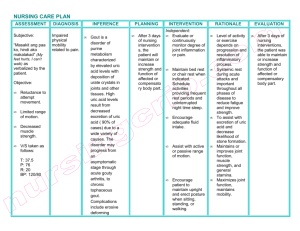
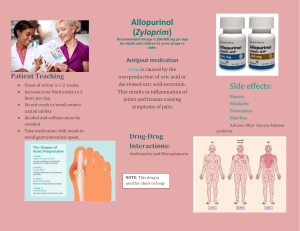
Common Orthopaedic Problems Part 2 Dr HL Wong Consultant, Dept. of O&T, TMH Honorary Clinical Associate Prof, CUHK Gout Nail disorders Trigger fingers Tennis elbow Ulnar nerve entrapments 痛風 扳機指 網球肘 肘管綜合徵 Gout 痛風 What is gout ? A metabolic disorder Monosodium urate crystal deposition Clinical presentation: gouty arthritis, gouty tophi, gouty nephropathy and uric acid stone Introductory Info Our kidneys work to eliminate the body of excess fluids water, salts, urea, and uric acid Uric acid is a waste of protein metabolism Gouty Arthritis Gout can also occur as a result of overproduction of uric acid Gout is an attack of uric acid deposits in joints Usually found in joints of feet and legs What is Gouty Arthritis Purines are not properly processed in our body Excreted through kidneys and urine Hyperuricemia- buildup of uric acid in body and joint fluid Which factors is associated with uric acid level ? Age Weight Gender Genetic distribution Alcohol Protein diet Diuretic Social class Hb Metabolism Ingested Purine and synthesized purine nucleotides Undergo catabolism and uric acid is formed 2/3 excreted by kidney,1/3 excreted in GIT Raised serum uric acid level 90% due to reduced excretion 10% due to increased production Stages of Gout Asymptomatic Acute Chronic Asymptomatic hyperuricaemia No treatment if there is : - no Hx of gout - no FHx of gout - no clinical evidence of gout Look for secondary cause CHRONIC Continuous or persistent over a long period of time Treatment required Not easily or quickly resolved Acute gout 5x to 8x more common in men Rare: boys before puberty women before menopause Usually: men between 30 to 60 Acute gout Precipitated by: -Trauma -unusual physical exercise -surgery -severe systemic disease -severe dieting -dietary excess -alcohol -drugs (diuretic, allopurinol, cytotoxic drug treatment etc) Acute gout Usually mono-articular, only 10% polyarticular 70% in 1st MTP joint Others: ankle, knee, wrist, elbow, hands and feet Rare: hips shoulder, axial skeleton Tenosynovitis, bursitis, cellulitis Chronic Tophaceous Gout Asymmetrical joint swelling Tophi (microcrystal's of uric acid, amorphous urate , histiocytes, giant cell fibrosis) Periarticular, ear. Bursa, tendon sheath Rare sites: eye, larynx, heart 60% untreated gout will develop this in 10 years Clinical features Chronic Tophaceous gout Other history: renal colic, renal stone hypertension FHx of gout Investigation Increase serum uric acid level X-ray Microscope: needle shaped -ve birefringent crystals of monosodium X-ray features Periarticular bone erosion Punch-out lesion with well defined cortical margins Joint space usu. Preserved No osteoporosis Overhanging edge Tips Synovial fluid analysis right after aspiration Only 60% has elevated uric acid at acute attack Asymptomatic hyperuricaemia is common Acute Treatment 1) NSAID -any NSAID except aspirin -aspirin cause uric acid accumulation except in high dose -avoid in recent peptic ulcer, renal failure, severe heart failure Acute treatment 2) oral Colchicine - 1mg, followed by 0.5mg Q4h - early side effect: nausea, diarrhoea abdomen pain Acute treatment 3) Others: -NSAID suppository -intra-articular steroid injection Tips Allopurinol should not be started until 3/52 after the acute attack because it prolongs acute attack or trigger further episode LONG TERM TREATMENT Reduce alcohol intake Increase water intake Watch diet for food rich in purines “Disease of Kings ” Rich foods have a higher concentration of protein. This could cause major problems for a person afflicted with gout. ORGAN MEATS WILD GAME SEAFOOD PEAS ASPARAGUS YEAST BEER Long term treatment When should we start long term drug treatment? 1) recurrent attack 2) evidence of tophi or chronicgouty arthritis 3) associated renal disease 4) young patient with high uric acid level 5) can’t achieve normal acid level after lift-style modification Long term treatment Allopurinol reduce urate production + NSAID or Colchicine for breakthrough attack Probenecid Increase excretion The end WORKS CITED Kamienski, Mary. 2003. Health Source: Nursing/Academic Edition. Gout: Not Just for the Rich and Famous. Vol. 22, Issue 1 www.ask.com www.acfas.org/brgoutft.html www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article 000424.htm Nail Disorders Anatomy of the Nail NAIL SIGNS Nail clubbing Nail pitting Hutchinson’s sign - melanoma Subungual hematoma ONYCHOMYCOSIS Distal subungual hyperkeratosis and onycholysis involving most of the nail bed of the great toenails; these findings are usually associated with tinea pedis. ONYCHOMYCOSIS PARONYCHIA甲溝炎 The nail fold is erythematous, edematous, with early abscess formation, and is very painful. PARONYCHIA PARONYCHIA PARONYCHIA FELON Ingrown toenail 嵌趾甲 Ingrown toe nail Surgery Peri-operative antibiotics .Local anaesthesia .digital tourniquet Wedge (segmental) excision of matrix lateral nail plate & nail-bed excised with edematous tissue & redundant nail fold -wedge of tissue excised down to periosteum -germinal matrix excised Ingrown toe nail Radical ( Zadik’s) excision of matrix -elderly with recurrence -nail avulsion -entire germinal matrix removed Simple avulsion of nail XX high recurrence TRIGGER THUMB & FINGERS 扳機指 Adult- ring & middle fingers Infant- thumb Conservative treatment, Surgery NSAID Physiotherapy Local Steroid injection Open release ? Percutaneous Release Injection Surgical Release Lateral Elbow Pain Elbow Pain Tennis elbow (網球肘) Passive and resisted stretch tests Counterforce brace position Tennis elbow Elbow Pain Open release for tennis elbow Nerve Entrapment Problems Ulnar Nerve 尺神經 Nerve Entrapment Problems Ulnar Nerve Entrapment sites Cubital tunnel syndrome (肘管綜 合徵) Nerve Entrapment Problems Ulnar nerve Exposed to trauma bumping, pressing on table or arm rest Stretched by anatomy and position holding telephone receiver, sleeping with elbow flexed Nerve Entrapment Problems Ulnar nerve at the elbow Nerve Entrapment Problems Numbness Nerve Entrapment Problems Weakness Nerve Entrapment Problems Treatment Remove sources of pressure or external injury Splint at night surgery Extension brace Surgery Thank you Dr HL Wong