiently Documented. False True Or False Abutments For A Screw-Retained Bridge Should Have A Non-Engaging Design. True True Or False Abutments May Be Incorporated Into The Implant. True Multiple Choice Zirconium Dioxide Abutments Made With Cad/ Cam Technology (Similar To Those Seen In The Illustration) Can Be Used For Both Screw- And Cement-Retained ImplantSupported Crowns And Bridges. Screw- And Cement-Retained ImplantSupported Crowns And Only Screw-Retained Bridges. Screw- And Cement-Retained ImplantSupported Crowns And Only Cemented Bridges. screw- and cement-retained implant-supported crowns and only cemented bridges. Match Match The Statements On The Left With Their Counterpart On The Right Using Drag & Drop: Gold As An Abutment Material Is Recommended For Most Applications. Titanium Standard Abutments Are Recommended For Customized Abutments, Single Crowns, Bridges And Bars Pmma Abutments Are Recommended For Provisional Restorations Gold as an abutment material is recommended for customized abutments, single crowns, bridges and bars Titanium standard abutments are recommended for most applications. PMMA abutments are recommended for provisional restorations Multiple Response What Are The Advantages Of Customizing An Abutment With The Use Of Cad/Cam Technology: Time Efficient Stable Quality And Precise Outcomes The Use Of Materials Like Zirconium Dioxide Is Possible Which Offers An Esthetic Advantage (E.G. In Cases With A Thin Periodontal Phenotype (Biotype) Individualization Of Angulation And Support For Veneering Material Individualized Emergence Profile And Margin Of Final Restoration (Two Piece Implants) stable quality and precise outcomes The use of materials like zirconium dioxide is possible which offers an esthetic advantage (e.g. in cases with a thin periodontal phenotype (biotype) Individualization of angulation and support for veneering material Individualized emergence profile and margin of final restoration (two piece implants) Multiple Response To Customize An Abutment, The Following Different Manufacturing Processes Are Possible. Lost Wax/Casting Method To Produce A Gold Abutment. Cad/Cam Designed And Manufactured Titanium Or Zirconium Dioxide Abutment. A Bonded Ceramic Abutment On A Titanium Base. Pressed Method To Fabricate An Anatomic Abutment Of A Wax-Up Design Which Is Embedded And Pressed In Ceramic. Lost wax/casting method to produce a gold abutment. CAD/CAM designed and manufactured titanium or zirconium dioxide abutment. A bonded ceramic abutment on a titanium base. Multiple Response Which Of These Abutment Materials Are Recommended For Posterior Sites? Zirconium Dioxide Aluminum Oxide Gold Feldspathic Ceramic Titanium Gold Titanium True Or False An Implant Supported Abutment Offers A Similar Function As A Tooth That Is Prepared To Serve As An Abutment For A Tooth Supported Crown. True True Or False Peri-Implant Soft Tissue Formation And Appearance Is Important For The Esthetic Outcome . One Of The Factors That May Influence This Result Is The Underlying Abutment Material. True Multiple Response Which Of These Abutment Materials Are Recommended In The Esthetic Zone? Zirconium Dioxide Aluminium Oxide Gold Feldspatic Ceramic Pmma (Polymethyl Methacrylate) For Provisionals Zirconium dioxide Gold PMMA (Polymethyl methacrylate) for provisionals Match Match The Statements On The Left With Their Counterpart On The Right Using Drag & Drop: Column A: Aluminium Oxide Ceramic Abutments Cad/Cam Zirconium Dioxide Abutments Titanium Abutments Column B: Are Indicated For Anterior And Posterior Sites Are Not Recommended For Clinical Use Because Of A Higher Risk Of Fracture Are Only Indicated For Anterior Sites Aluminium oxide ceramic abutments are not recommended for clinical use because of a higher risk of fracture CAD/CAM zirconium dioxide abutments are only indicated for anterior sites Titanium abutments are indicated for anterior and posterior sites Fill In The Blank In The Anterior Maxilla, When The Soft Tissue Esthetic Demands Are High And The Patient Has A Thin Gingival Phenotype, ______ Abutments Are Recommended. Aluminum Oxide Cad/Cam Fabricated Zirconium Dioxide (Either Prefabricated Or Individualized) Titanium Standard Titanium Cad/Cam Fabricated Cast Gold zirconium dioxide (either prefabricated or individualized) Fill In The Blank Engaged Abutment Connection Designs ______________. Provide Precise Fit And Prevent Rotation Have Less Precise Fit Allowing Simultaneous Insertion Of Multiple Abutments In A Multi-Unit Prostheses. provide precise fit and prevent rotation Multiple Response Disadvantages Of Titanium Base Abutments Include The Following: The Tissue Reaction To The Small Bonding Gap Between The Two Components Is Not Known. The Resulting Hybrid Construction Combines The Disadvantages Of Metal And Ceramic Abutments. There Is Limited Clinical Evidence Available For This Abutment Type. There Is Often Insufficient Vertical Space To Use These Abutments. Fracture Of These Components Has Been Frequently Reported. The tissue reaction to the small bonding gap between the two components is not known. There is limited clinical evidence available for this abutment type True Or False The Prosthodontic Platform Is Always Part Of The Abutment. False True Or False Cad/Cam Manufactured Abutments Made Of Zirconium Dioxide Are Only Indicated In Anterior Sites. True True Or False The Selection Of An Implant Abutment Is Dependent On The Type Of Implant, The IntraOral Location, The Number Of Replaced Units, The Retention Type And The Abutment Material Selection. True Multiple Choice Abutments Cast In Gold Have The Advantage Of Providing A Fast And Therefore Time Efficient Workflow In The Dental Laboratory. Providing The Best Esthetic Results. Facilitating Screw Retention With ImplantSupported Bridges. facilitating screw retention with implant-supported bridges. Multiple Response An Implant Abutment Serves To Support And Retain An Implant Supported Prosthesis Is The Link Between The Implant And The Prosthesis Is Always Attached To The Implant By A Screw. May Provide The Prosthodontic Platform serves to support and retain an implant supported prosthesis is the link between the implant and the prosthesis may provide the prosthodontic platform Biological Principles of Bone Grafting Sequence Incorporation Of A Bone Graft Substitute Resembles That Of Autogenous Bone. Bring The Processes Involved Into The Correct Order Using Drag & Drop: Granulation Tissue Hematoma Formation And Inflammation Osteoconduction Various Degrees Of Resorption Hematoma formation and inflammation Granulation tissue Osteoconduction Various degrees of resorption Match Bone Grafts And Bone Substitutes May Be Classified According To Their Source Of Origin In Relation To The Intended Recipient: Column A Autogenous Bone Graft Allogeneic Bone Graft Xenogeneic Bone Graft Alloplastic Bone Substitute Column B The Graft Is A Synthetic Material The Graft Is Obtained From A Different Species Than The Intended Recipient The Graft Is Obtained From A Genetically Distinct Individual Of The Same Species The Graft Is Obtained From The Same Individual Autogenous bone graft The graft is obtained from the same individual Allogeneic bone graft The graft is obtained from a genetically distinct individual of the same species Xenogeneic bone graft The graft is obtained from a different species than the intended recipient Alloplastic bone substitute The graft is a synthetic material Sequence Bone Remodeling Is A Lifetime Process Of Bone Renewal And Consists Of Four Phases: Formation Mineralization Resorption Reversal Resorption Reversal Formation Mineralization True Or False The Process Of Stimulation Of Undifferentiated Mesenchymal Cells Into Osteoblastic Phenotypes That Produce Bone Is Called Osteoconduction. False True Or False The Extracellular Bone Matrix Consists Of About 10% Organic And 90% Inorganic Material. False Multiple Response The Bone Marrow Is A Specialized Connective Tissue Which Produces Red Blood Cells Bone-Forming Cells Platelets Many White Blood Cells red blood cells bone-forming cells platelets many white blood cells True Or False In Bone Modeling, Appositional Growth Of Bone Tissue Occurs On The Outer And Inner Surfaces Of The Bones And Generally Enhances The Total Amount Of Bone Mass. True True Or False Cancellous Bone Consists Mainly Of Osteons, Which Are Also Known As Haversian Systems. False Multiple Response The Organic Phase Of Extracellular Bone Matrix Consists Of: Collagen Type I Fibers Growth Factors Various Non-Collagenous Proteins Different Kinds Of Bone Cells collagen type I fibers growth factors various non-collagenous proteins True Or False Xenogeneic Bone Grafts Most Commonly Originate From Cattle. True Multiple Choice Osteoclasts: Are Bone Forming Cells Are Bone Resorbing Cells Provide Nutritional Transfer From The Surface Of The Bone To Osteocytes Within The Calcified Matrix May Play A Role In Regulation Of Lining Cells And Osteocytes are bone resorbing cells Multiple Response Allogeneic Bone Graft Refers To Bone Originating From Another Human. The Bone Graft Can Be: Fresh Fresh-Frozen Freeze-Dried Demineralized Freeze-Dried Bone fresh-frozen freeze-dried demineralized freeze-dried bone Multiple Response Autogenous Bone Grafts Can Be Harvested From Intraoral Or Extraoral Sites. The Intraoral Sites Could Be: Mandibular Ramus Mandibular Symphysis Adjacent To The Defect mandibular ramus mandibular symphysis adjacent to the defect Microscopically, Bone Can Be Categorized As Woven Or Lamellar. True Multiple Choice Woven Bone Is Characterized By: A Regular, Parallel Orientation Of The Collagen Fibrils Immature Bone Without Collagen Fibrils A Random Orientation Of The Collagen Fibrils a random orientation of the collagen fibrils True Or False Osteogenesis Is The Mechanism Whereby New Bone Is Formed By Osteoblasts That Are Present In The Graft. True True Or False Differences In Physicochemical Characteristics Among Bone Substitutes May Influence The Outcome Of Healing In Terms Of Amount Of New Bone Formation As Well As Residual Biomaterial In A Site Grafted With A Given Bone Substitute. True Multiple Response Particulated Autogenous Bone Has The Advantage Of Relatively Fast Incorporation In Comparison With Autogenous Bone Blocks. However, These Particles: Lack Structural Stability Undergo Extensive And Unpredictable Resorption Require Containment lack structural stability undergo extensive and unpredictable resorption require containment True Or False The Process By Which Bones Acquire Their Shape And Size Is Called Bone Modeling. True Multiple Response Alloplastic Bone Substitutes Are Synthetically Produced In The Laboratory. These Include: Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate Sea Coral Hydroxyapatite Sea Algae Polymers beta-tricalcium phosphate hydroxyapatite polymers Conventional Implant Impressions for Fixed Dental Prostheses True Or False An Implant Analogue Is An Exact Replica Of The Restorative Platform And/Or Implant-Abutment Interface That Is Incorporated Into The Laboratory Cast. True Multiple Choice This Image Demonstrates An Example Of: The Direct Pick-Up Impression Technique The Indirect Transfer Impression Technique An Open Tray Impression the indirect transfer impression technique Multiple Choice The Photograph Shows A Flexible Anatomic Soft Tissue Cast. Why Is This Used? It Allows The Implants To Move In The Model To Allow Passive Fit. The Flexible Material Mimics The Compressability Of Natural Soft Tissues. It Prevents Damage To The Model From Repeated Placement And Removal Of The Prosthesis During Manufacture. The flexible material mimics the compressability of natural soft tissues True Or False 'Soft Tissue Emergence Profile' Is The Term Used To Describe The Shape Of Soft Tissue In The Transition Zone From Top Of The Implant To The Mucosal Margin. True Sequence Place The Statements Regarding Conventional Implant Impression Workflow In The Correct Order Using Drag & Drop. Make The Impression Whilst Supporting The Tray And Clearing Access To The Impression Components If Needed Prepare The Site, Seat The Impression Coping, And Confirm That The Impression Tray Fits Without Conflict Make The Laboratory Working Cast With The Analog Securely Fitted To The Impression Component Select The Correct Impression Components, Tray, And Impression Technique Select the correct impression components, tray, and impression technique Prepare the site, seat the impression coping, and confirm that the impression tray fits without conflict Make the impression whilst supporting the tray and clearing access to the impression components if needed Make the laboratory working cast with the analog securely fitted to the impression component Multiple Choice The Image Shows Impression Copings Used With Which Of The Following Techniques? Direct Pick-Up Indirect Transfer Closed Tray Direct pick-up True Or False The Published Literature Supports The Direct Pick-Up (Open Tray) Technique As Leading To More Accurate Impressions. True True Or False A Radiograph Should Be Used To Confirm The Correct Seating Of All Impression Components. False True Or False Implant Impressions Can Be Taken At Both The Implant Level And The Abutment Level Depending On The Clinical Need And The Prosthodontic Plan. The Implant Analogs Used In Both Situations Are Identical. False Multiple Response Impression Trays For Use In Implant Impressions Must: Be Custom-Made For Each Case Be Perforated To Assist In Retaining The Impression Be Rigid Cover All Of The Area Of Interest Not Touch The Structures Or Components Being Recorded be rigid cover all of the area of interest not touch the structures or components being recorded Multiple Response Which Of The Following Types Of Impression Materials Are Suitable For Use In Implant Impressions? Irreversible Hydrocolloid Polyvinyl Siloxane Polyether Impression Compound Polyvinyl siloxane Polyether True Or False Stock Trays (Similar To That In The Image) May Be Used For Implant Impressions. Your Answer To This Question Was Correct. True True Or False Implant Manufacturers Make Impression Copings That Are Specific For Each Implant Type. True True Or False A Custom Impression Tray Is The Best Option For Achieving An Impression With An Optimal Thickness And Confinement Of Impression Material Around The Hard And Soft Structures And Implant Components To Be Recorded. True Multiple Response Implant Impression Components Must: Precisely Fit The Implant Be Made Of Commercially Pure Titanium Be Well Retained In The Impression Be Rigid precisely fit the implant be well retained in the impression be rigid True Or False When Using The Indirect Transfer Impression Technique, Inaccuracies May Occur When Reseating The Impression Components In The Impression. True Multiple Response What Is Needed For A Conventional Implant Impression? Impression Component Impression Tray Analog Temporary Abutment Impression Material Impression component Impression tray Analog Impression material True Or False Implant Level Impressions Offer Greater Prosthodontic Flexibility For The Selection Of Abutments. True True Or False Implant Impressions Must Be Very Accurate Because Of The Rigid Fixation Of Implants And The Precision Of Implant Components. True True Or False A Customized Impression Component Should Be Used To Support Soft Tissues And Transfer The Contours Of The Customized Emergence Profile In Cases Where A Provisional Prosthesis Has Been Used To Develop The Transition Zone. True Dental Materials Selection for FDPs True Or False Acrylic Resins Are Highly Biocompatible Materials. False True Or False Ceramics Are Ductile Materials. False Multiple Choice Which Of The Following Surface Configurations Will Be The Easiest For The Patient To Keep Clean? Convex Glazed Porcelain Convex Polished Metal Convex Polished Acrylic Concave Glazed Porcelain Concave Polished Metal Convex glazed porcelain True Or False A Material’S Color And Translucency Will Impact On The Esthetic Outcome. True False True Multiple Response A Patient With A Strong Bruxing Habit Is Having A 3-Unit Implant Fdp Made To Replace His Missing Upper Right Premolars And First Molar. His Bruxing Puts Him At Greater Risk Of Technical Complications And Wear On Opposing Teeth. What Strategies Might Be Employed To Minimize These Risks? Use A Monolithic Zirconia Fdp For Its Strength Use A Resin-Veneered Fdp That Can Be Repaired Easily Have The Occlusal Surfaces Of The Fdp Made In Metal That Will Cause Less Wear To The Opposing Teeth Ensure That The Fdp Is Designed With GroupFunction Occlusion Make The Fdp Framework With CobaltChromium Alloy To Reduce Flexure Use a resin-veneered FDP that can be repaired easily Have the occlusal surfaces of the FDP made in metal that will cause less wear to the opposing teeth Multiple Choice Flexure Of A Beam That Is Supported At Each End And Loaded In The Middle (A Three-Point Flexure Test) Is Related To The Thickness Of The Beam. Which Of The Following Describes The Relationship Between Flexural Stress And Beam Thickness (T)? Stress Is Proportional To Thickness Stress Is Proportional To The Square Of The Thickness Stress Is Inversely Proportional To The Thickness Stress Is Inversely Proportional To The Square Of The Thickness Stress Is Proportional To The Square Root Of The Thickness Stress is inversely proportional to the square of the thickness Multiple Response The Cost Of Making Implant-Supported Fdps Is An Important Consideration. Which Of The Following Factors Can Significantly Impact On Manufacturing Cost? The Type Of Veneering Ceramic Used The Mode Of Manufacture – Conventional Vs. Cad/Cam The Metal Alloy Used In Frameworks The Impression Technique Used – Open Tray Vs. Closed Tray Vs. Digital Whether Digital Planning Software And Guided Surgery Were Used To Place The Implants The mode of manufacture – conventional vs. CAD/CAM The metal alloy used in frameworks True Or False The Hardness Of A Dental Material Has No Impact On The Opposing Teeth. False True Or False The Skill And Artistry Of A Dental Ceramist Cannot Ever Overcome The Esthetic Limitations Of The Materials Used To Make Implant Fdps. False True Or False The Biocompatibility Of Dental Materials Used In Implant Fdps Is Of Little Importance To The Long-Term Survival Of The Prosthesis. False True Or False Flexure In Implant Fdps Is Related To Increased Risks Of Veneering Porcelain Fracture And Screw Loosening. True True Or False Zirconia Is A Highly Translucent Material. False True Or False Ceramic Restorations Are Easily Repaired If The Veneering Material Fractures. False True Or False Design And Processing Problems Can Cause Premature Failure In All-Ceramic Abutments And Prostheses. True True Or False Cad/Cam Technologies Have Good Long-Term Data To Support Their Use In The Manufacturing Of Implant Fdps. False Multiple Response A Full-Arch Implant-Supported Fdp Is Being Made For A Patient With Low-To-Moderate Esthetic Needs And Expectations. Which Of The Following Materials Could Be Used To Make A Cost-Effective Prosthesis? Stained Monolithic Zirconia Lithium Disilicate Ceramic Acrylic Resin On A Milled Titanium Framework Composite Resin Porcelain Fused To Gold Stained monolithic zirconia Acrylic resin on a milled titanium framework Multiple Choice Biocompatibility Is Normally Tested Using: Computer Simulations Of The Spread Of Components Of The Material In The Blood Stream Tissue Culture Tolerance Tests Samples Subcutaneously Embedded In Human Volunteers Immunofluorescence Assays Allergen Challenge Tests tissue culture tolerance tests Fill In The Blank Shear Stress Indicates A(N) ______ Force. Stretching Crushing Tearing Twisting Undulating tearing Multiple Choice A Patient Wih Full-Arch Implant Fdps In Both Jaws Is Able To Sense Tooth-Contact Via Proprioceptors In: Alveolar Bone Periodontal Ligaments The Facial Muscles And Tmjs The Schneiderian Membrane Surrounding Mucosa the facial muscles and TMJs Fill In The Blank Most Metallic Alloys Used In The Manufacture Of Fdps Have ______ Surface Hardness When Compared To Dental Enamel. Much Higher Higher Similar Lower Much Lower similar Digital Implant Impression True Or False Powder Systems Can Be Beneficial If Large Edentulous Areas With Stable Soft Tissues Are Scanned Intraorally. True True Or False The Wand Is A Type Of Abutment Which Is Recognized By An Intraoral Scanner. False True Or False Dicom (Digital Imaging And Communications In Medicine) Is The File Format To Store Raw Data Obtained From A Computed Tomograph. True True Or False The Largest Benefit Of Intraoral Scans Is The Shorter Time Needed For A Full Arch Impression False Multiple Response Advantages Of Digital Impressions Include: Easier Bite Registrations Less Environmental Load Generally Faster With Full Arch Reconstructions Removable Dental Prostheses Possible Easier Impressions Of Posterior Teeth Easier bite registrations Less environmental load A Benefit Of Intraoral Scanning Is The Low Acquisition Cost. That In-Office Milling Of Restorations Is Possible. That No Training Or Experience Is Needed. that in-office milling of restorations is possible. Multiple Response Which Of The Following Statements Regarding Intraoral Scanning Are True? Continuous Capture May Be Faster Than Stable Image Capture When Used By A Well Trained Dentist. The Wand Can Be Stabilized In Stable Image Capture By Resting The Tip Of The Wand On One Of The Neighboring Teeth. Stable Image Capture Systems Work With A Foot Switch Or In An Auto Detection Mode. Continuous capture may be faster than stable image capture when used by a well trained dentist. The wand can be stabilized in stable image capture by resting the tip of the wand on one of the neighboring teeth. Stable image capture systems work with a foot switch or in an auto detection mode. Generally, The Information From Intraoral Scans Is Saved As Stl (Standard Tessellation Language) Data. True True Or False Stl (Standard Tessellation Language) Is The File Format In Which An Intraoral Scanner Stores Its 3D Image. True True Or False Every Scanner Is Compatible With The Scan Bodies Of All Implant Brands False True Or False In Intraoral Scanning, Powder Free Systems Require Only The Scanned Area To Be Air Dry. True Multiple Response Advantages Of Conventional Impressions Include: Easier Bite Registrations Less Environmental Load Generally Faster With Full Arch Reconstructions Removable Dental Prostheses Possible Generally faster with full arch reconstructions Removable dental prostheses possible Multiple Response The Disadvantages Of Intraoral Scanning Include: An Initial Cost Investment Is Required The Process Is Prone To Errors The Cost Of Manufacturing Implant Supported Prostheses Is Usually Higher Training And Experience Are Needed Patient Acceptance Can Be Problematic An initial cost investment is required Training and experience are needed True Or False The Technique Of Continuous Capture Can Be Faster Than Stable Image Capture, When The Dentist Is Well Trained. True True Or False Cad/Cam Implant Restorations Based On Intraoral Scans Are Generally Less Expensive (Per Unit) Than The Ones Made With Plaster Models. True Multiple Choice A Challenging Situation For Using An Intraoral Scanner Is An Implant Close To Neighboring Teeth. A Single Tooth Replacement. A Patient With A Large Mouth Opening. an implant close to neighboring teeth. Multiple Choice In Which Of The Following Indications Can IntraOral Scanning Be Used? Single Tooth Replacement Long-Span, Multi-Implant Fdps Complete Dentures Single tooth replacement True Or False Scientific Studies Have Clearly Shown That The Continuous Capture Allows More Accurate Results To Be Obtained Than The Stable Image Capture. False Fill In The Blank Chair Side Restorations On Implants Are Most Often Made On ______ Abutments. Titanium Base Temporary Zirconia titanium base True Or False Continuous Capture Devices Always Require Powder Or Dust Application To Scan. False Flap Closure Multiple Response Primary Closure Of An Oroantral Communication Will Result In: A Coronal Displacement Of The Mucogingival Junction A Horizontal Displacement Of The Mucogingival Junction A Need For A Sinus Floor Elevation Procedure Prior To Implant Placement A Potential Need For A Combined HorizontalVertical Bone Augmentation Procedure a coronal displacement of the mucogingival junction a need for a sinus floor elevation procedure prior to implant placement a potential need for a combined horizontal-vertical bone augmentation procedure True Or False The Resorption Of Bone That Occurs Subsequent To Reflection Of The Periosteum Can Be Minimized By Avoiding Elevation Of A Flap. True Multiple Choice Delayed Complications Resulting From Flap Closure Include: Formation Of A Hematoma Secondary To Insufficient Hemostasis Development Of Wound Infection Scar Formation And Persistent Stitch Marks scar formation and persistent stitch marks Multiple Response Before An Elevated Flap Is Sutured, A Periosteal Releasing Procedure Must Be Performed In The Following Situations: Implant Placement With Simultaneous Bone Augmentation Bone Augmentation With A Bone Block One-Stage Implant Placement implant placement with simultaneous bone augmentation bone augmentation with a bone block Multiple Response The Figure-Of-Eight Suture: Can Secure A Hemostatic Dressing Is For Closure Of A Vertical Releasing Incision Only Can Secure Bone Grafting Material In A Ridge Preservation Procedure can secure a hemostatic dressing can secure bone grafting material in a ridge preservation procedure True Or False The Suturing Of A Repositioned Flap Is Performed From The Immobile Soft Tissue To The Adjacent Raised Flap. False Multiple Response Flap Elevation For Tooth Extraction May Be Necessary If: An Implant Is To Be Placed Afterwards There Is Significant Destruction Of The Tooth There Is A Root Deformity A Communication To The Maxillary Sinus Is Expected there is significant destruction of the tooth there is a root deformity a communication to the maxillary sinus is expected Multiple Response Tension-Free Flap Closure Is A Prerequisite To Suturing. This May Be Obtained By: Passive Repositioning Of The Flap Repositioning The Flap Over Healthy Bone Using A Firm Grip On The Wound Edges With The Tissue Forceps A Horizontal Periosteal Releasing Incision passive repositioning of the flap repositioning the flap over healthy bone a horizontal periosteal releasing incision Sequence The Steps Involved In A Two-Stage Implant Placement Procedure Are Different From Those In A One-Stage Implant Placement Procedure. In Terms Of The Sequence Of Steps Involved: Exposure Of Implant Implant Placement Placement Of Appropriate Abutment Placement Of Cover Screw Removal Of Cover Screw Repositioning Of Flap For Primary Closure Implant placement Placement of cover screw Repositioning of flap for primary closure Exposure of implant Removal of cover screw Placement of appropriate abutment Multiple Choice Healing By Secondary Intention May Lead To: A Rapid But Weak Soft Tissue Union Scar Tissue Formation A Rapid And Strong Soft Tissue Union scar tissue formation True Or False When Available Bone For Implant Placement Is Limited, Flap Elevation Can Reduce The Risk Of Bone Fenestrations. True Multiple Choice A Flapless Surgical Approach In Connection With Implant Placement May Be Used: To Get An Overview Of Anatomical Landmarks In Conjunction With A Simultaneous Bone Augmentation Procedure When There Is Adequate Bone Volume Available when there is adequate bone volume available True Or False The Specific Aims Of Flap Closure Include Repositioning Of The Soft Tissues In The Right Anatomical Position In Order To Achieve Hemostasis. True Multiple Response Great Care Must Be Taken With Flap Design And Flap Mobilization In The Esthetic Zone. Great Care Must Also Be Taken With Flap Closure. Damage To Papillae From Suturing Can Result In A Compromised Esthetic Outcome With: Hemorrhage Recession Scarring recession scarring True Or False An Extraction Socket Heals By Primary (First) Intention. False Sequence Wound Healing By Primary (First) Intention Is A Set Of Steps Resulting In Soft Tissue Union. Formation Of A Fibrin Net Formation Of Collagen Localized Coagulation Migration Of Fibroblasts Proliferation Of Capillaries Proliferation Of Epithelial Cells Localized coagulation Proliferation of epithelial cells Formation of a fibrin net Proliferation of capillaries Migration of fibroblasts Formation of collagen Multiple Response A Wound Dehiscence Is Defined As Incomplete Wound Healing In Which The Wound Edges Open Up Again Following Closure By Suturing. Both Local And Systemic Factors Can Contribute To The Occurrence Of Dehiscence. Among The Local Factors Are: Too Much Tension In The Flap Insufficient Blood Supply Smoking Compromised Healing Excessive Postsurgical Bleeding Lack Of Patient Compliance With Postoperative Instructions too much tension in the flap insufficient blood supply compromised healing excessive postsurgical bleeding True Or False The Horizontal Flap Is Commonly Sutured By Interrupted Single Sutures, Two At Each Papilla. False Sequence Wound Healing By Secondary Intention Is A Set Of Steps Resulting In Prolonged Soft Tissue Healing. Platelets Aggregate To Form A Thrombus (Clot) Macrophages Remove Necrotic Tissue And Fibrin Growth Factors Promote Tissue Proliferation Small Blood Vessels Hemorrhage Into Wound Granulation Tissue Repairs Wound From Base Upwards Epithelial Cells Proliferate To Cover The Wound Small blood vessels hemorrhage into wound Platelets aggregate to form a thrombus (clot) Macrophages remove necrotic tissue and fibrin Growth factors promote tissue proliferation Granulation tissue repairs wound from base upwards Epithelial cells proliferate to cover the wound Multiple Response The Purpose Of Flap Closure Is To: Reduce Chair Time Promote And Optimize Healing Reduce Complications Reduce Costs promote and optimize healing reduce complications ITI Disadvantages Of Conventional ToothSupported Fixed Dental Prostheses Include: Long Treatment Time Need For High Clinical Skill And Complex Laboratory Procedures Unpredictable Structural Performance Complications Including Caries And Loss Of Vitality Of The Abutment Teeth Low Patient Acceptance need for high clinical skill and complex laboratory procedures unpredictable structural performance complications including caries and loss of vitality of the abutment teeth Implant and Prosthesis Survival and Success Multiple Response Which Of The Following Technical Complications Are Shown Here? Prosthetic Screw Or Abutment Loosening Prosthetic Screw Or Abutment Fracture Fracture Of The Veneering Material Framework Fracture Loss Of Retention Of The Reconstruction Fracture of the veneering material Framework fracture Match Match The Statements On The Left With Their Counterpart On The Right Using Drag & Drop: Peri-Implant Mucositis Reversible And Not Associated With Bone Loss Peri-Implantitis Associated With Bone Loss Peri-implant mucositis Reversible and not associated with bone loss Peri-implantitis Associated with bone loss Multiple Response Which Of The Following Are Risk Factors For Peri-Implant Diseases? Poor Oral Hygiene Or Inaccessibility For Oral Hygiene Thin Periodontal Phenotype (Biotype) Smoking History Of Periodontal Disease Thick Periodontal Phenotype (Biotype) Poor oral hygiene or inaccessibility for oral hygiene Smoking History of periodontal disease Which Of The Following Mechanical Complications Is Shown Here? Prosthetic Screw Or Abutment Loosening Prosthetic Screw Or Abutment Fracture Fracture Of The Veneering Material Implant Fracture Loss Of Retention Of The Reconstruction Implant fracture True Or False Overall, The 5-Year Survival Rates Of ImplantSupported Prostheses In Newer Publications (After The Year 2000) Are Better Than The Ones Reported In Older Publications (Before The Year 2000) Suggesting An Improvement In The Learning Curve Relating To Implant Dentistry. True True Or False The Most Marked Improvement In 5-Year Survival Rate Is Seen For Screw-Retained Prostheses When Comparing Studies Before The Year 2000 To Studies After The Year 2000. True Multiple Response Which Of The Following Criteria Are Currently Considered In Assessment Of Implant Success? Function Mobility Outcome Of The Prostheses Esthetics Overall Treatment Time Function Mobility Outcome of the prostheses Esthetics True Or False Implant Survival And Success Are Based On Different Criteria And Should Both Be Considered When Reporting Implant-Related Outcomes And Predictability. True True Or False The 5-Year Implant Body Survival Rate For Implant-Supported Multi-Unit Prostheses Has Increased To More Than 96% In Studies Published Since 2000. True True Or False There Is No Significant Difference Reported In The Incidence Of Fracture Of The Prostheses’ Framework When Comparing Studies From Before The Year 2000 And Studies Published Later Than 2000. True Multiple Response Which Of The Following Are Technical/ Mechanical Complications? Prosthetic Screw Or Abutment Loosening Prosthesis Looseness Due To Cement Failure Fracture Of The Veneering Material Implant Or Framework Fracture Mucosal Recession Exposing The ImplantAbutment Interface Prosthetic screw or abutment loosening Prosthesis looseness due to cement failure Fracture of the veneering material Implant or framework fracture True Or False It Has Been Shown That Peri-Implantitis Is Associated With Poor Or No Access For Appropriate Oral Hygiene Measures, While Good Accessibility For Plaque Control Is Rarely Associated With Peri-Implantitis. True True Or False Implant Survival Indicates Whether Complications Are Present. False Multiple Response Peri-Implant Mucositis And Peri-Implantitis Share Similar Clinical Presentations Such As Redness And Swelling Suppuration Implant Mobility Bleeding On Probing (Bop) redness and swelling suppuration Bleeding On Probing (BOP) True Or False Implant Fractures And Fracture Of The Prostheses’ Framework Are The Most Common Implant-Related Complication. False True Or False It Has Been Shown That Patients In Supportive Periodontal Therapy Who Developed ReInfections Are At Greater Risk For PeriImplantitis And Implant Loss Than Periodontally Stable Patients. True True Or False When Analyzing Technical Complications, The Presence Of Cantilever Extensions < 15 Mm In Short-Span Fixed Dental Prostheses (Fdps) May Increase The Risk Of Failures. False Which Of The Following Biological Complications Is Shown Here? Chronic Periodontitis Localized Apical Periodontitis Peri-Implant Mucositis Peri-Implantitis Crestal Remodeling Peri-implantitis True Or False It Has Been Shown That Patients Who Smoke Are At Greater Risk Of Developing Peri-Implant Mucositis, But Not Peri-Implantitis Or Bone Loss. False Multiple Response Which Of The Following Is Associated With An Increased Risk For Technical Complications: Absence Of A Metal Framework In Overdentures Bruxism One-Piece Implant Designs Length Of The Reconstruction (I.E. Single And Double Units Vs 3 To 4-Unit Fixed Dental Prostheses) History Of Repeated Complications Absence of a metal framework in overdentures Bruxism Length of the reconstruction (i.e. single and double units vs 3 to 4-unit fixed dental prostheses) History of repeated complications Implant-Supported Provisional Prosthesis True Or False When Fabricating A Screw-Retained Provisional Utilizing The Intra-Oral Approach, It Is Imperative That Interproximal Undercuts Be Blocked Out To Prevent Locking The Provisional In The Mouth. True Multiple Response What Are The Clinical Benefits Of A Provisional Prosthesis? It Provides An Opportunity To Load The Implants. It Assists In Maintaining Interproximal Contacts. It Improves Occlusal Development. It Improves Communication With The Laboratory. It provides an opportunity to load the implants. It assists in maintaining interproximal contacts. It improves communication with the laboratory. True Or False Provisional Restorations Provide An Opportunity To Load The Implant. True True Or False Fabrication Of The Provisional Prosthesis Can Be Performed Via An Extra-Oral Or Intra-Oral Approach. True True Or False For Cement-Retained Prostheses With Deep Restorative Margins (> 2 Mm Submucosal Depth), A Custom Abutment Should Be Used To Move The Cement Line Closer To The Mucosal Margin. True True Or False The International Team For Implantology (Iti) Fourth Consensus Conference Recommends The Use Of Provisional Implant Prostheses In The Esthetic Zone. True True Or False Teflon Tape (Ptfe) Is A Good Material For Protecting Abutment Screw Heads. True Multiple Response Which Of The Following Can Be Used As A Crown Former? Vacuform Matrix Preformed Crown Denture Tooth Previous Prosthesis Vacuform matrix Preformed crown Denture tooth Previous prosthesis True Or False Titanium Provisional Abutments Are Best Utilized For Screw-Retained Provisional Restorations. True Multiple Response Which Materials Can Be Used As An Adjunct To Prevent Complications In The Fabrication Of The Provisional Implant Prosthesis. Peek (Polyether Ether Ketone) Methyl Methacrylate Teflon Tape Opaquing Material Block-Out Material Light-Cured Composite Resin Teflon tape Opaquing material Block-out material Fill In The Blank When Using Titanium Abutments For Provisional Fabrication, _________ Will Aid In Preventing Titanium From Showing Through. Composite Resin Glaze Caulking Agent Opaquing Material Sand Blasting Cement opaquing material True Or False One Advantage Of A Peek (Polyether Ether Ketone) Abutment Is That It Can Be Prepared/ Modified Intra-Orally. True True Or False Block-Out Material Can Be Placed In Undercuts To Aid In Removing A Provisional Prosthesis During Intra-Oral Fabrication. True True Or False Block-Out Material Can Be Placed In Undercuts To Aid In Removing A Provisional Prosthesis During Intra-Oral Fabrication. True True Or False A Provisional Implant Prosthesis Can Help Maintain The Position Of The Interproximal Contact Areas During The Fabrication Of The Definitive Restoration, Thus Reducing The Chair Time For Delivery. True True Or False In The Esthetic Zone, The Soft Tissues Around An Implant Need To Be Reshaped To A Scalloped Contour To Achieve Optimal Esthetic Results. True True Or False When Implants Are Located In The Posterior Zone, Provisional Prostheses Aid In Maintaining Interproximal And Occlusal Contacts. True True Or False Tissue Shaping With A Provisional Prosthesis Will Assist The Technician In Creating A Definitive Prosthesis That Allows For An Optimal Emergence Profile And Support For The Interproximal Tissues. True True Or False Pmma Abutments Are Used For Both CementRetained And Screw-Retained Provisionals True Multiple Response Which Of The Following Can Be Used As Core Material For Provisional Implant Prostheses? Peek (Polyether Ether Ketone) Methyl Methacrylate Pmma (Polymethyl Methacrylate) Ethyl Methacrylate Bisphenol-A-(Di)-Methacrylate (Bis-Gma) Light-Cured Composite Resin PEEK (polyether ether ketone) PMMA (polymethyl methacrylate) Ethyl methacrylate Bisphenol-A-(di)-methacrylate (Bis-GMA) Managing Biological Complications True Or False A Plastic Periodontal Probe Must Be Used When Assessing Implants. False True Or False Supramucosal Plaque Formation And The Development Of Peri-Implant Mucositis Are The Precursors To Peri-Implantitis. True How Much Probing Force Should Be Used When Assessing Peri-Implant Mucosa? Light Moderate Heavy Light True Or False If Peri-Implantitis Is Left Untreated, It Is Likely That There Will Be Progression Of Bone Loss, Which Could Result In The Eventual Loss Of The Implant. True Rue Or False Surgical Debridement Should Be Undertaken In The Treatment Of All Cases Of Peri-Implantitis. False True Or False Systemic Antibiotics Are Indicated In The Management Of Peri-Implant Mucositis. False Multiple Response Treatment Of Peri-Implantitis Always Includes: Identification Of Causes Management Of Risk Factors Debridement And Decontamination Of The Implant Surface Regenerative Procedures Aimed At Treating The Peri-Implant Bone Defect identification of causes management of risk factors debridement and decontamination of the implant surface True Or False The Treatment Of Peri-Implantitis Should Initially Include Non-Surgical Debridement To Remove As Much Of The Bacterial Biofilm As Possible. True Multiple Response Risk Factors That Should Be Addressed In The Treatment Of Peri-Implantitis Include: A Poorly Designed Prosthesis That Prevents Access For Cleaning Smoking Diabetes A Cantilever Pontic Attached To A Single Implant Crown a poorly designed prosthesis that prevents access for cleaning smoking diabetes Multiple Choice This Radiograph Illustrates Stable Bone Levels Related To This Implant. If There Is Clinically Detectable Bleeding On Probing Associated With This Implant, What Diagnosis Can Be Made Regarding The Status Of The Peri-Implant Tissues? Peri-Implant Health Peri-Implant Mucositis Peri-Implantitis Peri-implant mucositis Clinically, Peri-Implant Mucositis May Present With Which Of The Following Signs? Swelling Pus Exudate Redness Pain Swelling Pus exudate Redness True Or False Early Consideration Of Possible Implant Removal Is Recommended In Cases Of Advanced Peri-Implantitis. True Multiple Choice The Bacteria That Are Associated With PeriImplant Mucositis And Peri-Implantitis Are: The Same Similar Completely Different similar Fill In The Blank Reassessment Of An Implant Affected By PeriImplantitis Should Be Undertaken ________ After The Non-Surgical Debridement Phase. 1 To 2 Months 3 To 4 Months 6 Months 9 Months 1 to 2 months True Or False Peri-Implant Mucosal Problems Are Obvious To Patients, And They Present Seeking Assistance Early In The Course Of The Disease. False In The Case Illustrated Here, The Clinical Photograph Shows Bleeding And Pus Exudate On Probing, And The Radiograph Shows Bone Loss (Red Arrows) Around The Implant. What Diagnosis Can Be Made? Peri-Implant Health Peri-Implant Mucositis Peri-Implantitis Peri-implantitis In Peri-Implantitis, Bone Loss Is Usually Found: In Close Approximation To The Overhang On An Ill-Fitting Crown At The Apex Of The Implant Only On The Interproximal Aspects Of The Implant Circumferentially Around The Implant circumferentially around the implant The Goals Of Treatment For Peri-Implantitis Are: Resolution Of Infection And Establishment Of Tissue Health Preservation Of Peri-Implant Soft Tissue Volume Prevention Of Recurrence Of Disease resolution of infection and establishment of tissue health prevention of recurrence of disease Following Surgical Treatment For PeriImplantitis, The Soft Tissues Associated With The Implant Prosthesis: Remain Stable May Become Hyperplastic Often Recede often recede True Or False Decontamination Of The Implant Surface With Chlorhexidine Has Been Shown To Be Effective In Managing Peri-Implantitis And Is Recommended For All Cases. False Minimally Traumatic Extraction Techniques True Or False Socket Healing In The Dog Model Closely Correlates With Healing In Humans. True Fill In The Blank A __________ Is A Stronger Type Of Luxation Device That Allows Elevation Of The Tooth. Periotome Proximator Powered Periotome proximator Sequence Place The Steps In The Use Of An Anchor-AndPulley Extraction Device In The Correct Order: A 7 Mm Channel Is Prepared Into The Tooth Root Using A Twist Drill. A Periotome Is Used To Separate The Tooth From The Alveolus. The Extraction Screw Is Secured Into The Root. The Hand Screw On The Extractor Device Is Turned Slowly To Elevate And Extract The Tooth. The Traction Cable Is Attached To The Screw. The Traction Cable Is Then Guided Onto The Extractor Device. A periotome is used to separate the tooth from the alveolus. A 7 mm channel is prepared into the tooth root using a twist drill. The extraction screw is secured into the root. The traction cable is attached to the screw. The traction cable is then guided onto the extractor device. The hand screw on the extractor device is turned slowly to elevate and extract the tooth. True Or False Minimally Traumatic Extraction Techniques Can Facilitate Subsequent Ridge Preservation Or Immediate Implant Procedures. True Multiple Response Disadvantages Of The Use Of Orthodontic Extrusion Include Length Of Time For Treatment Additional Cost The Need For Significant Bone And Soft Tissue Regeneration Esthetic Impact Of Treatment length of time for treatment additional cost esthetic impact of treatment True Or False Sectioning A Multi-Rooted Tooth Makes Tooth Removal More Difficult. False Multiple Response Which Of The Following Statements About Ridge Resorption Following Tooth Extraction Are True? Most Of The Resorption Occurs On The Buccal Aspect Resorption Results In Loss Of Bone Height And Bone Width Most Of The Resorption Occurs During The First 4 Months Following Extraction Most Of The Resorption Occurs On The Lingual Aspect Most of the resorption occurs on the buccal aspect Resorption results in loss of bone height and bone width Most of the resorption occurs during the first 4 months following extraction True Or False Using A Surgical Mallet Or A Power Source To Seat A Periotome Into The Periodontal Ligament Space Offers A Distinct Advantage Over Using A Periotome Alone. True Match Match The Statements On The Left With Their Counterpart On The Right Using Drag & Drop: Column A: Type I Type Ii Type Iii Type Iv Column B: Late Implant Placement Immediate Implant Placement Early Implant Placement With Soft Tissue Healing Early Implant Placement With Partial Bone Healing Type Type Type Type I placement Immediate implant placement II placement Early implant placement with soft tissue healing III placement Early implant placement with partial bone healing IV placement Late implant placement Fill In The Blank Piezosurgery Results In ______ Osseous Healing Compared To Carbide And Diamond Burs. More Favorable Less Favorable No Significant Benefit In more favorable Multiple Response Which Of The Following Statements Are True For The Anchor-And-Lever Extraction System: It Has Longer And Wider Anchor Screws. The Use Of Impression Material Is Optional. Impression Material Provides Additional Lateral Support. It Can Be Used In Regions Distal To The Second Premolar. It has longer and wider anchor screws. Impression material provides additional lateral support. The Thick Or Thin Periodontal Phenotype (Biotype) Correlates With Probe Visibility. Alveolar Crest Position. Severity Of Periodontal Disease. Keratinized Tissue Width. Bleeding On Probing. probe visibility. alveolar crest position. keratinized tissue width. True Or False All Of The Following Dental Diseases/Conditions Can Lead To Tooth Loss: Caries, Periodontal Disease, Pulpal Infection/Inflammation, And Trauma. True True Or False A Periotome Is Made To Elevate A Tooth Utilizing A Twisting Motion. It Very Rarely Fractures When Used In This Manner. False Multiple Response The Aim Of A Minimally Traumatic Tooth Extraction Technique Is: To Reduce Trauma To The Surrounding Tissues Make The Process As Quick As Possible Maintain Socket Wall Integrity to reduce trauma to the surrounding tissues maintain socket wall integrity Fill In The Blank Removal Of A Tooth May Result In ______ Resorption Of The Alveolar Process. No Significant Insignificant significant True Or False Piezosurgical Instruments Cut Hard Tissue Without Soft Tissue Damage. True Sequence Place The Sequence Of Healing Events In PostExtraction Sites In The Correct Order: Blood Clot Formation Lysis Of Erythrocytes, Clot Replaced By Vascularized Tissue New Blood Vessel Formation Socket Filled With Woven Bone Some Lamellar Bone Being Replaced By Bone Marrow Spaces Woven Bone Formation On Socket Walls Woven Bone Replaced By Lamellar Bone Blood clot formation Lysis of erythrocytes, clot replaced by vascularized tissue New blood vessel formation Woven bone formation on socket walls Socket filled with woven bone Woven bone replaced by lamellar bone Some lamellar bone being replaced by bone marrow spaces True Or False Periotomes And Powered Periotomes Can Safely Be Applied To The Buccal Surface Of A Tooth That Is About To Be Extracted. False Multiple Choice Use Of The Following Instrument(S) Requires Copious Irrigation To Prevent Damage To The Alveolar Bone: Periotome Powered Periotome Piezosurgery Anchor-And-Pulley Device Piezosurgery Monitoring Peri-Implant Tissue Health True Or False Most Studies Agree That At Least A 5-Mm Band Of Keratinized Tissue Is Needed To Maintain The Health Of The Peri-Implant Tissues. False True Or False The Microbial Biofilm Forms On All Implant Surfaces Exposed To The Oral Environment. True True Or False Probing Depth May Increase Due To Inflammation In The Absence Of Bone Loss. True Multiple Response Assessment Of Crestal Bone Loss May Include Which Of The Following? Radiographs The Relationship Of The Implant Shoulder Position To The Bone Crest Bleeding On Probing Probing Depths Plaque Index Radiographs The relationship of the implant shoulder position to the bone crest Probing depths True Or False The Sulcular Epithelium Attaches To The Implant Surface Through Hemi-Desmosomal Attachments. False True Or False Connective Tissues Around Implants Contain Collagen Fibers That Orient Primarily Perpendicular To The Implant Surface, Similar To Periodontal Tissues. False Multiple Choice Which Of The Following Statements Is True Regarding Keratinization Of The Soft Tissues? It Is Determined By The Underlying Connective Tissues. It Represents The Thickness Of The Underlying Connective Tissues. It Leads To More Tissue Mobility At The Implant Interface. It is determined by the underlying connective tissues. True Or False Crestal Bone Loss May Be A Consequence Of The Apical Position Of The Implant-Prostheses Interface Or Inflammation. True Multiple Response Which Of The Following Assessments Should Be Carried Out As Part Of The Periodic Evaluation Of The Peri-Implant Tissues? Plaque Index Probing Depths Bleeding On Probing Plaque index Probing depths Bleeding on probing Multiple Response Comparing Labial And Proximal Probing Around The Implant Indicated By The Arrow, Which Of The Following Findings Are Likely? There Is Bleeding On The Facial Aspect Greater Probing Depths Are Noted Proximally Suppuration Is Evident Proximally There is bleeding on the facial aspect Greater probing depths are noted proximally Multiple Choice Which Of The Following Is Most Important To Accurate Interpretation Of Periimplant Probing Depths? Determination Of Bleeding Wiping For Plaque Establishing A Baseline For Health Establishing a baseline for health True Or False Once Implants Have Been Integrated And Restored Monitoring Should Focus Only On The Management Of Prosthodontic Complications. False True Or False Non-Keratinized Lining (Alveolar) Mucosa Has More Elastic Fibers And Less Collagen Fibers Making It Less Stable. True True Or False Keratinization Leads To Soft Tissue Stability By Increasing The Thickness Of The Connective Tissue False True Or False Keratinized Peri-Implant Soft Tissue May Be Helpful In Minimizing Long-Term Complications. True Multiple Response Current Thinking Suggests That Benefits Of Keratinized Peri-Implant Soft Tissues Include Which Of The Following? Easier To Perform Oral Hygiene Less Inflammation Less Recession Greater Cell Turn-Over No Occurrence Of Peri-Mucositis Easier to perform oral hygiene Less inflammation Less recession Multiple Response Which Of The Following Statements Are True In Regard To The Biologic Width? It Includes A Junctional Epithelium Attachment. The Junctional Epithelium Extends Along The Implant Surface To The Osseous Crest. It May Vary In Dimension. It Always Includes Both Epithelial And Connective Tissue Components. It includes a junctional epithelium attachment. It may vary in dimension. It always includes both epithelial and connective tissue components. True Or False Design Features Of Implants Such As The Implant-Abutment Interface May Contribute To Biofilm Formation. True Multiple Choice A Patient Presents For A 1-Year Checkup On Their Implant Prosthesis. No Bleeding On Probing Is Detected, But There Has Been Some Radiographic Change In The Bone Level Associated With This Implant. The Crestal Bone Loss Seen On This Periapical Radiograph Is Most Likely Related To: Poor Oral Hygiene Remodeling Following Implant Placement And Healing Stress Shielding A Chronically Loose Abutment Screw Submucosal Retained Cement remodeling following implant placement and healing Multiple Response Which Of The Following Have Been Shown To Contribute To Biofilm Formation? Platform Switching The Position Of The Prostheses Margin The Surface Roughness Of Implant And Prostheses Components The position of the prostheses margin The surface roughness of implant and prostheses components Occlusion on Fixed Implant Prostheses Multiple Choice Indicate Which Site Shows The Recommended Contact Positions For Implant Prostheses 16 26 16 Match Match The Statements On The Left With Their Counterpart On The Right Using Drag & Drop: Column A: For Anterior Guidance In Dynamic Occlusion For Posterior Implant Restorations In Dynamic Occlusion Column B: Avoid Lateral Working And Non-Working Contacts. Use Adjacent Teeth Where Possible For Their Proprioceptive Feedback. For anterior guidance in dynamic occlusion use adjacent teeth where possible for their proprioceptive feedback. For posterior implant restorations in dynamic occlusion avoid lateral working and non-working contacts. Match Match The Statements On The Left With Their Counterpart On The Right Using Drag & Drop: Column A: - Working Side Contacts: - Non-Working Side Contacts Column B: - On The Opposite Side To The Side The Mandible Is Moving Towards In Excursion - On The Side The Mandible Is Moving Towards In Excursion Working side contacts are on the side the mandible is moving towards in excursion Non-working side contacts are on the opposite side to the side the mandible is moving towards in excursion In The Clinical Situation Pictured, Shimstock Should _________ Between 16 And 46 When The Patient Bites Together With Light Force. Hold Just Pull Through Pull Through Easily pull through easily Multiple Response Occlusal Risk Assessment Using The Iti Sac Classification Includes Evaluation Of: Occlusal Scheme The Number Of Implants The Presence Of Cantilevers Involvement Of Implant Prostheses In Occlusion Occlusal Parafunction occlusal scheme involvement of implant prostheses in occlusion occlusal parafunction True Or False The Risk Of Technical Complications Affecting Implant Prostheses Is Significantly Higher Than That For Teeth. True True Or False Implant Fracture Is A Frequent Complication. False Fill In The Blank Occlusal Guidelines Are Based On ______ Concept Of Occlusion. An Evidence-Based A Consensus Opinion And Empirical Experience An Implant-Specific Evidence-Based a consensus opinion and empirical experience True Or False During Parafunctional Activity, Occlusal Force Is Always The Same. False True Or False Occlusal Force Varies. True Fill In The Blank In The Clinical Situation Pictured, Shimstock Should _________ Between 16 And 46 When The Patient Bites Together With Light Force. Hold Just Pull Through Pull Through Easily just pull through True Or False Occlusal Overload, In Combination With PeriImplant Inflammation, May Be Detrimental To Crestal Bone Levels. True Multiple Choice The Axial Movement Of A Tooth Is In The Range Of: 3 To 5 Μm 10 To 50 Μm 25 To 100 Μm 56 To 108 Μm 100 To 200 Μm 25 to 100 µm Fill In The Blank The Technical Complication Rate Of Implant Restorations Is Close To ______ Over 5 Years. 0% 5% 15% 25% 40% 40% Multiple Choice Occlusal Forces During Parafunction Are In A Physiological Range. Can Reach Considerable Magnitude And Duration. Can Lead To Risk Of Disuse And Loss Of Bone Mass. can reach considerable magnitude and duration. Match The Statements On The Left With Their Counterpart On The Right Using Drag & Drop: Column A: Mechanical Complications Refer To Technical Complications Refer To Column B: Complications Involving The Implant Prostheses Complications Involving Implant Components Mechanical complications refer to complications involving implant components Technical complications refer to complications involving the implant prostheses True Or False There Is Always Conscious, Protective Feedback From Teeth – Even During Sleep False True Or False Occlusal Feedback From Implants Is Less Than For Teeth But More Than From Complete Dentures. True True Or False Occlusal Overload Has Been Proven To Prevent Osseointegration. False Multiple Response Occlusal Feedback From Implant Prostheses Is Thought To Arise From Mechanoreceptors In Jaw Joints. Peri-Oral Musculature. Periodontal Ligaments. jaw joints. peri-oral musculature. Principles of Managing Hardware Complications Associated with Fixed Dental Protheses True Or False A Complication Can Be Defined As An Unexpected Deviation From The Normal Treatment Outcome. True Match Match The Statements On The Left With Their Correct Counterparts On The Right By Connecting Them With Drag & Drop: Column A: Major Complication Minor Complication Column B Can Be Rectified Chairside And At Minimal Cost Requires Numerous Visits And Is Associated With Higher Costs Major complication Requires numerous visits and is associated with higher costs Minor complication Can be rectified chairside and at minimal cost Multiple Choice The Fracture Of The Implant-Supported Crown Shown In The Illustration Is Most Likely Related To: Insufficient Framework Support For The Veneering Material Incompatibility Between The Veneering Ceramic And The Underlying Framework Material Surface Contamination Of The Framework During Veneering insufficient framework support for the veneering material Multiple Response Biophysical Differences Between Implants And Teeth Include: The Capacity For Movement And Sensory Feedback Is Reduced The Demands On Materials For Absorption Of Force Is Greater Avoidance Of Occlusal Overload Is More Difficult Due To Limited Proprioception The Physiological Reaction Of The Bone-Implant Interface To Loading Is Different Than That Of The Periodontal Ligament the capacity for movement and sensory feedback is reduced the demands on materials for absorption of force is greater avoidance of occlusal overload is more difficult due to limited proprioception the physiological reaction of the bone-implant interface to loading is different than that of the periodontal ligament Multiple Response Technical Complications Can Arise From Failures In: Prosthesis Design Prosthesis Fabrication Material Choice Material Handling prosthesis design prosthesis fabrication material choice material handling True Or False Ultrasonic Scalers With Stainless Steel Tips Are Safe To Use On Implant Surfaces. False Fill In The Blank The Risk Of Complications ______ When Components Are Designed In A Manner That Is Incompatible With Physical And Mechanical Laws. Increases Decreases Remains Unchanged Increases ______ Complications Are Those Related To Dental Laboratory Procedures And Materials. Mechanical Technical Hardware Implantological Technical Multiple Response In Implant Dentistry, Hardware Complications Refer To Unexpected Issues Associated With: Implants Abutments Prostheses Peri-Implant Mucosa Adjacent Restorations implants abutments prostheses True Or False Diagnosis Of The Cause Of A Hardware Complication Helps The Treating Clinician To Avoid The Same Complication In The Future. True True Or False Hardware Complications Are Always Related To Only A Single Causative Factor. False Multiple Choice Which Hardware Complication Is Most Likely To Present In The Case Illustrated Below? Veneering Material Fracture Screw Loosening Peri-Implant Inflammation Screw loosening True Or False A Deep Overbite Can Increase The Risk Of Hardware Complications True Multiple Choice Techniques For Long-Term Management Of Loss Of Veneering Ceramic, Such As That Illustrated, Include: Intraoral Repair With Bonded Composite Resin Smoothing Over The Rough Edges Of The Fracture Removing And Replacing The Crown removing and replacing the crown True Or False Forces During Bruxism, Intense Sports, Or Trauma Can Exceed Physiological Limits Of Normal Function. True True Or False The Use Of Non-Original Parts In Combination With Original Components Can Easily Lead To Mechanical Complications. True Multiple Choice Indicate What Comprises The Body Of The Implant. Area 1 Area 2 Area 3 area 1 The Metal Framework In A Metal-Ceramic Crown Provides Support To The Veneering Ceramic. In The Case Illustrated, The Framework Is Sufficient To Prevent Fracture Under Normal Loading Sufficient To Prevent Fracture Under Parafunctional Loading Inadequate inadequate Multiple Choice Which Of These Abutment-Implant Interfaces Is Likely To Be More Stable? Interface 1 Interface 2 interface 1 Techniques To Remove A Broken Screw Fragment, Such As That Illustrated Below, Include: Applying A Counter-Rotational Force With A Sharp Probe Or Scaler Using A High-Speed Handpiece And Diamond Bur To Drill Out The Fragment Using An Ultrasonic Scaler To Vibrate The Screw Loose applying a counter-rotational force with a sharp probe or scaler using an ultrasonic scaler to vibrate the screw loose Prosthodontic Planning Principles for Implant Placement Multiple Response Biological Factors That May Have An Impact On Prosthodontic Planning Include: Failing Teeth Due To Caries Treatment With Anticoagulants Endodontic Issues Failing Teeth Due To Trauma Failing Teeth Due To Fracture failing teeth due to caries endodontic issues failing teeth due to trauma failing teeth due to fracture The Amount Of Teeth And Surrounding Soft Tissue That Is Visible On Full Smile Is A Key Factor In Esthetic Assessment. The Height Of The Lip At Full Smile Is Known As The ‘Smile Line.’ The Smile Line Is Categorized As: Non-Existing High Low Medium Compromised high low medium Multiple Response Dimensions And Characteristics Of Teeth To Be Replaced Can Be Determined By Examination Of: Older Dental Casts Extracted Teeth Older Photographs Contralateral Remaining Teeth Existing Panoramic Radiographs older dental casts extracted teeth older photographs contralateral remaining teeth Multiple Response The Prosthodontic Space Is Influenced By Variations In The Features That Border The Space Such As: Adjacent Teeth Opposing Teeth Mucosal Thickness Adjacent Roots Residual Ridge Morphology adjacent teeth opposing teeth residual ridge morphology True Or False The Purpose Of A Diagnostic Work-Up For Implant Placement Is To Determine The Desired Surgical Outcome. False True Or False To Be Ready For Treatment, The Patient’S Symptomatic Conditions Must Be Appropriately Managed First. True True Or False The Patient’S Presenting Pathological Conditions Should Be Addressed Before The Prosthodontic Planning Is Commenced. True Multiple Response Indications For A Provisional Implant-Supported Prosthesis Might Include: Management Of Peri-Implant Soft Tissue Management Of Peri-Implant Hard Tissue Observation Of Peri-Implant Health Observation Of The Patient’S Ability To Maintain Adequate Oral Hygiene management of peri-implant soft tissue observation of peri-implant health observation of the patient’s ability to maintain adequate oral hygiene True Or False The Periodontal Phenotype Is Classified As Thick Or Thin. True True Or False In A Case Where A Site For A Planned Implant Is Within A Segment Of Crowded Teeth, Orthodontic Treatment Should Be Performed After The Placement Of Implants. False True Or False Treatment Planning For Elderly Patients Should Aim For Complex Rather Than Simple Solutions Due To Their Level Of Dexterity And Motivation. False Multiple Response Diagnostic Set-Ups And Wax-Ups Offer 3D Visualization Of: Definitive Tooth Positions Esthetic Details Functional Details Bony Anatomy definitive tooth positions esthetic details functional details Multiple Response The Modified Pink Esthetic Score (Pes) Assesses Various Parameters In Comparison To Contralateral Teeth, Including: Soft Tissue Color And Texture Level Of The Papillae Curvature Of The Facial Mucosa Level Of The Facial Mucosa Crown Convexity Root Convexity soft tissue color and texture level of the papillae curvature of the facial mucosa level of the facial mucosa root convexity True Or False A Thin Periodontal Phenotype Generally Poses Lower Esthetic Risk Since It Is Usually Resistant To Recession. False Multiple Choice The Purpose Of A Diagnostic Work-Up For Implant Placement Is To Determine The Desired Definitive Prosthodontic Outcome. It Will Also Disclose The Need For Additional Procedures Such As: Orthodontic Treatment Treatment Of Periodontitis Treatment Of Tmj (Temporomandibular Joint) Symptoms orthodontic treatment True Or False Diagnostic Set-Ups Allow The Patient To Give Informed Consent Based On Realistic Expectations Of The Outcome. True True Or False The Timing Of Extractions Is Relevant To The Subsequent Timing Of Implant Placement. True Multiple Response Removal Of Teeth Can Lead To Positional Issues With Adjacent And Opposing Teeth. These Positional Issues Include: Supraeruption Tilting Drifting Ankylosis supraeruption tilting drifting True Or False Pink Components Of The Prosthesis To Replace Missing Soft Tissue Volume Are Only Useful For Fixed Dental Prostheses. False True Or False Diagnostic Work-Ups Can Be Converted Into Radiographic And Surgical Templates. True Protocol for Fixed Implant Supported Prostheses Delivery Multiple Response When A Prosthesis Fails To Seat, The Reason Could Be: Failure To Correctly Engage The Connection Between The Abutment And The Implant The Retention Screws Have Not Been Sufficiently Tightened The Proximal Contacts Are Too Tight Soft Tissue Impingement Is Preventing Seating The Prosthesis Was Made On An Inaccurate Model failure to correctly engage the connection between the abutment and the implant the proximal contacts are too tight soft tissue impingement is preventing seating the prosthesis was made on an inaccurate model Multiple Response Which Properties Are Desirable In A Luting Agent For Cement-Retained Implant Prostheses? Radio-Opaque High Bond Strength High Film Thickness Brittle Translucent Radio-opaque Brittle Multiple Choice When Assessing Static Occlusion, It Is Important To Ensure That Shimstock Is Held Between Occluding Natural Teeth On Light Closure. Shimstock Can Just Be Withdrawn Between Occluding Teeth And Implants On Firm Closure. Occlusal Contacts Are On Inclined Planes In Order To Avoid Axial Loading Of The Implant. shimstock is held between occluding natural teeth on light closure. True Or False It Is Recommended That Occlusal Contacts On An Implant Prosthesis Should Be Even And Simultaneous With The Contacts On The Rest Of The Dentition. False Multiple Response Ptfe Tape Is Used To Protect Screw Heads Because It Forms An Anti-Bacterial Seal. Does Not Degrade Over Time. Can Be Easily Removed If Needed. Is Made Of Teflon. does not degrade over time. can be easily removed if needed. True Or False With Cement-Retained Prostheses, The Cement Margin Should Be Less Than 1 Mm SubMucosally. True True Or False It Is Important To Avoid Periodontal Probing Around Dental Implants As This May Disrupt The Soft Tissue Adhesion To The Implant And Could Contribute To The Breakdown Of The Peri-Implant Tissues. False Multiple Choice Passive Fit Of A Prosthesis Is Important To Help Reduce The Likelihood Of Biological Complications. Technical Complications. technical complications. True Or False It Is A More Straightforward Process To Deliver Implant-Supported Prostheses Than ToothSupported Restorations As The Components Are Machined To Fit One Another. False True Or False Dynamic Occlusion On An Implant Prosthesis Can Be Assessed Using 3 Different Colors Of Articulating Paper. True Fill In The Blank When Cementing An Implant Prosthesis ______ In Order To Reduce The Chance Of Developing Peri-Implantitis. Use A High Viscosity Cement Avoid Peri-Implant Probing Remove Any Excess Cement Avoid Soft Cements remove any excess cement When Splinting Implants It Is Important To ______ To Verify Passive Fit Of The ScrewRetained Restoration. Fully Tighten All Screws Finger-Tighten The Restoration Screws Carry Out The Sheffield Test Link The Impression Copings Section The Framework And Make A Soldering Jig At The Framework Try-In Appointment carry out the Sheffield test Put The Elements Of The Delivery Protocol In The Correct Order Using Drag & Drop: Evaluate The Prosthesis On The Model Fit The Prosthesis Provide Oral Hygiene Instruction Rehearse Prosthesis Assembly Take Baseline Records To Facilitate Continuing Care Try-In And Verify That The Prosthesis Is Clinically Acceptable Evaluate the prosthesis on the model Rehearse prosthesis assembly Try-in and verify that the prosthesis is clinically acceptable Fit the prosthesis Provide oral hygiene instruction Take baseline records to facilitate continuing care Multiple Choice When Assessing The Dynamic Occlusion On Posterior Implant Prostheses Ensure Lateral Guidance Is Shared Equally Between Natural Teeth And Implants. Identify Non-Working Side Interferences On The Prosthesis. Use Shimstock To Indicate Location Of NonAxial Contacts. identify non-working side interferences on the prosthesis. True Or False Excess Cement, Retained Sub-Mucosally On Cemented Implant Supported Prostheses, Is Related To Periimplant Mucosal Problems (Periimplant Mucositis And Periimplantitis). True Multiple Response What Could Be Causing This Implant Prosthesis Linking 2 Implants, To Fail To Seat On The Most Anterior Implant? Soft Tissue Impingement Restoration Manufactured On An Inaccurate Cast Light Proximal Contacts Uneven Screw Tightening Soft tissue impingement Restoration manufactured on an inaccurate cast Uneven screw tightening Multiple Response When Assessing The Static Occlusion On Posterior Implant Prostheses Ensure There Can Be No Differential Axial Movement Between Teeth And Implants. Use Shimstock To Indicate Presence Of Occlusal Contacts. Ensure Shimstock Is Held Equally On All Occluding Teeth And Prostheses With Firm Closure. use shimstock to indicate presence of occlusal contacts. ensure shimstock is held equally on all occluding teeth and prostheses with firm c Multiple Response Which Of The Following Post-Operative Records Should Be Taken After Placing An Implant Supported Prosthesis: Peri-Apical Radiographs Plaque And Bleeding On Probing Scores Peri-Implant Probing Depths Clinical Photographs Peri-apical radiographs Plaque and bleeding on probing scores Peri-implant probing depths Clinical photographs Fill In The Blank On Removing The Healing Abutment, The Prosthesis Needs To Be Tried-In Without Delay To Prevent __________ . Periimplantitis Movement Of Adjacent Teeth Soft Tissues From Collapsing Into The Space. soft tissues from collapsing into the space. True Or False Static Occlusion On An Implant Prosthesis Is Assessed Using 3 Different Colors Of Articulating Paper. False Ridge Preservation Techniques True Or False Graft Materials For Ridge Preservation With Slow Resorption Rates May Be Inferior To Materials With High Resorption Rates In Regard To Maintaining Ridge Volume In The Long Term. False True Or False The Alveolar Bone, Periodontal Ligament, Cementum, And Tooth Constitute A Developmental Unit, As They Form Together. True True Or False The Alveolar Process Of The Jaw Develops Along With The Eruption Of Teeth, Ongoing Root Formation, And Subsequent Growth. True True Or False Surgical Trauma From Tooth Extraction May Induce Microtrauma In Surrounding Bone, Which Accelerates Bone Resorption. True Multiple Response The Literature Is Inconclusive As To Which Bone Substitute Material Provides The Best Outcome, But In General The Material Should Be: Slow Resorbing Fast Resorbing Biocompatible Biomechanically Stable Osteoconductive slow resorbing biocompatible osteoconductive True Or False Soft Tissue Dehiscence Can Result In Exposure Of An Applied Membrane. If The Membrane Is Resorbable, The Treatment Is Mechanical And Antiseptic Plaque Control Of The Site. Normally, The Soft Tissue Will Heal By Secondary Intention Without Further Complications. True Fill In The Blank The Thickness Of The Socket Wall Is Fundamental In The Alveolar Resorption Process. If It Is Thin, That Is, Less Than ______, It Will Quickly Resorb. 10 Mm 1 Mm 3 Mm 5 Mm 6 Mm 1 mm True Or False Ridge Preservation Can Increase The Predictability Of Simultaneous Bone Augmentation Procedures At The Time Of Implant Placement. True Multiple Choice Two-Thirds Of The Reduction In Width Of The Alveolar Ridge After Tooth Extraction Will Occur Within The First: 3 Months 3 Weeks 2 Weeks Week Month 3 months Multiple Choice At The Time Of Extraction Any Remaining Pathology Inside The Socket Must Be Removed. For This Procedure One Of The Following Instruments May Be Used: A Trephine A Curette An Elevator A Luxator A Twist Drill a curette True Or False Bone Loss During Socket Healing Is Greater In The Lingual Than The Buccal Wall. False True Or False Ridge Preservation Procedures Ensure That Further Bone Augmentation Will Not Be Needed At The Time Of Implant Placement. False Multiple Response Ridge Preservation Procedures Are Contraindicated: When There Is Acute Infection At The Extraction Site In Patients With Medical Conditions That Limit Nonessential Surgical Procedures Other Than The Necessary Tooth Extraction In Patients With A Thick Periodontal Phenotype In Patients With Incomplete Growth In Patients With A Thin Periodontal Phenotype when there is acute infection at the extraction site in patients with medical conditions that limit nonessential surgical procedures other than the necessary tooth extraction Ridge Preservation May Be Indicated: When Implant Placement Must Be Deferred Due To Medical Reasons In Patients With Incomplete Growth When The Patient Cannot Afford Implant Placement At The Moment In Patients With Thick Undisrupted Socket Walls When Implants Are To Be Placed 6 To 8 Weeks After Tooth Extraction when implant placement must be deferred due to medical reasons in patients with incomplete growth when the patient cannot afford implant placement at the moment Multiple Response After Placement Of The Graft Material Into The Extraction Socket And Possible Use Of A Membrane, The Socket Entrance Could Be Closed By: A Free Gingival Graft A Pediculated Split-Thickness Palatal Flap An Extracellular Matrix Membrane A Coronally Advanced Gingival Flap A Titanium Net a free gingival graft a pediculated split-thickness palatal flap a coronally advanced gingival flap True Or False Changes In Alveolar Ridge Height After Tooth Extraction Are More Significant Than Horizontal Changes. False Multiple Choice Complications May Occur After Ridge Preservation. Loss Of The Socket Seal Is Significant If It Takes Place Within The First: Your Answer To This Question Was Correct. Your Response 2 Months Of Healing 30 Days Of Healing 15 Days Of Healing 3 Months Of Healing 2.5 Months Of Healing 15 days of healing True Or False If A Nonresorbable Membrane Covering The Graft Material Becomes Exposed, Removal Is Not Necessary As Potential Infection Is Easy To Control. False Sequence Describe The Ridge Preservation Procedure. Atraumatic Tooth Extraction Debridement Of Potential Pathology In The Socket Definitive Placement Of Membrane Placement Of Graft Material Soft Tissue Covering Atraumatic tooth extraction Debridement of potential pathology in the socket Placement of graft material Definitive placement of membrane Soft tissue covering Multiple Response A Ridge Preservation Procedure May On Occasion Result In Infection In The Socket. If So, Then: All Infected Biomaterial Should Be Removed New Biomaterials Should Be Placed Immediately The Ridge Preservation Procedure Should Be Considered Lost Antibiotic Therapy May Be Implemented Plaque Control Procedures Should Be Performed Until There No Clinical Signs Of Acute Inflammation all infected biomaterial should be removed the ridge preservation procedure should be considered lost antibiotic therapy may be implemented plaque control procedures should be performed until there no clinical signs of acute inflammation Multiple Response A Ridge Preservation Procedure May On Occasion Result In Infection In The Socket. If So, Then: All Infected Biomaterial Should Be Removed New Biomaterials Should Be Placed Immediately The Ridge Preservation Procedure Should Be Considered Lost Antibiotic Therapy May Be Implemented Plaque Control Procedures Should Be Performed Until There No Clinical Signs Of Acute Inflammation all infected biomaterial should be removed the ridge preservation procedure should be considered lost antibiotic therapy may be implemented plaque control procedures should be performed until there no clinical signs of acute inflammation Transitional Prostheses Used During Implant Therapy True Or False Transitional Prostheses Can Be Either Fixed Or Removable. Column 1: Functional Indication Biologic Indication Esthetic Indication Patient-Driven Indication Column 2: Observation Of The Outcome Of Initial Treatment To Arrest Active Dental Disease Testing The Patient’S Tolerance Of The Proposed Prosthodontic Replacement Restoration Of Lip And Facial Support Testing The Parameters Of A Prosthodontic Rehabilitation Functional indication Testing the parameters of a prosthodontic rehabilitation Biologic indication Observation of the outcome of initial treatment to arrest active dental disease Esthetic indication Restoration of lip and facial support Patient-driven indication Testing the patient’s tolerance of the proposed prosthodontic replacement True Or False All Patients Will Need A Transitional Prosthesis Both Prior To And During Implant Treatment. False True Or False Transitional Prostheses Can Be Either Fixed Or Removable. True Multiple Choice There Are A Variety Of Fixed Transitional Prostheses. Among These Are: Conventional Fixed Dental Prostheses Vacuum-Formed Retainers Provisional Implants conventional fixed dental prostheses Multiple Response The Following Treatment Factors Should Be Considered Before Selecting The Transitional Prosthesis Type: Treatment Site Treatment Duration Treatment Risks Type Of Implants treatment site treatment duration treatment risks Multiple Choice The Following Patient Considerations Should Be Evaluated Before Selecting The Transitional Prosthesis Type: Esthetics Type Of Implants Treatment Risks esthetics Multiple Response A Transitional Partial Denture Can Be An Existing Prosthesis; However, A New Prosthesis Can Be Designed To Provide Which Of The Following Advantages: Tooth Support To Reduce Denture Pressure On The Implant Site Potential For Modification Of The Denture At The Implant Site Hygienic Design To Safeguard The Remaining Dentition Tooth support to reduce denture pressure on the implant site Potential for modification of the denture at the implant site Hygienic design to safeguard the remaining dentition Multiple Response Reinforcement Of Conventional Fixed Transitional Prostheses Can Be Achieved Using: A Polyethylene Mesh A Metal Framework Acrylic Or Composite Materials a polyethylene mesh a metal framework True Or False A Vacuum-Formed Retainer As A Transitional Prosthesis Can Be Produced At Low Cost. True Multiple Response Transitional Prostheses May Be Supported By: Soft Tissues Adjacent Teeth Existing Implants Provisional Implants soft tissues adjacent teeth existing implants provisional implants Multiple Choice Removable Transitional Prostheses Have Several Advantages, Including: Patients Prefer Them To Fixed Solutions Can Be Used In Combination With Fixed Transitional Prostheses No Need For Removal For Cleaning Or Eating Can be used in combination with fixed transitional prostheses Multiple Response All Transitional Prostheses Must Have A Design That Allows: Surgical Access At The Planned Site Access For Effective Daily Plaque Removal By The Patient Reshaping As Needed For Hard Tissue Management Of The Implant Site Reshaping As Needed For Soft Tissue Management Of The Implant Site Easy Removal By The Patient If Needed surgical access at the planned site access for effective daily plaque removal by the patient reshaping as needed for hard tissue management of the implant site reshaping as needed for soft tissue management of the implant site Multiple Response Denture Modification To Avoid Pressure On Implant Sites Can Result In: Enhanced Stability Instability Poor Retention Risk Of Fracture Of Weakened Prostheses Higher Retention instability poor retention risk of fracture of weakened prostheses Multiple Response Conventional Fixed Dental Prostheses Can Be Supported By: Adjacent Teeth Orthodontic Appliances Provisional Implants adjacent teeth provisional implants True Or False Removable Transitional Prostheses Are Always Preferred To Fixed Transitional Prostheses Because Intervention Of The Adjacent Teeth Is Omitted False True Or False A Transitional Prosthesis May Prevent Unwanted Movement Of Teeth, Thereby Preserving The Prosthodontic Space. True True Or False Removable Transitional Prostheses Could Be Partial Dentures, Complete Dentures, Or Vacuum-Formed Retainers True Multiple Choice Fixed Transitional Prostheses Have Several Advantages, Including: Usually Less Expensive Than Removable Solutions No Need For Removal For Cleaning Or Eating Easy Access To Treatment Site On Each Visit No need for removal for cleaning or eating True Or False A Fixed Orthodontic Appliance Can Serve As Anchorage For A Replacement Tooth. True Multiple Response Selecting The Transitional Prosthesis Type Depends On: Indications Treatment Factors Patient Considerations Type Of Implants indications treatment factors patient considerations