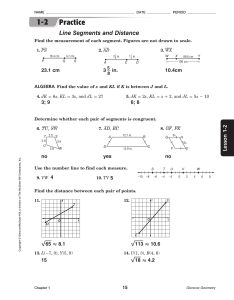
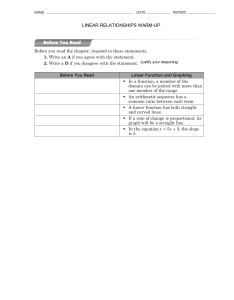
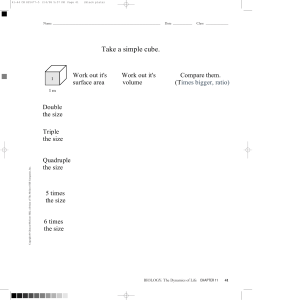
Unit 2 The Basic Accounting Cycle Chapter 3 Business Transactions and the Accounting Equation Chapter 4 Transactions That Affect Assets, Liabilities, and Owner’s Capital Chapter 5 Transactions That Affect Revenue, Expenses, and Withdrawals Chapter 6 Recording Transactions in a General Journal Chapter 7 Posting Journal Entries to General Ledger Accounts Chapter 8 The Six-Column Work Sheet Chapter 9 Financial Statements for a Sole Proprietorship Chapter 10 Completing the Accounting Cycle for a Sole Proprietorship Chapter 11 Cash Control and Banking Activities Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 0 Chapter 4 Transactions That Affect Assets, Liabilities, and Owner’s Capital What You’ll Learn Prepare a chart of accounts. Explain the purpose of double-entry accounting. Identify the normal balance of accounts. Use T accounts to illustrate the rules of debit and credit for asset accounts, liability accounts, and the owner’s capital account and to express the accounting equation. Use T accounts to analyze transactions that affect assets, liabilities, and the owner’s capital account. Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Chapter 4 Transactions That Affect Assets, Liabilities, and Owner’s Capital What You’ll Learn Calculate the account balances after recording business transactions. Define the accounting terms introduced in this chapter. Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 2 Chapter 4, Section 1 Accounts and the Double-Entry Accounting System What Do You Think? Based on what you have reviewed about transactions, why do you think we use a double-entry accounting system? Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 SECTION 4.1 Accounts and the Double-Entry Accounting System Main Idea The double-entry accounting system uses debits and credits. Debit means “left side” and credit means “right side.” You Will Learn about the chart of accounts. about the double-entry accounting system. Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 4 Accounts and the Double-Entry Accounting System SECTION 4.1 Key Terms chart of accounts ledger double-entry accounting debit credit T account normal balance Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 5 SECTION 4.1 Accounts and the Double-Entry Accounting System The Chart of Accounts A chart of accounts is a list of accounts used by a business. Accounts are grouped together in a ledger, also known as a general ledger. “Keeping the books” refers to maintaining accounts in the ledger. Accounts are easier to locate in the ledger if they are numbered. A typical numbering system is as follows: Asset accounts begin with 1. Liability accounts begin with 2. Owner’s equity accounts begin with 3. Revenue accounts begin with 4. Expense accounts begin with 5. Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 6 SECTION 4.1 Accounts and the Double-Entry Accounting System Double-Entry Accounting If a business has many accounts, accountants use the double-entry accounting system to analyze and record a transaction. The double-entry accounting system recognizes both the debit and credit side of a business transaction. Account Name Left Side Right Side Debit Side Credit Side Debit Credit Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 7 SECTION 4.1 Accounts and the Double-Entry Accounting System T Accounts The T account is a tool for using the double-entry accounting system. It shows the dollar increase and decrease caused by a transaction. The T account gets its name from being shaped like a T: Account name is on the top. The left side is used for debits. The right side is used for credits. Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 8 SECTION 4.1 Accounts and the Double-Entry Accounting System The Rules of Debit and Credit In double-entry accounting, for each debit in one account, there must be an equal credit in another account. The rules of debit and credit vary depending on the type of account. Each account has a normal balance to record increases to the account. The word normal in this case means usual. Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 9 SECTION 4.1 Accounts and the Double-Entry Accounting System Rules for Asset Accounts Asset accounts follow three rules for debit and credit: It is increased on the debit side (left side). It is decreased on the credit side (right side). The normal balance is the increase or debit side. Because the increase side is always on the debit side, asset accounts have a normal debit balance. Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 10 SECTION 4.1 Accounts and the Double-Entry Accounting System Rules for Liability and Owner’s Capital Accounts Liability and owner’s capital accounts follow three rules for debit and credit: It is increased on the credit side (right side). It is decreased on the debit side (left side). The normal balance is the increase or credit side. Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 11 SECTION 4.1 Accounts and the Double-Entry Accounting System Key Terms Review chart of accounts A list of all accounts used by a business. ledger A group of accounts; also referred to as a general ledger. double-entry accounting A system that recognizes the different sides of business transactions as debits and credits. debit An entry on the left side of an account. Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 12 SECTION 4.1 Accounts and the Double-Entry Accounting System Key Terms Review credit An agreement to pay for a purchase at a later time; an entry on the right side of an account. T account A visual representation of a ledger account. The T account is a tool used to analyze transactions. normal balance The increase side of an account. The word normal here means usual. Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 Chapter 4, Section 2 Applying the Rules of Debit and Credit What Do You Think? How many T accounts would you need to analyze a transaction? Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 14 SECTION 4.2 Applying the Rules of Debit and Credit Main Idea Use T accounts to analyze transactions. You Will Learn a step-by-step method for analyzing transactions. how to apply the method to asset, liability, and owner’s capital transactions. Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 15 SECTION 4.2 Applying the Rules of Debit and Credit Asset and Equities Transaction When analyzing business transactions, you should apply the rules of debit and credit, and complete the entry in T-account form. Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 16 SECTION 4.2 Applying the Rules of Debit and Credit Asset and Equities Transaction When analyzing business transactions, you should follow this method: Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 17 SECTION 4.2 Applying the Rules of Debit and Credit Asset and Equities Transaction When analyzing business transactions, you should follow this method: Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 18 SECTION 4.2 Applying the Rules of Debit and Credit Asset and Equities Transaction When analyzing business transactions, you should follow this method: Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 19 SECTION 4.2 Applying the Rules of Debit and Credit Assets and Owner’s Capital Use a T account to analyze an owner’s investment in the business: Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 20 SECTION 4.2 Applying the Rules of Debit and Credit Assets and Owner’s Capital Use a T account to analyze an owner’s investment in the business: Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 21 SECTION 4.2 Applying the Rules of Debit and Credit Assets and Owner’s Capital Use a T account to analyze an owner’s investment in the business: Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 22 SECTION 4.2 Applying the Rules of Debit and Credit Assets and Liabilities Increase an asset and decrease another asset: Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 23 SECTION 4.2 Applying the Rules of Debit and Credit Assets and Liabilities Increase an asset and decrease another asset: Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 24 SECTION 4.2 Applying the Rules of Debit and Credit Assets and Liabilities Increase an asset and decrease another asset: Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 25 SECTION 4.2 Applying the Rules of Debit and Credit Assets and Liabilities Increase an asset and increase a liability: Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 26 SECTION 4.2 Applying the Rules of Debit and Credit Assets and Liabilities Increase an asset and increase a liability: Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 27 SECTION 4.2 Applying the Rules of Debit and Credit Assets and Liabilities Increase an asset and increase a liability: Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 28 SECTION 4.2 Applying the Rules of Debit and Credit Assets and Liabilities Increase an asset and decrease another asset: Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 29 SECTION 4.2 Applying the Rules of Debit and Credit Assets and Liabilities Increase an asset and decrease another asset: Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 30 SECTION 4.2 Applying the Rules of Debit and Credit Assets and Liabilities Increase an asset and decrease another asset: Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 31 SECTION 4.2 Applying the Rules of Debit and Credit Assets and Liabilities Decrease a liability and decrease an asset: Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 32 SECTION 4.2 Applying the Rules of Debit and Credit Assets and Liabilities Decrease a liability and decrease an asset: Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 33 SECTION 4.2 Applying the Rules of Debit and Credit Assets and Liabilities Decrease a liability and decrease an asset: Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 34 SECTION 4.2 Applying the Rules of Debit and Credit Assets and Liabilities Increase an asset and decrease another asset: Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 35 SECTION 4.2 Applying the Rules of Debit and Credit Assets and Liabilities Increase an asset and decrease another asset: Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 36 SECTION 4.2 Applying the Rules of Debit and Credit Assets and Liabilities Increase an asset and decrease another asset: Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 37 CHAPTER 4 Chapter 4 Review Question 1 Identify the normal balance for each of the following accounts by indicating Debit or Credit. Cash in Bank __________ Accounts Receivable __________ Richard Sims, Capital __________ Computer Equipment __________ 1st National Bank (mortgage on building) __________ Car Wash Equipment __________ Building __________ Office Supplies __________ Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 38 CHAPTER 4 Chapter 4 Review Answer 1 Step 1: Determine the account classification of each account. Step 2: Determine the normal balance side. a. Cash in Bank is an asset account. Since assets are on the left side of the accounting equation, they increase on the left side of the account and their normal balance is the debit side. b. Accounts Receivable is an asset account. Assets increase on the left side of the account so their normal balance is debit. (continued) Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 39 Chapter 4 Review CHAPTER 4 Answer 1 Step 2 c. d. Richard Sims, Capital is an owner’s capital account. Capital accounts are on the right side of the accounting equation. Therefore, they increase on the right side of the account and their normal balance is the credit side. Computer Equipment is an asset account. Assets increase on the left side of the account so their normal balance is debit. (continued) Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 40 Chapter 4 Review CHAPTER 4 Answer 1 Step 2 e. f. The First National Bank account for the mortgage is a liability account. Liabilities are on the right side of the accounting equation. Therefore, increases are shown on the right side of the account and their normal balance is the credit side. Car Wash Equipment is an asset account. Increases for assets appear on the left side of the account so their normal balance is debit. (continued) Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 41 Chapter 4 Review CHAPTER 4 Answer 1 Step 2 (continued) g. h. Building is an asset account. Increases for assets appear on the left side of the account so their normal balance is debit. Office Supplies is an asset account. Increases for assets appear on the left side of the account so their normal balance is debit. Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 42 CHAPTER 4 Chapter 4 Review Question 2 On October 18 Dick’s Car Wash bought $10,000 worth of car wash equipment by issuing Check #111. Using the Business Transaction Analysis method in your book, list the steps you would use to record this transaction. Assume that asset accounts for Cash in Bank and Car Wash Equipment exist. Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 43 CHAPTER 4 Chapter 4 Review Answer 2 Step 1: Identify the accounts affected. The accounts Car Wash Equipment and Cash in Bank are affected. Step 2: Classify the accounts affected. Car Wash Equipment is an asset account. Cash in Bank is an asset account Step 3: Determine the amount of increase or decrease for each account affected. Car Wash Equipment is increased by $10,000. Cash in Bank is decreased by $10,000. (continued) Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 44 CHAPTER 4 Chapter 4 Review Answer 2 Step 4: Which account is debited and for what amount? Increases in asset accounts are recorded as debits. Debit Car Wash Equipment for $10,000. Step 5: Which account is credited and for what amount? Decreases in asset accounts are recorded as credits. Credit Cash in Bank for $10,000. Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 45 CHAPTER 4 Chapter 4 Review Question 3 What does “double-entry accounting” mean? Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 46 CHAPTER 4 Chapter 4 Review Answer 3 Every transaction has two sides: a debit (left) side and a credit (right) side. If a business were to buy supplies for cash, two things would happen. First, the amount of supplies would go up, and since supplies are assets, the increase to the Supplies account would be recorded as a debit. Second, the balance in the Cash in Bank account would go down, and since cash is an asset, the decrease in Cash in Bank would be recorded as a credit. Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 47 Resources Glencoe Accounting Online Learning Center English Glossary Spanish Glossary Glencoe Accounting Unit 2 Chapter 4 Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 48