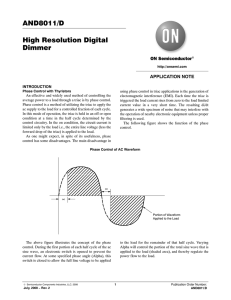
Republic of the Philippines Polytechnic University of the Philippines Office of the Vice President for Academic Affairs College of Engineering ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING (ECE) DEPARTMENT ECEN 3364-INDUSTRIAL ELECTRONICS AND PLC APPLICATIONS Group Members Group No.: 2 Belinario, John Orville T. Delos Reyes, Arvin Godfrey Duran, Reineir Mampusti, Jayron Rivera, Shawn Ivan BEN B. ANDRES, DEM, PECE Professor ________________________________ ________________________________ Rating EXPERIMENT NO. 3 TRIAC I. OBJECTIVES 1. To become familiar with the structure, operation, characteristics parameters and applications of TRIAC. 2. To demonstrate how AC current to a load can be controlled by a TRIAC. II. DISCUSSION The TRIAC is basically a three-layer PN device with added N regions. It can be triggered into conduction in either direction, making it a bilateral switching device having the official name of “bi-directional triode thyristor”.3 Structure, Equivalent Circuit and Schematic symbol of TRIAC Figure 2.1 a) Structure 1|P age Republic of the Philippines Polytechnic University of the Philippines Office of the Vice President for Academic Affairs College of Engineering ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING (ECE) DEPARTMENT Terminal 1 Gate (G) Terminal 2 b) Equivalent Transistor Circuit c) Schematic Symbol Operation of a TRIAC The TRIAC conducts when the voltage across its main terminals (T 1 and T2) exceeds the break over points or if it is triggered by a positive or negative voltage pulse applied to the gate lead. Figure 2.2 Four Modes of Triggering TRIAC a) Positive Terminal V with Positive Gate V b) Positive Terminal V with Negative Gate V 2|P age Republic of the Philippines Polytechnic University of the Philippines Office of the Vice President for Academic Affairs College of Engineering ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING (ECE) DEPARTMENT c) Negative Terminal V with Positive Gate V d) Negative Terminal V with Negative Gate V Current-Voltage Characteristics of a TRIAC Figure 2.3 3|P age Republic of the Philippines Polytechnic University of the Philippines Office of the Vice President for Academic Affairs College of Engineering ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING (ECE) DEPARTMENT AC Control Using a TRIAC Figure 2.4 AC Triggering of a TRIAC 0o 90o 180o 270o 360o current through the load TRIAC on TRIAC off TRIAC on a) Resistive Triggering Time= 0o to 90o and 180o to 270o 0o 90o 180o 270o 360o current through the load TRIAC off TRIAC on TRIAC on b) RC Triggering Time= entire cycle 4|P age Republic of the Philippines Polytechnic University of the Philippines Office of the Vice President for Academic Affairs College of Engineering ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING (ECE) DEPARTMENT TRIAC Definitions +V Table 2.1 Forward voltage or positive alternation applied to main terminals of device -V Reverse voltage or positive alternation applied to main terminals of device +VBO Forward breakover voltage -VBO Reverse breakover voltage VT1 Voltage from terminal 1 to ground VT2 Voltage from terminal 2 to ground +I Forward current when the TRAIC is on -I Reverse current when the thyristor is off III.MATERIALS NEEDED: 1 1 1 2 24-V rms transformer or ac source Oscilloscope (use only one channel) 2N5752 TRIAC or equivalent 1N5231 zener diodes or equivalent (Z1 and Z2) 2 1 1 1 100-ohm resistors at 0.5W (Rl and RA) 10k-ohm potentiometer (RG) 5.0 uF capacitor at 50 WV dc (CG) Breadboard for constructing circuit IV.PROCEDURES: Part 1. The first part of this experiment uses only a variable resistor to vary the trigger time from 0o to 90o and 180o to 270o. An oscilloscope is used to view the voltage waveforms across the TRIAC and RL. 1. Construct a circuit shown in the Figure 2.4a. 2. Place the oscilloscope across the TRIAC. 3. Vary RG back and forth and view the voltage waveform across the TRIAC. 4. Adjust RG so that the TRIAC triggers about halfway between 0 o and 90o and 180o and 270o.voltage). 5. Place the oscilloscope across RL. 6. Draw the voltage waveform across RL in the space provided, making sure to align it with the proper degrees for one cycle. (Indicate peak-to-peak voltage). 5|P age Republic of the Philippines Polytechnic University of the Philippines Office of the Vice President for Academic Affairs College of Engineering ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING (ECE) DEPARTMENT Waveform across TRIAC Waveform across RL 75% 10k ohm potentiometer Peak to peak voltage = 47.262V 75% 10k ohm potentiometer Peak to peak voltage = 2.786 V Part 2. In the second part of this experiment, a capacitor is added to the original circuit to extend the trigger time for nearly the entire cycle. The zenerdiodes simulate a DIAC, which makes the trigger more symmetrical. 7. Modify the circuit shown in Figure 2.4b by adding the capacitor. 8. Place the oscilloscope across the TRIAC. 9. Vary RG back and forth and view the voltage waveform across the TRIAC. 10. Adjust RG so that the TRIAC triggers past 90o and 270o. 11. Draw the voltage waveform across the TRIAC in the space provided, making sure to align it with the proper degrees. 12. Place the oscilloscope across RL. Waveforms across TRIAC Vp = 25.790V at 75% 10k ohm potentiometer Peak to peak voltage = 51.58V Waveform across RL 75% 10k ohm potentiometer Peak to peak voltage = 6.3V 6|P age Republic of the Philippines Polytechnic University of the Philippines Office of the Vice President for Academic Affairs College of Engineering ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING (ECE) DEPARTMENT V. OBSERVATION: The place which firing signal was sent will determine how much signal will only pass. By varying the time between zero cross and firing pulse we can control the power. By adding capacitor it helps more to control the power for the load. VI.CONCLUSION: o By applying a firing pulse on the gate of the TRIAC we can control the power on both positive and negative side of the wave. o By adding capacitor it is used as trigger voltage, which has its phase varies by changing the variable resistor. VII.QUESTIONS: 1. a.) b.) c.) d.) A TRIAC can be triggered into conduction when the voltage on: Its T2 terminal is positive and the gate is positive. Its T2 terminal is positive and the gate is negative. Its T2 terminal is negative and the gate is positive. All of the above 2. The device that has a low-voltage drop across its main terminal in either direction when conducting is a: a.) SCR c.) DIAC b.) TRIAC d.) none of the above 3. The combination of DIAC and TRIAC forms a: a.) QUADRAC c.) Thyristor b.) VARIAC d.) LASCR 4. The approximate trigger times for a TRIAC circuit without a capacitor are: a.) 0o to 45o and 180o to 270o c.) 0o to 90o and 180o to 270o b.) 0o to 90o and 270oto 360o d.) 0o to 180o and 180o to 360o 7|P age Republic of the Philippines Polytechnic University of the Philippines Office of the Vice President for Academic Affairs College of Engineering ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING (ECE) DEPARTMENT 5. The approximate trigger times for a TRIAC circuit with a capacitor can be: a.) 0o to 90o and 180o to 270o c.) 0o to 180o o o o o b.) 0 to 90 and 270 to 360 d.) nearly the entire cycle 6. The turning off a thyristor is known as: a.) Gating b.) Commutating c.) Forward biasing d.) Interrupting 7. Suppose a TRIAC is used to control the speed of a motor. Also assume that the motor is highly inductive and causes loss of commutation. What is the likely result? a.) The TRIAC will short and be ruined. c.) Power control will be lost. b.) The TRIAC will open and be ruined. d.) The motor will lost. 8. The TRIAC is primarily: a.) An RF device. b.) An AC power control device. c.) A dc power control device. d.) A bidirectional diode. 9. The best device to use as a light dimmer in an ac circuit is the: a.) Bipolar transistor. c.) TRIAC b.) SCR. d.) Rheostat. 10. Which of the following statements is incorrect? a.) The gate lead of a TRIAC is used to turn the device on and off. b.) A TRIAC can be tested with an ohmmeter. c.) The TRIAC is similar to two SCRs connected in inverse parallel with the gates tied together. d.) A TRIAC can be triggered on the positive and negative alternations of a sine wave. VIII. TRIAC CIRCUITS AND APPLICATIONS 1. CIRCUIT OPERATION/APPLICATION TRIAC Switching Circuit - Can be used for switching of and of of lights such as traffic lights 8|P age Republic of the Philippines Polytechnic University of the Philippines Office of the Vice President for Academic Affairs College of Engineering ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING (ECE) DEPARTMENT 2. CIRCUIT OPERATION/APPLICATION Modified TRIAC Switching Circuit -Can be used for speed control such as using electric fans. 3. CIRCUIT OPERATION/APPLICATION TRIAC Phase control -Used to control the speed of the motor such as generator applications etc. 4. CIRCUIT OPERATION/APPLICATION Lamp Dimmer Circuit -Primary used for dimming lights. 9|P age Republic of the Philippines Polytechnic University of the Philippines Office of the Vice President for Academic Affairs College of Engineering ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING (ECE) DEPARTMENT 10 | P a g e