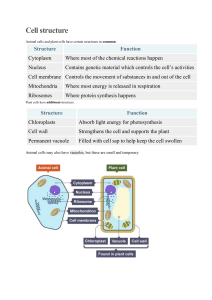
Animal Cell Cytoplasm Nucleus Plant Cell Nucleus Cytoplasm Chloroplasts Mitochondria Ribosomes Cell membrane Vacuole Cell wall Mitochondria Cell membrane Ribosomes Root Hair Cell Palisade Cell Function Function To absorb water and minerals from the soil. To carry out photosynthesis to make glucose for the plant. Adaptations Adaptations Long root hair to give it a large surface area for absorption of water and minerals into the cell. Lots of chloroplasts to absorb light energy for photosynthesis. No chloroplasts due to being underground. Tall, thin shape to give it a large surface area to maximise the absorption of light. Sperm Cell Egg Cell Function Function To fertilise an egg cell. To be fertilised by a sperm cell. Adaptations Adaptations Long tail to help it swim to the egg. Cytoplasm contains nutrients for the developing embryo. Lots of mitochondria to release energy to allow the sperm to move. Membrane changes after fertilisation to stop any more sperm getting in. Muscle Cell Nerve Cell Function Function To help the body to move. To carry nerve impulses around the body. Adaptations Adaptations Bands of protein that change shape to contract and relax the muscle. Long fibres allow it to carry electrical impulses up and down the body. Lots of mitochondria to release energy for muscle contraction. Branching dendrites at each end to connect to other nerves or muscles. Ciliated Epithelial Cell Red Blood Cell Function Function To move dust and microorganisms away from the lungs. To transport oxygen around the body. Adaptations Adaptations Tiny hairs called cilia to help to waft the mucus along the airways. No nucleus so there is more room for haemoglobin, which binds to oxygen molecules. Lots of mitochondria to release energy for cilia to move. Biconcave shape to give a large surface area for diffusion of oxygen. White Blood Cell Function To fight pathogens that cause disease. Adaptations Produce antibodies to kill pathogens and antitoxins to neutralise toxins. Can change shape to squeeze out of blood vessels and engulf pathogens.