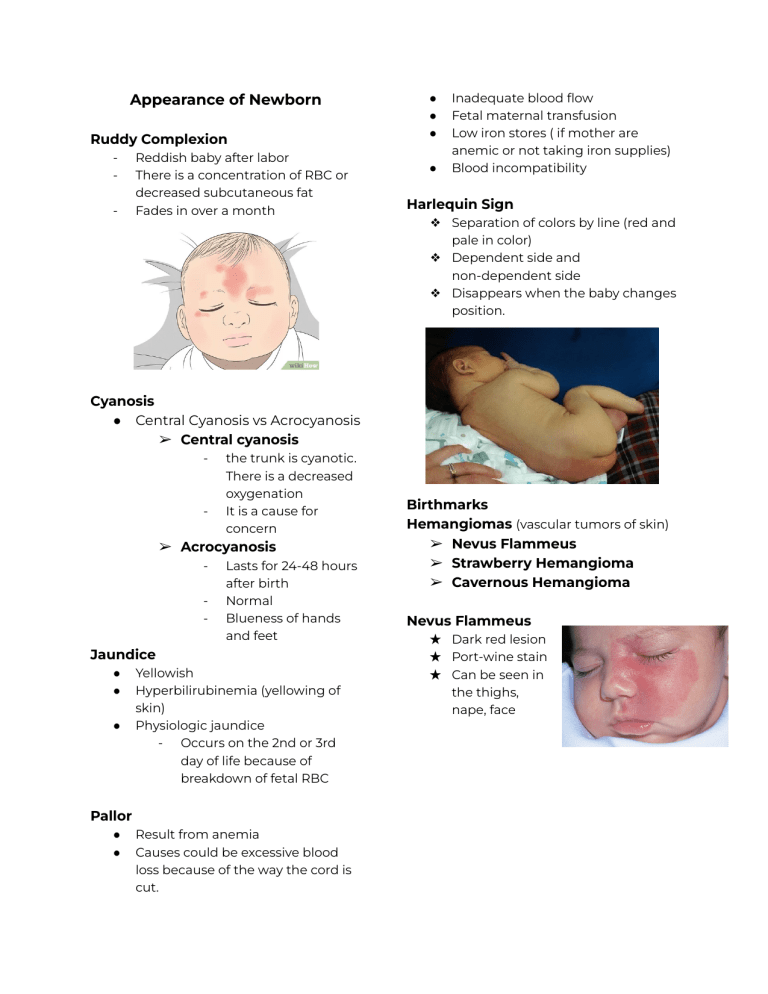
Appearance of Newborn Ruddy Complexion - Reddish baby after labor There is a concentration of RBC or decreased subcutaneous fat Fades in over a month ● ● ● ● Inadequate blood flow Fetal maternal transfusion Low iron stores ( if mother are anemic or not taking iron supplies) Blood incompatibility Harlequin Sign ❖ Separation of colors by line (red and pale in color) ❖ Dependent side and non-dependent side ❖ Disappears when the baby changes position. Cyanosis ● Central Cyanosis vs Acrocyanosis ➢ Central cyanosis - - the trunk is cyanotic. There is a decreased oxygenation It is a cause for concern ➢ Acrocyanosis - Lasts for 24-48 hours after birth Normal Blueness of hands and feet Jaundice ● ● ● Yellowish Hyperbilirubinemia (yellowing of skin) Physiologic jaundice - Occurs on the 2nd or 3rd day of life because of breakdown of fetal RBC Pallor ● ● Result from anemia Causes could be excessive blood loss because of the way the cord is cut. Birthmarks Hemangiomas (vascular tumors of skin) ➢ Nevus Flammeus ➢ Strawberry Hemangioma ➢ Cavernous Hemangioma Nevus Flammeus ★ Dark red lesion ★ Port-wine stain ★ Can be seen in the thighs, nape, face Strawberry Hemangioma ● ● ● Elevated; raised immature capillaries (endothelial cells) Caused by increased levels of estrogen during pregnancy Disappears when the child reaches 7 years old Lanugo - Cavernous Hemangioma ● ● ● Dilated vascular spaces Does not disappear with time Can be surgically removed Fine downy hair Can be seen at the shoulders, back, upper-arms If the baby was born during 37-39 weeks then lanugo is abundant If the baby was born 40 weeks then lanugo is less observable If 42 weeks and above, then it is rare or no lanugo. The beddings of the baby should be white to check for insects and lanugo Desquamation ➔ The skin of the newborn is extremely dry during the first 24 hours of birth ➔ Peeling of skin ➔ Evident in palms and soles of the feet Mongolian spots - Collection of pigmented cells Green in color Can be seen in the legs, thighs, buttocks, and arms Vernix Caseosa - - - - When assessing we must wear gloves It is white, cream, cheese-like substance It is a lubricant while the baby is in utero If the color is green, then meconium is present (poop) Millia ➢ White points on baby ➢ It is caused by immature sebaceous glands ➢ Pinpoint white papule ➢ Can be found in the nose and cheeks ➢ Disappears after 2-4 weeks Erythema toxicum - Flea bite rash No specific pattern since it can be seen all over the body Disappears after a few hours and should not last for days Skin turgor - When assessing the skin turgor, pinch the skin on the abdomen If well hydrated the skin should return to its normal appearance If it doesn’t then the newborn is severely dehydrated Craniotabes ● ● Softening of cranial bones Usually becomes normal Head Fontanelles Anterior ➢ ➢ ➢ ➢ Diamond in shape, 2-3cm width 3-4 cm length Soft space Closes 12-18 months Posterior ➢ Fusion of parietal and frontal lobe ➢ Located in the junction of the parietal and occipital lobe ➢ Closes in 2-3 months Suture ● ● Separating lines of skull If the suture is wide then the newborn has increased intracranial pressure Molding ● ● Elongates the head of baby Will return to normal after 24 hours Eyes - - The nurse’s duty is to get the vital statistics and signs, APGAR score, Administer vaccine (hepa b and vitamin k) administer erythromycin (protects the baby from chlamydial infection and ophthalmia neonatorum) Ears - Cephalohematoma ● ● Collection of blood between periosteum Swells 24 hours after birth Tears will appear in 3 months Babies cry without tears because the lacrimal ducts mature at 3 months Permanent eye color can be observed after 12 months Check if it is at level with the center canthus Low set ears can be related to down syndrome Small tags (buslot sa ears), assess if it is related to chromosomal abnormality and kidney problems Nose - If distress is noted then submit for observation Mouth - If teeth are present then check for stability of tooth if loose/wiggly then extract. Chest - Spina bifida Oculta (dimpling) Measure the chest it should be 2cm less from head circumference Assess respiratory rate Supernumerary nipple (extra nipple) Witch's milk (thin watery fluid leaking from nipple) - Happens if mother lacks folic acid during pregnancy Abdomen - - Assess if the newborns abdomen is protruding, if sunken then there are missing abdominal parts. Bowel sounds should be present after birth Extremities Simian crease Umbilical Cord - During the first hour it appears white/ gelatinous structure - ! hour after, it will dry or shrink - After 1 day, the color turns to brown ➢ Never attempt to remove ➢ If it is swelling then it might have some problems ➢ It will remove itself ● ● It is the lines found on the palms One simian crease is related to children with down syndrome Syndactyly ● Webbing of fingers Anogenital area Imperforate anus - No stool after 24 hours Polydactyly ● extra fingers Male genitalia ● Undescended testis (cryptorchidism) ● Epispadias ➢ Urethral opening on dorsal surface (up) ● ● Hypospadias ➢ Urethral opening on ventral surface (down) If said problems are present then do not circumcise. Female genitalia -pseudomenstruation (fake) happens because of maternal hormones Clubfoot - The foot turns inward Certain shoes are designed to train baby Can be corrected surgically Care of newborn at birth ● Place identification (colored) ➢ Name of mom, date and time of birth, hospital number, gender ➢ Place on wrist and on feet ● Birth certificate Bathing - 6 hours after birth Do not forcefully remove the vernix caseosa Sleeping - Palace baby in supine position Do not prone, and do not put big pillows SIDS (sudden infant death syndrome)




