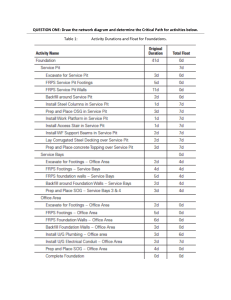
Chapter 2 CURRICULUM FOUNDATIONS OBJECTIVES: In this chapter , you should be able to: 1. Discuss different curriculum foundations; and 2. Discuss different conceptions of curriculum. CURRICULUM FOUNDATIONS • PHILOSOPHICAL FOUNDATIONS of CURRICULUM Philosophy provides educators, teachers and curriculum makers with framework for planning, implementing and evaluating curriculum in schools. It helps in answering what school are for, what subjects are important, how students should learn and what materials and methods should be used. In decision making, philosophy provides the starting point and will be used for the succeeding decision making. CURRICULUM FOUNDATIONS • Historical Foundations of Curriculum Curriculum theorists and how they view curriculum from a historical Perspective. CURRICULUM FOUNDATIONS • Historical Foundations of Curriculum Curriculum theorists and how they view curriculum from a historical Perspective. CURRICULUM FOUNDATIONS • Historical Foundations of Curriculum Curriculum theorists and how they view curriculum from a historical Perspective. CURRICULUM FOUNDATIONS • Historical Foundations of Curriculum Curriculum theorists and how they view curriculum from a historical Perspective. Psychological Foundations of Curriculum Psychology provides a basis for the teaching and learning process. 1. Behaviorist Psychology a. connectionism – Edward Thorndike (which influenced Tyler and Taba, the well known curricularists) b. classical conditioning – Ivan Pavlov c. operant conditioning – B. F. Skinner d. modeling and observation theory – (Bandura) e. hierarchical learning – Robert Gagne Psychological Foundations of Curriculum Psychology provides a basis for the teaching and learning process. 2. Cognitive Psychology a. cognitive development stages – Jean Piaget b. social constructivism – Lev Vgotsky c. multiple intelligences – Howard Gardner d. learning styles – Felder and Silverman e. emotional intelligences – Daniel Goleman Psychological Foundations of Curriculum Psychology provides a basis for the teaching and learning process. 3. Humanistic Psychology Humanist psychologist are concerned with how learners can develop their human potential. a. Gestalt theory b. theory of human needs and for self actualizing persons - Maslow c. Carl Roger’s non directive lives Social Foundations of Education Schools exist within the social context. In considering the social foundations of curriculum, we must recognize that schools are the only one of the many institutions that educate society. The home, the family, community likewise educate the people in the society. But schools are formal institutions that address more complex and interrelated societies and the world. Six (6) Curriculum Conceptions 1. Academic Rationalist Conception- it is considered the oldest among the curriculum conceptions. It stresses the importance of different bodies of knowledge, known as discipline or subject areas, as the the focus of the curriculum. 2. Cognitive Process Conception- seek to develop a repertoire of cognitive skills that are applicable to a wide range of intellectual problems.The subject matters are instruments or tools for developing these cognitive skills that are lasting in the lives of individuals. Six (6) Curriculum Conceptions 3. Humanistic Conception- stresses the idea that the curriculum or education is an instrument for developing the full potential of individuals. It seeks to help individual to discover and develop their unique identities. It stresses that the curriculum should focus on the needs and interest of individuals. 4.Social Reconstructionist Conception- views the school or schooling as an agency for social change. Hence it stresses that curriculum should respond to the different issues,needs, problems, and the demands of the society. Six (6) Curriculum Conceptions 5. Technological Conception- is preoccupied with the development of means to achieve curriculum or educational goals. It views schooling as a complex system that can be analyzed into its constituent components. 6. Eclectic Conception- is where curriculum workers find themselves aligning their ideas with two or more curriculum conceptions. Hence, this curriculum conceptions reiterates the realities in curriculum development that each of the curriculum conception is to be considered and is influential to a certain extent in designing the curriculum. LEARNING ACTIVITY Examine a particular curriculum. Analyze what curriculum conception is leaning to. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UeK_YEqdqv0