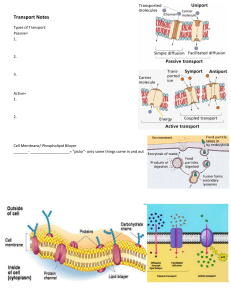
Cell membranes June 2002 Question 3 (a) –i-Phospholipid molecule. -ii- It is consists of one phosphate group forming the hydrophilic head , one glycerol and two fatty acids forming the hydrophobic tail. -iii-It is fluid because phospholipid molecules are in continuous vibrating movement, exchanging positions with each other but within their monolayer, also it is mosaic due to the pattern of distribution of proteins among phospholipids heads. (b) Receptors are proteins formed of different amino acids with different R-groups, therefore the primary structure which is the specific sequence of amino acids leads to the formation of specific globular shape as a result of formation of different bonds between its Rgroups, and this specific shape is complementary to specific antigen. November 2003 Question 5 (a) Glycoproteins Can be used as cell surface antigens for cell recognition also can be used as receptors or structures for hormonal attachment, and can form hydrogenbonds with the surrounding water to stabilize membrane structure. Carrier proteins Can be used to carry certain molecules or ions such as sodium ions by activetransport ( against their concentration gradient using energy from ATP) or used in the process of facilitated diffusion in which polar molecules or ions which cannot pass across phospholipids bilayer can cross the membrane down their concentration gradient. Cholesterol Regulates fluidity of cell membranes as it prevents membranes from being too rigid or too fluid also it has a role in controlling leakage of water and watersoluble molecules through the cell membranes. (b) A can cross the cell surface membrane from inside the cell where its concentration is lower to the surrounding medium where its concentration is higher only by active transport using energy and carrier protein. B can cross the cell surface membrane from the surrounding medium where its concentration is higher to the inside of the cell where its concentration is lower by simple diffusion through the phospholipids bilayer as it is a non-polar molecule. (c) Bacteria can be marked by antibodies or plasma proteins known as opsonin which can bind to specific receptors on the cell surface membrane of the phagocyte and this induces phagocyte to surround and envelope bacteria to be taken in a vesicle or a phagosome. (d) Lysosomes contain hydrolytic or digestive enzymes such as protease to act on the engulfed bacteria. November 2005 Question 2 (a)Notice :Annotated diagram means diagram with labels and brief description or explanation. Phospholipid heads being hydrophilic are directed outwards to form bonds with the surrounding water while its tails being hydrophobic are directed inwards to be away from water attracting each other with hydrophobic interaction, so they can form a phospholipids bilayer. Question 5 (a) To have the same volume as that of the large cube. (b) In both there is rapid increase in mass for the first three hours but after that the % increase starts to be slower between 3 to about 25 hours, then the percentage increase remains constant . The difference between the two results is that the % increase for the 8 cubes is higher as it reaches about 17% while that of the large cube is only about 7.5%. (c) The cells of the cubes of yam have lower water potential than that of the surrounding medium as they contain different solutes especially in their sap vacuole such as sugars and amino acids therefore water enters cells by osmosis down its concentration gradient through the partially permeable cell membranes of the cells. (d) Because the surface area to volume ratio in the 8 cubes is (6:1) larger than that of the cube of sides 2cm which is (3:1) therefore more water per unit time enter the cells, also the outer cells of the large cube may become fully turgid restricting inner cells from obtaining water and become enlarged. June 2007 Question 6 (a) 7.0 nm (b)K : Allow the movement of ions or polar molecules and water soluble molecules through the plasma membrane by facilitated diffusion or active transport. L : Acts as surface antigen for cell recognition or to act as receptors or binding sites for certain molecules such as hormones and to form hydrogen bonds with the surrounding water molecules to stabilize membrane structure. M : Necessary for membrane fluidity, and act as barrier for water and water soluble compounds and ions but allow the passage of lipid soluble substances. N : Regulates fluidity of the plasma membrane and has a role in controlling leakage of water. (c) Because glucose is a large water soluble ( hydrophilic) molecule therefore it cannot diffuse through the phospholipids bilayer . (d) Increase concentration of glucose leads to an increase in rate of uptake of glucose indicating that diffusion takes place down its concentration gradient and because the rate of diffusion remains constant above concentration 30 arbitrary units, this indicates that facilitated diffusion takes place as no enough protein channels are available to increase rate of diffusion by increasing concentration of glucose in the surrounding medium. (e) Active transport requires energy while facilitated diffusion is a passive process does not need energy also in facilitated diffusion molecules move down their concentration gradient while in active transport molecules move against their concentration gradient. June 2008 Question 2 (d)–i- As a general trend, increasing temperature leads to a decrease in % transmission of light. Between 20 and 60 oC % transmission decreases from 95% to 70%, but between 60 and 70 oC % transmission decreases sharply from 70 to 19% ,between 70 and 80 oC % transmission decreases from 19 to 6%. -ii- By increasing temperature diffusion of betalain increases as temperature causes membrane proteins to be denatured and this alters their tertiary structure making betalain released easily out the membranes also temperature increases fluidity of membranes as it increases kinetic energy of phospholipid molecules to vibrate faster. November 2008 Question 1 (a) -i- Draw a bracket across the whole bilayer . -ii-Fluid means that phospholipid molecules and proteins are in continuous motion , vibrating , and exchanging position with each other within their monolayer. Mosaic refers to the pattern of distribution of protein between the phospholipid molecules of the cell membrane. November 2009/21 Question 1 (c) 1- Can act as a carrier protein for active transport where molecules canbe carried against their concentration gradient. 2- Can act as channel protein for facilitated diffusion where ions that cannot pass through the phospholipid bilayer can pass down their concentration gradient. 3- Can be used as cell recognition structures. 4- Can act as an enzyme attached to the membranes such as enzyme in mitochondrial membranes used for ATP synthesis. 5- Can be used as receptors for hormonal attachment. 6- Can be used as receptors on the surface of lymphocytes and phagocytes. November 2009/22 Question 1 (a) –i- Because calcium ions are charged and water soluble therefore they cannot pass through the hydrophobic tails of the phospholipid molecules. -ii-Name active transport or active uptake (Notice that facilitated diffusion cannot be involved in this question as it states that molecules are forced against their concentration gradient, also this is shown in the diagrams) (a) (ii)Description calcium ions bind to the specific binding site of the protein carrier,and then using energy supplied by ATP, the carrier protein changes its shape making ions to be forced outside against their concentration gradient. (b) Bacterial cells are taken in vesicles, lysosomes fuse with the vesicles where lysosomal enzymes such as protease act on proteins to be digested into amino acids and lipase to act on its lipids, also contains enzymes to act on bacterial cell walls and nucleic acids to be digested. November 2010/22 Question 1 (b) The materials needed to be exported outside the cell (such as enzymes , hormones and glycoprotein ) are carried in a vesicle which is directed towards the cell surface membrane using energy from ATP and guided by microtubules, cell surface membrane and membrane of vesicle fuse together so that the contents of the vesicle is released outside the cell. November 2010/23 Question 1 (a) –i- A- phospholipid B- protein -ii- It has a hydrophilic head directed outwards to form bond with the surrounding water while its tail being hydrophobic directed inwards as it is expelled by water ,at the same time it forms hydrophobic interaction with the other hydrophobic tails of the other phospholipid molecules. (b) C- Channel protein used in facilitated diffusion of polar molecules that cannot diffuse through the phospholipid bilayer. D- they are glycoproteins and glycolipids used in cell recognition, also act as receptors and stabilise cell membranes by formation of bonds with the surrounding water. November 2011/21