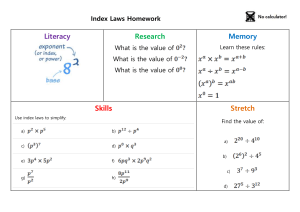
What we'll discuss • • • • Literacy, often spelled as "literacy," refers to the ability to read and write effectively. It is a fundamental skill that enables individuals to understand, interpret, and communicate through written language. Literacy is a critical aspect of education and plays a crucial role in personal development, communication, and participation in society. Literacy is a foundational skill that empowers individuals to access knowledge, participate in civic life, and pursue educational and career opportunities. Efforts to promote literacy include formal education, literacy programs, and initiatives to improve literacy rates in communities around the world. Literacy is not a monolithic concept but rather a multifaceted skill that encompasses various types or dimensions. Different types of literacy include: 1. Basic Literacy: This is the fundamental ability to read and write in one's native language. It includes the recognition of letters, words, and basic sentence structures. Basic literacy is often the first step in a person's educational journey. 2. Numeracy: Numeracy is the ability to understand and work with numbers. It involves basic mathematical skills such as counting, addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Numeracy is crucial for everyday tasks like budgeting, shopping, and understanding data. 3 Digital Literacy: Digital literacy refers to the ability to use digital devices (computers, smartphones, tablets) and navigate digital platforms effectively. It includes skills such as using word processing software, browsing the internet, understanding online safety and privacy, and using social media. 4. Media Literacy: Media literacy is the ability to critically analyze and evaluate media messages and information from various sources. It involves understanding bias, identifying misinformation and fake news, and being able to differentiate between credible and unreliable sources. 5. Visual Literacy: Visual literacy involves the interpretation and understanding of visual elements, such as images, charts, graphs, and symbols. It's essential for comprehending visual information in fields like art, science, and design. 6. Cultural Literacy: Cultural literacy is the knowledge and understanding of the cultural references, symbols, and norms within a particular society or group. It helps individuals navigate social interactions and understand cultural context. 7. Financial Literacy: Financial literacy is the ability to manage personal finances effectively. It includes skills like budgeting, saving, investing, understanding financial products, and making informed financial decisions. 8. Health Literacy: Health literacy is the capacity to access, understand, and apply health-related information to make informed decisions about one's health. It involves understanding medical terminology, reading prescription labels, and knowing how to navigate the healthcare system. 9. Scientific Literacy: Scientific literacy is the ability to understand and engage with scientific concepts and processes. It includes critical thinking skills, the ability to evaluate scientific claims, and an understanding of the scientific method. 10. Environmental Literacy: Environmental literacy involves understanding environmental issues, sustainability, and the impact of human activities on the environment. It includes knowledge about ecosystems, conservation, and environmental policies. 11. Legal Literacy: Legal literacy is the understanding of basic legal rights, responsibilities, and concepts within a legal system. It helps individuals navigate legal issues and make informed decisions about legal matters. 12. Information Literacy: Information literacy is the ability to locate, evaluate, and effectively use information from various sources. It's crucial for academic research, problem-solving, and decision-making. 13. Physical Literacy: Physical literacy refers to an individual's ability to move and engage in physical activities with competence and confidence. It goes beyond simply having physical fitness or motor skills; it encompasses a wide range of physical abilities, knowledge, and attitudes related to movement and physical activity. Physical literacy is essential for leading an active and healthy lifestyle throughout one's life. These different types of literacy are interconnected and often overlap. They are essential for personal development, education, and active participation in society, and they play a significant role in an individual's ability to thrive in various aspects of life. In addition to the types of literacy mentioned earlier, there are several other specialized forms of literacy that are important in specific contexts and fields. Here are some additional types of literacy: 1. Computer Programming Literacy: This involves the ability to write, understand, and work with computer programming code. It is essential for careers in software development and computer science. 2. Legal Research Literacy: Legal research literacy focuses on the skills required to access and navigate legal databases, statutes, case law, and legal literature. It's crucial for legal professionals and researchers. 3. Mathematical Literacy: While related to numeracy, mathematical literacy goes beyond basic math skills and involves a deeper understanding of mathematical concepts, problemsolving, and mathematical reasoning. 4. Spatial Literacy: Spatial literacy involves the ability to understand and interpret spatial information, such as maps, geographic data, and geographical concepts. It's valuable in fields like geography, urban planning, and navigation. 5. Musical Literacy: Musical literacy includes the ability to read and understand musical notation, as well as concepts related to music theory, composition, and performance. 6. Ethical Literacy: Ethical literacy pertains to an understanding of ethical principles, moral reasoning, and the ability to make ethical decisions in various situations. 7. Global Literacy: Global literacy involves knowledge of global issues, cultures, and international relations. It includes an awareness of global challenges, such as climate change and human rights. 8. Emotional Literacy: Emotional literacy, also known as emotional intelligence, is the ability to recognize, understand, and manage one's own emotions and the emotions of others. It is valuable in personal relationships and leadership roles. 9. Business Literacy: Business literacy involves understanding financial statements, business operations, and economic principles. It's essential for individuals in management, entrepreneurship, and finance. 10. Scientific and Technical Literacy: In addition to scientific literacy, this type involves specialized knowledge and understanding of scientific and technical fields, such as engineering, chemistry, or physics. 11. Statistical Literacy: Statistical literacy includes the ability to interpret and apply statistical data and concepts. It's important in fields like data analysis, research, and decision-making. 12. Civic Literacy: Civic literacy focuses on understanding government structures, political processes, and civic responsibilities. It's important for informed citizenship and participation in democratic societies. These specialized forms of literacy are often required in specific professions or academic disciplines. Developing expertise in one or more of these areas can enhance one's ability to excel in a particular field or context. The history of literacy is a complex and multifaceted story that spans thousands of years. The development of literacy has been closely tied to the evolution of human societies and the need for written communication. Here is a brief overview of the history and origin of literacy: 1. Prehistoric and Ancient Times: Early humans communicated primarily through spoken language and visual symbols, such as cave paintings. The earliest forms of writing were pictograms and ideograms, where symbols represented objects or ideas. Examples include the cuneiform script of Mesopotamia and the hieroglyphs of ancient Egypt. 2. Development of Alphabets: Over time, writing systems evolved from pictorial symbols to alphabets, where individual characters represented specific sounds. The Phoenician alphabet, developed around 1200 BCE, was a significant precursor to many modern alphabets, including Greek and Latin. 3. Ancient Civilizations: Writing and literacy played a vital role in the development of ancient civilizations. In Mesopotamia, scribes were trained to record information on clay tablets. In ancient Egypt, hieroglyphs were used for religious texts, monumental inscriptions, and administrative purposes. 4. Classical Antiquity: In ancient Greece, literacy was valued, and the Greeks developed a system of education that included reading, writing, and rhetoric. This emphasis on literacy had a profound impact on Western thought and culture. 5. Spread of Religious Texts: The religious texts of various cultures, such as the Bible, the Quran, and Buddhist scriptures, played a significant role in the dissemination of written language. Monasteries and religious institutions were often centers of literacy and education. 5. Spread of Religious Texts: The religious texts of various cultures, such as the Bible, the Quran, and Buddhist scriptures, played a significant role in the dissemination of written language. Monasteries and religious institutions were often centers of literacy and education. 5. Spread of Religious Texts: The religious texts of various cultures, such as the Bible, the Quran, and Buddhist scriptures, played a significant role in the dissemination of written language. Monasteries and religious institutions were often centers of literacy and education. 6. Medieval and Renaissance Periods: During the Middle Ages, literacy was largely limited to the clergy and the aristocracy. However, the invention of the printing press by Johannes Gutenberg in the 15th century made books more accessible and contributed to the spread of literacy. 7. Colonialism and Education: The colonial era saw efforts to impose European languages and literacy on indigenous populations in various parts of the world. Missionaries and colonial authorities played a role in teaching reading and writing. 8. 19th and 20th Centuries: The expansion of public education systems in the 19th and 20th centuries greatly increased literacy rates in many countries. Universal education became a goal in many societies, leading to significant improvements in literacy rates. 9. Digital Age: In the late 20th and early 21st centuries, digital technology and the internet transformed the way people access and share information. Digital literacy, the ability to navigate and use digital technologies, became increasingly important. Today, literacy is considered a fundamental skill in modern society, and efforts continue to ensure that education is accessible to all. Literacy rates vary widely from one region to another, with some countries achieving nearuniversal literacy, while others still face significant challenges in providing basic education and literacy skills to their populations.