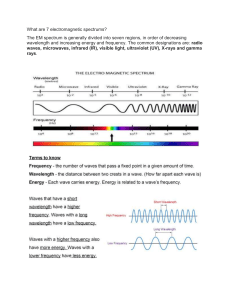
Electromagnetic wave (EM wave) Electromagnetic wave (EM wave) or electromagnetic radiation is a wave that is created as a result of vibrations between an electric field and magnetic field A changing electric field produces magnetic field and produced around a vibrating charge. And according to Michael Faraday, the changing magnetic field will produce electric field. A wave carries energy as it propagates. EM waves can travel through anything even on vacuum, meaning they do not need any medium to travel. They travel in a vacuum at a speed of 3x108 m/s. ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM EM waves are arranged in a gradual progression from the waves of lowest frequency to highest frequency. This arrangement of EM waves is called electromagnetic spectrum. How do moving charges create magnetic fields? ◦Any moving electric charge is surrounded by an electric field and a magnetic field. What happens when electric and magnetic fields change? ◦A changing magnetic field creates a changing electric field. ◦One example of this is a transformer which transfers electric energy from one circuit to another circuit. ◦In the main coil changing electric current produces a changing magnetic field ◦Which then creates a changing electric field in another coil producing an electric current ◦The reverse is also true. Making Electromagnetic Waves ◦When an electric charge vibrates, the electric field around it changes creating a changing magnetic field. Wavelengths decrease going along the EM spectrum from radio waves to gamma rays. Frequencies increase going along the EM spectrum from radio waves to gamma rays. Radio wave photons have the lowest frequency and the least energy, and gamma ray photons have the highest frequency and the most energy. The Electromagnetic Spectrum ◦Whenever radiation is absorbed by matter, photons transfer their energy to the matter. The Electromagnetic Spectrum Before ionisation After ionisation electro n photon Atom or molecule Chang ed atom or molecul e The photon hits the atom or molecule, and removes an electron. Some high energy EM radiation (ultraviolet, X-rays and gamma rays) are known as ionising radiation because they have enough energy to remove an electron from an atom or molecule) If cells are exposed to ionising radiation, they can damage the DNA in the nucleus of the cell. This can cause mutations, and the cells divide constantly without control – this is cancer. Very high doses of ionising radiation can kill cells. Excessive exposure to UV radiation can lead to sunburn or even skin cancer. Increased exposure = more damage Practical Applications Radio waves: Have the longest wavelengths and the lowest frequencies; wavelengths range from 1000s of meters to .001 m Used in: RADAR, cooking food, satellite transmissions Microwaves Microwaves are used to send signals between mobile phones and mobile phone masts. When you make calls on your mobile, your phone emits microwave radiation. Some of this is absorbed by your body and may cause heating of body tissues. This heating could result in medical conditions, possibly including cancer, but there is no conclusive evidence. Precaution: limit the amount of time you spend talking on a mobile phone! Ultraviolet Light: Wavelengths range from 400 nm to 10 nm; the frequency (and therefore the energy) is high enough with UV rays to penetrate living cells and cause them damage. Although we cannot see UV light, bees, bats, butterflies, some small rodents and birds can. UV on our skin produces vitamin D in our bodies. Too much UV can lead to sunburn and skin cancer. UV rays are easily blocked by clothing. Used for sterilization because they kill bacteria. X-Rays: Used to look at solid structures, such as bones and bridges (for cracks), and for treatment of cancer. ◦X-rays are used by radiographers in hospitals to check for broken bones. ◦X-rays pass easily through flesh, but are absorbed by denser materials like bone and metal. ◦X-ray imaging is also used in airports to check the contents of bags. ◦Precautions: radiograhers wear lead aprons or stand behind concrete to protect themselves. Gamma Rays: Carry the most energy and have the shortest wavelengths, less than one trillionth of a meter (10-12). Gamma rays have enough energy to go through most materials easily; you would need a 3-4 ft thick concrete wall to stop them! Gamma rays are released by nuclear reactions in nuclear power plants, by nuclear bombs, and by naturally occurring elements on Earth. Sometimes used in the treatment of cancers.