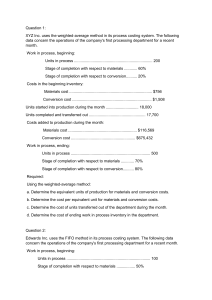
QUIZ 7_PROCESS COSTING _T or F 1. In a process costing system, the costs of one processing department become part of the costs of the next processing department. -True 2. The equivalent units of production will be the same under the weighted-average and the FIFO method if there is no beginning work in process inventory. -True 3. Under the weighted-average method, the equivalent units used to compute the unit costs of ending inventories relate only to work done during the current period. -False 4. In order to equitably allocate costs in a process costing system, dissimilar products are restated in terms of equivalent units by weighting the number of units produced by their market values. -False 5. In a process costing system, units transferred to the next processing department are presumed to be 100% complete with respect to the work performed by the transferring department. -True 6. Under a weighted-average process costing system when all materials are added at the beginning of the production process, the equivalent units for materials is equal to the units completed and transferred out. -False 7. In calculating cost per equivalent unit under the weighted-average method, prior period costs are combined with current period costs. -True 8. The equivalent units of production for a department using the FIFO process costing method is equal to the number of units completed plus the equivalent units in the ending inventory. -False 9. In a process costing system, direct labor cost combined with manufacturing overhead cost is known as conversion cost. -True 10. The units in beginning work in process inventory plus the units started into production must equal the units transferred out of the department plus the units in ending work in process inventory. -True 11. Abnormal spoilage is always accounted for on an equivalent unit basis. -True 12. A discrete loss is assumed to occur at a specific point in the production process. -True 13. A continuous loss is assumed to occur at a specific point in the production process. -False 14. Costs of normal shrinkage and normal continuous losses in a process costing environment are handled by the method of neglect. -True 15. Normal continuous losses are absorbed by all units in ending inventory and transferred out on a EUP basis. -True QUIZ 8_PROCESS COSTING _MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The weighted-average method of process costing differs from the FIFO method of process costing in that the weighted-average method: A. considers ending work in process inventory to be fully complete. B. All of the above. 2. 3. 4. 5. C. does not consider the degree of completion of beginning work in process inventory when computing equivalent units of production. D. will always yield a higher cost per equivalent unit. ABC Company uses a weighted-average process costing system. All materials at ABC are added at the beginning of the production process. The equivalent units for materials at ABC would be the sum of: A. units in ending work in process and the units started and completed. B. units in beginning work in process and the units started. C. units in ending work in process and the units started. D. units in beginning work in process and the units started and completed. In the computation of costs per equivalent unit, the weighted-average method of process costing considers: A. costs incurred during the current period only. B. costs incurred during the current period plus cost of ending work in process inventory. C. costs incurred during the current period plus cost of beginning work in process inventory. D. costs incurred during the current period less cost of beginning work in process inventory. Under which of the following conditions will the FIFO method of process costing result in the same amount of cost being transferred to the next department as the weighted-average method? A. When units in the beginning inventory are all completed and transferred at the same time. B. When there is no ending inventory. C. When there is no beginning inventory. D. When the beginning and ending inventories are each fifty percent complete. In order to compute equivalent units of production using the FIF0 method of process costing, work for the period must be broken down into parts: A. completed during the period and units in ending inventory. B. completed from beginning inventory, started and completed during the month, and units in ending inventory. C. processed during the period and units completed during the period. D. started during the period and units transferred out during the period 6. The Assembly Department started the month with 83,000 units in its beginning work in process inventory. An additional 334,000 units were transferred in from the prior department during the month to begin processing in the Assembly Department. There were 34,000 units in the ending work in process inventory of the Assembly Department. How many units were transferred to the next processing department during the month? A. 383,000 B. 451,000 C. 417,000 D. 285,000 7. Unacceptable units of production that are discarded or sold for reduced prices are referred to as: A. spoilage. B. scrap. C. reworked units. D. defective units. 8. Unacceptable units of production that are subsequently repaired and sold as acceptable finished goods are: A. reworked units. B. scrap. C. defective units. D. spoilage. 9. The primary difference between the FIFO and weighted average methods of process costing is: A. in the treatment of beginning Work in Process Inventory. B. in the treatment of current period production costs. C. in the treatment of started and completed units. D. in the treatment of spoiled units. 10. Transferred-in cost represents the cost from: A. the last production cycle. B. the last department only. C. all prior departments. D. the current period only. 11. In a process costing system, the journal entry to record the transfer of goods from Department #2 to Finished Goods Inventory is a: A. debit Cost of Goods Sold, credit Work in Process Inventory #2. B. debit Finished Goods Inventory, credit Work in Process Inventory #2. C. debit Finished Goods Inventory, credit Work in Process Inventory #1. D. debit Work in Process Inventory #2, credit Finished Goods Inventory. 12. Material is added at the beginning of a process in a process costing system. The beginning Work in Process Inventory for the process was 30 percent complete as to conversion costs. Using the FIFO method of costing, the number of equivalent units of material for the process during this period is equal to the: A. units started and completed this period in the process. B. units started and completed this period plus the units in ending Work in Process Inventory. C. beginning inventory this period for the process. D. units started this period in the process plus the beginning Work in Process Inventory. 13. In a cost of production report using process costing, transferred-in costs are similar to the: A. conversion cost added during the period. B. cost transferred out to the next department. C. cost of material added at the beginning of production. D. cost included in beginning inventory. 14. The first step in determining the cost per EUP per cost component under the weighted average method is to: A. divide the current period's production cost into the EUP. B. subtract the beginning Work in Process Inventory cost from the current period's production cost. C. divide the current period's production cost by the equivalent units. D. add the beginning Work in Process Inventory cost to the current period's production cost. 15. Equivalent units of production are equal to the: A. number of whole units that could have been completed if all work of the period had been used to produce whole units. B. units completed by a production department in the period. C. number of units worked on during the period by a production department. D. identifiable units existing at the end of the period in a production department. Process Costing_QUIZ 3_Problem Solving