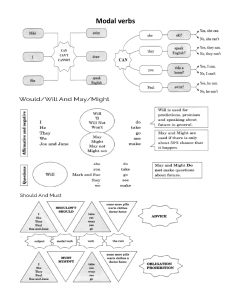
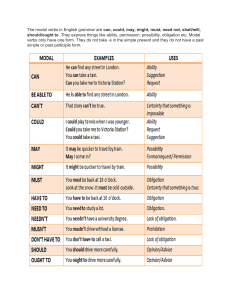
Modal Verb Uses and Examples in Sentences. Read more at: https://www.adda247.com/teaching-jobs-exam/modal-verbs/ What is a Modal Verb? A Modal Verb is an auxiliary verb that is used along with main verbs to contextually indicate a modality such as likelihood, ability, permission, request, capacity suggestion, order, obligation, necessity, possibility or advice. In simple words, a modal verb is used alongside the main verb to express ideas such as the possibility, intention, or necessity of a subject to do an action. Some of the common examples include can, could, might, etc. Modal verb vs Helping Verb At this point, you might be thinking about how Modal Verbs are different from Help Verbs. Well, to simplify things, you can think of it as all Modal Verbs are Helping verbs. Helping verbs does not alter the meaning of the main verb but only assists the main verb in forming tense, mood, and voice. Difference Between Modal Verbs and Helping Verbs. Modal verbs Modifies the meaning of the main verb depending on the context Do not have their own specific meaning. Followed by the base form (infinitive). Examples – Might, Must, Shall, Should, etc.... Helping verbs Assists the main verb in forming various verb tenses, moods, and voices. May have their own meaning and can also function as the main verb. Can be followed by base form, present participle, or past participle. Examples – be, have, do, etc. Types of Modal Verbs The Modal Verbs are used to express various situations, such as attitudes, possibilities, obligations, permission, and more. They are combined with the main verb depending on the context to convey meaning. There are a total of nine primary modal verbs in English. Many say there are ten modal verbs too. Here are all of them. Can Could Shall Should Will Would May Might must ought to Can and Could “Can” and “Could” are used to express ability, possibility, and permission. Depending on the context and how you use it alongside the main verb, it can modify the meaning. May and Might “May” and “might” are used to indicate permission, possibility, or uncertainty. Must “Must” expresses a strong obligation. Example – You must come to my party. Will and Would “Will” and “Would” are used to indicate future actions, intentions or preferences. Shall “Shall” is used mainly in formal contexts for suggestions or offers. Should “Should” is used to give advice, make recommendations, or express obligation.