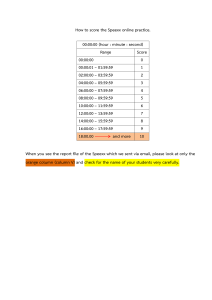
6/21/23, 3:51 PM about:blank SQL Cheat Sheet: FUNCTIONS and Implicit JOIN Command Syntax COUNT SELECT COUNT(column_name) FROM table_name WHERE condition; AVG SELECT AVG(column_name) FROM table_name WHERE condition; SUM SELECT SUM(column_name) FROM table_name WHERE condition; MIN SELECT MIN(column_name) FROM table_name WHERE condition; MAX SELECT MAX(column_name) FROM table_name WHERE condition; ROUND SELECT ROUND(2number, decimals, operation) AS RoundValue; LENGTH(column_name) LENGTH SELECT FROM table; UCASE SELECT UCASE(column_name) FROM table; DISTINCT(column_name) DISTINCT SELECT FROM table; DAY Description Example COUNT function returns the COUNT(dep_id) FROM number of rows that matches a SELECT employees; specified criterion. AVG function returns the SELECT AVG(salary) FROM average value of a numeric employees; column. SUM function returns the total SELECT SUM(salary) FROM employees; sum of a numeric column. MIN function returns the SELECT MIN(salary) FROM smallest value of the employees; SELECTed column. MAX function returns the largest SELECT MAX(salary) FROM value of the SELECTed employees; column. ROUND function rounds a ROUND(salary) FROM number to a specified number SELECT employees; of decimal places. LENGTH function returns the SELECT LENGTH(f_name) FROM employees; length of a string (in bytes). UCASE function that displays the UCASE(f_name) FROM column name in each table in SELECT employees; uppercase. DISTINCT function is used to SELECT display data without DISTINCT(UCASE(f_name)) FROM employees; duplicates. SELECT DAY(column_name) FROM DAY function returns the day table the month for a given date DAY(b_date) FROM of SELECT employees where emp_id = 'E1002'; is used to display SELECT YEAR(CURRENT DATE CURRENT SELECT (CURRENT DATE the current date.This can be b_date) As AGE, COLUMN) FROM table; DATE subtracted from the previous CURRENT_DATE, b_date FROM employees; date to get the difference. SELECT emp_id, fmame, lname, Subquery SELECT column_name [, Subquery is a query within column_name ] FROM table1 [, another SQL query and salary table2 ] WHERE column_name employees embedded within the WHERE FROM OPERATOR (SELECT column_name where salary [, column_name ] FROM table1 clause. < (SELECT AVG(salary) CURRENT DATE [, table2 ] [WHERE]) about:blank A subquery is used to return data that will be used in the FROM employees); 1/2 6/21/23, 3:51 PM about:blank main query as a condition to further restrict the data to be retrieved. SELECT * FROM ( SELECT emp_id, f_name, l_name, dep_id FROM employees) AS emp4all; SELECT * FROM employees WHERE job_id IN (SELECT job_ident FROM jobs); combines the two or more records but displays only matching values SELECT * FROM employees, jobs where employees.job_id in both tables. Inner join = jobs.job_ident; applies only the specified columns. Implicit Cross Join defines as a Cartesian product where SELECT * FROM employees, the number of rows in the first jobs; table multiplied by the number of rows in the second table.. Implicit Inner Join SELECT column_name(s) FROM Implicit table1, table2 WHERE Inner Join table1.column_name = table2.column_name; Implicit SELECT column_name(s) FROM Cross Join table1, table2; Author(s) Lakshmi Holla Changelog Date Version Changed by Change Description 2023-05-04 1.1 Benny Li Formatting changes 2021-07-28 1.0 Lakshmi Holla Initial Version about:blank 2/2