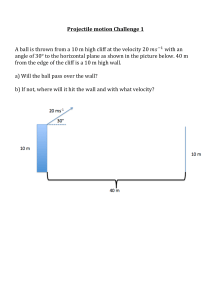
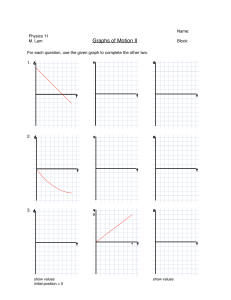
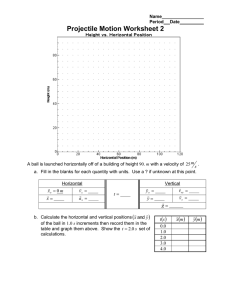
Projectile-Any object upon which the only force acting on is gravity! • Neglecting air resistance- all objects fall with the same acceleration. • Two objects of different weights, dropped from the same height, hit the ground at the same time. • A horizontally launched object will reach the ground in the same time as an object dropped vertically from rest. • The initial horizontal velocity is irrelevant. Horizontal Vertical Motion Motion Forces No The force of gravity (down) Acceleration No Velocity Constant Yes "g" is downward at -9.8 m/s2 Changing by -9.8 m/s each second All projectiles follow a parabolic path • Horizontal Motion – Constant, no acceleration. • Vertical Motion – Free fall, acceleration due to gravity. A horizontally launched projectile The x-component of the velocity never changes Which hits the ground first? A Package Dropped from an airplane Initial vertical velocity equals zero The time of flight for all horizontally launched projectile Vi=20 m/s vxi 20m / s vyi 0 Same as if it were dropped from rest 1 2 d at 2 Calculate the time of flight for the projectile vi = 20 m/s t 4.5s d = 100 m 0 1 2 d vi t at 2 1 2 d at 2 1 100m (10m / s 2 )t 2 2 Projectile launched from ground level at an angle Projectile launched from ground level at an angle Finding the initial vertical and horizontal components of the initial velocity given the total velocity, magnitude and direction! v yi vi sin vxi vi cos A football is punted at 600 to the horizontal at 50 m/s, calculate the initial horizontal and vertical components of the velocity. Given the initial horizontal and vertical velocities you can find the total velocity ( speed and direction.) V vxf v yf 2 tan v yf vxf 2 tan 1 v yf vxf A motorcycle daredevil is attempting to jump across as many buses as possible. The takeoff ramp makes an angle of 180 above the horizontal, and the landing ramp is identical to the takeoff ramp. Each bus is 2.74 m wide. The cyclist leaves the ramp with a speed of 33.5 m/s. What is the maximum number of buses over which the cyclist can jump? A projectile launched at an angle above the horizontal Firing at Different Angles What launch angle(s) give the greatest range? What launch angle(s) give the greatest range? 300 300 and 600 450 150 and 750 Range of a Projectile for vi = 50 m/s Angles Summary Paths for different Launch Angles y (meters) 4000 3000 45 deg 60 deg 30 deg 2000 1000 0 0 2000 4000 6000 x (meters) 1. 2. 3. 4. Complimentary angles give the same range 450 gives the greatest range 900 gives the greatest time of flight 900 gives the greatest height 8000 10000 Air Resistance Both car and ball have the same horizontal velocity link Two assumptions: 1. Free-fall acceleration g is constant. 2. Air resistance is negligible. The path of a projectile is parabolic. The initial velocity is vi The launched angle is Velocity vector changes in magnitude and direction Acceleration in y-direction (vertical) is g Acceleration in x-direction (horizontal) is 0 Superposition of motion in x-direction and motion in y-direction Acceleration in x-direction is 0. (Constant velocity) Acceleration in y-direction is g. (Constant acceleration) d x vxi t 1 2 d y v yi t a y t 2 vxf vxi v yf v yi at v yf v yi a y t dy 1 (v yf v yi )t 2 The horizontal motion and vertical motion are independent of each other; that is, neither motion affects the other. Relative Motion Moving frame of reference A boat heading due north crosses a river with a speed of 10.0 km/h. The water in the river has a speed of 5.0 km/h due east. a. Determine the velocity of the boat. b. If the river is 3.0 km wide how long does it take to cross it? o Displacement vs. time d (m) If position is recorded, a parabolic d - t graph is formed. d - displacement t - time t (s) Velocity vs. Time v (m/s) d(m) 0 0 t (s) If the velocity is recorded, a v-t linear graph is formed. v - velocity t - time t (s) Velocity vs. Time v (m/s) Ball is moving up, positive velocity t (s) 0 highest point, the velocity is zero. Ball is moving down negative velocity Velocity vs. Time v (m/s) Speed of the ball is reducing gradually. negative acceleration t (s) 0 speed is zero, at rest. speed is increasing Areas in a Velocity vs. Time graph v (m/s) Area A = (+ displacement) A t (s) 0 B The relationship between A and B ? Area B = (- displacement) Velocity vs. Time graph The slope is : v (m/s) What is the slope? v 0 y v vo s g x t tt g = the acceleration due to gravity , about -9.81 m/s2 t (s) Slope = acceleration! A ball tossed upward has initial velocity components 30 m/s vertical, and 5 m/s horizontal. The position of the ball is shown at 1-second intervals. Air resistance is negligible, and g = 10 m/s². Motion of a ball falling off of a table. Which is the correct path? A stone was thrown straight upward at t =0 with 20 m/s initial velocity on the roof of a 50 m high building 1. Find the time the stone reaches at maximum height (v=0) 2. Find the maximum height 3. Find the time the stone reaches its original height 4. Find the velocity of the stone when it reaches its original height 5. Find the velocity and position of the stone at t=5.0s 1. v f vyi ayt 20.0 9.80t 0.00 t 20.0 2.04 s 9.80 3. t 2.04 2 4.08s 1 2. yf yi vyit ayt 2 2 1 50.0 20 2.04 (9.80) (2.04)2 2 50.0 20.4 70.4(m) 4. vyf vyi ayt 20.0 (9.80) 4.08 20.0(m / s) 5. vyf vyi ayt 20.0 ( 9.80) 5.00 29.0(m / s ) 5. yf yi vyit 1 ayt 2 2 50.0 20.0 5.00 1 ( 9.80) (5.00) 2 27.5( m) 2 Find the horizontal and vertical components of the initial velocity. Carl Lewis at the 1992 Olympics in Barcelona, Spain, Lewis won gold medals for the long jump (28 feet 5.5 inches), this resulted from an initial velocity of 9.5 m/s at an angle of 40 degrees to the horizontal. Vxi vi cos (9.5m / s) cos 40 7.3m / s Vyi vi sin (9.5m / s)sin 40 6.1m / s Michelle Wie “The Big Wieasy” hits a nine iron with a velocity of 25 m/s at an angle of 600 to the horizontal. Vxi vi cos Adam Vinatieri the New England Patriot kicker launches a kick at an angle of 300 at a velocity of 30 m/s Vxi vi cos (25m / s) cos 60 (30m / s) cos 30 12.5m / s 25.9m / s Vyi vi sin Vyi vi sin (25m / s)sin 60 (30m / s)sin 30 21.7m / s 15m / s A melon truck brakes right before a ravine and looses a few melons. The melons skit over the edge with an initial velocity of v = 10 m/s a. Determine the velocity just before in hits the ground b. Calculate the velocity and the speed of the melon at t = 5.0 s c. Determine the time it takes to hit the ground d. Graph the path of a melon Wiley Coyote has missed the elusive roadrunner once again. This time, he leaves the edge of the cliff at 50 m/s horizontal velocity. If the canyon is 100 m deep, how far from the edge of the cliff does the coyote land? Throwing a ball out from a rooftop A ball is thrown horizontally from the Empire State building at 20 m/s and lands 34.2 seconds later. Find: initial horizontal motion final 1. The distance the ball lands from the base of the Empire State building. 2. The final velocity of the ball. Bear Canyon Jump Malik is stranded on the wrong side of a 95 meter wide canyon with a grizzly bear. In a desperate attempt to escape from the bear he runs right off the edge of a cliff. He leaves at a velocity of 10 m/s horizontally. The canyon was 150 m deep, how long does he take to hit the ground? Or, does he make it to the other side? d y 12 at 2 150m 12 (10m / s 2 )t 2 vi t 5.5s d x vxi t 150 m 95 m d x (10m / s)(5.5s) d x 55m A rescue plane flies at 40 m/s and an elevation of 100 m toward a point directly over a hiking accident victim. The pilot wants to release a rescue capsule so that it hits the ground very close to the victim. How far in front of the victim should he release the package? A banana thrown at a monkey with no gravity A banana thrown straight at the monkey A banana thrown at a slow speed at the monkey An arrow leaves the bow horizontally at a speed of 20 m/s. If the target is 100 meters away and the archer aimed directly at the center of the bulls eye how far below the bulls eye will the arrow land? Projectiles undergo simultaneous and independent vertical and horizontal motion.