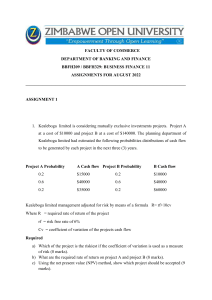
Aftab Hussain (Shaheed) APS&C MZD Test 01(Total Marks: 40) Class: XII-A Time allowed: 60 minutes Subject: STATISTICS Student Name: ________________________ Section A (01 X 07=07 Marks) 1. If ᵡ2 =5.8 and df=1, we make the following decision a. We reject 𝐻0 𝑎𝑡 𝛼 = 0.05 c. We accept 𝐻0 𝑎𝑡 𝛼 = 0.05 b. We reject 𝐻1 𝑎𝑡 𝛼 = 0.05 d. We reject 𝐻0 𝑎𝑡 𝛼 = 0.01 2. For a 3×3 contingency table, the degrees of freedom is, a. 3 c. 9 b. 4 d. 6 3. The computer-assisted method that helps in the recording and analysis of a hypothetical or an existing system is known as: a. Data processing c. Data flow b. Data capture d. Data transmission None 4. Two attributes A and B are said to be independent if a. b. 𝐴𝐵 ≠ 𝐴𝐵 𝑁 c. 𝐴𝐵 > 𝐴𝐵 𝑁 d. 𝐴𝐵 = 𝐴𝐵 𝑁 5. A list of various coded instructions is known as: a. Flowchart c. Algorithm b. Utility programs d. Computer program 6. The range of Yule’s coefficient is a. 0 to 1 c. 0 to 1.5 b. -1 to 0 d. -1 to +1 7. If for a contingency table, df=12 and number of rows is 4 then the number of columns will be a. 2 c. 4 b. 3 d. 5 Section B (07 X 03 = 21 Marks) 1. Convert the octal numbers 25 and 140 into binary. 2. How does association is different from correlation? 3. Out of 1800 candidates appeared for a competitive examination 625 were successful; 300 had attended a coaching class and of these 180 came out successful. Test for the association of attributes (using Yule’s coefficient) attending the coaching class and success in the examination. 4. Differentiate between negative and positive attributes. 5. Verify whether the given data: N = 100, (A) = 75, (B) = 60 and (AB) = 15 is consistent. 6. Mention the applications of chi-square distribution. 7. Calculate the Spearman Rank correlation test. Y 11 16 11 14 13 17 X2 20 18 22 21 27 26 X3 8.1 8.4 8.5 8.5 8.8 9 Section C (02 X 06=12 Marks) 3. (a) A survey was conducted with 500 female students of which 60% were intelligent, 40% had uneducated fathers, while 30 % of the not intelligent female students had educated fathers. Test the hypothesis that the education of fathers and intelligence of female students are independent. (b) The following table gives the performance of 500 students classified according to age in a computer test. Test whether the attributes' age and performance are independent at 5% of significance.