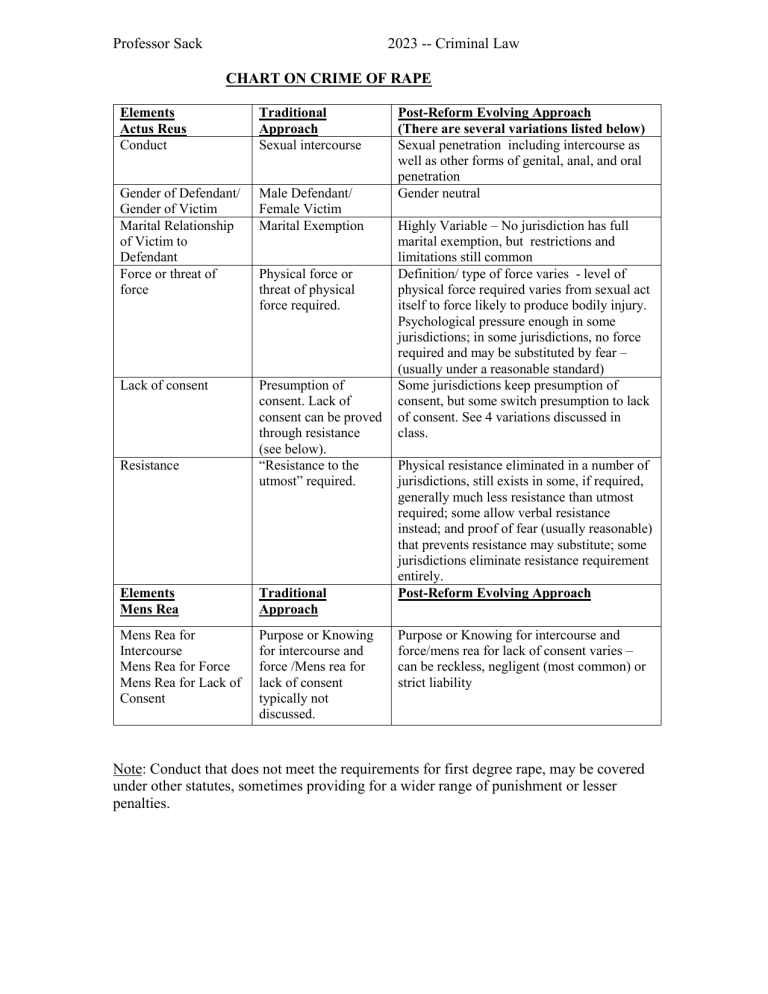
Professor Sack 2023 -- Criminal Law CHART ON CRIME OF RAPE Elements Actus Reus Conduct Traditional Approach Sexual intercourse Gender of Defendant/ Gender of Victim Marital Relationship of Victim to Defendant Force or threat of force Male Defendant/ Female Victim Marital Exemption Lack of consent Presumption of consent. Lack of consent can be proved through resistance (see below). “Resistance to the utmost” required. Resistance Physical force or threat of physical force required. Elements Mens Rea Traditional Approach Mens Rea for Intercourse Mens Rea for Force Mens Rea for Lack of Consent Purpose or Knowing for intercourse and force /Mens rea for lack of consent typically not discussed. Post-Reform Evolving Approach (There are several variations listed below) Sexual penetration including intercourse as well as other forms of genital, anal, and oral penetration Gender neutral Highly Variable – No jurisdiction has full marital exemption, but restrictions and limitations still common Definition/ type of force varies - level of physical force required varies from sexual act itself to force likely to produce bodily injury. Psychological pressure enough in some jurisdictions; in some jurisdictions, no force required and may be substituted by fear – (usually under a reasonable standard) Some jurisdictions keep presumption of consent, but some switch presumption to lack of consent. See 4 variations discussed in class. Physical resistance eliminated in a number of jurisdictions, still exists in some, if required, generally much less resistance than utmost required; some allow verbal resistance instead; and proof of fear (usually reasonable) that prevents resistance may substitute; some jurisdictions eliminate resistance requirement entirely. Post-Reform Evolving Approach Purpose or Knowing for intercourse and force/mens rea for lack of consent varies – can be reckless, negligent (most common) or strict liability Note: Conduct that does not meet the requirements for first degree rape, may be covered under other statutes, sometimes providing for a wider range of punishment or lesser penalties.


