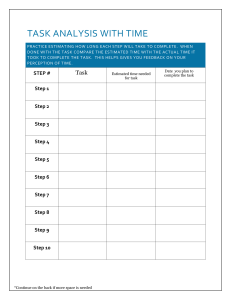
CompTIA Project+ Study Guide CompTIA Project+ Chapter 5: Creating the Project Schedule PK0-004 2 5.1 Schedule Planning » Steps used to construct a project schedule: 1. Determine tasks 2. Sequence tasks 3. Allocate resources 4. Determine task durations including start and end dates 5. Determine milestones 6. Construct the schedule 7. Determine the critical path 8. Set the baseline and obtain approval 9. Set quality gates 10. Establish the governance process. PK0-004 3 5.3 Task Sequencing PK0-004 4 5.2 Defining Tasks » Foundation for developing a project schedule to complete the project deliverables » Iterative process that involves further decomposing the WBS work packages into individual tasks PK0-004 5 5.3 Task Sequencing Types of Dependencies Logical Relationships Creating a Network Diagram PK0-004 6 Types of Dependencies » Four categories are: Mandatory dependency is directly related to the type of work being performed. Discretionary dependency is defined by the project management team and is usually process driven. External dependency is a relationship between a project task and some factor outside the project that drives the scheduling of that task. Internal dependency is a relationship between tasks within an individual project and is under the control of the project team. PK0-004 7 Logical Relationships » Four logical relationships are: In a finish-to-start relationship, the successor activity cannot begin until the predecessor activity has completed. In a start-to-finish relationship, the predecessor activity must start before the successor activity can finish. A finish-to-finish relationship is where the predecessor activity must finish before the successor activity finishes. In a start-to-start relationship, the predecessor activity must start before the successor activity can start. 8 PK0-004 Creating a Network Diagram » Great tool to develop with the project team » Depicts the project activities and the interrelationships among these activities » Most commonly used network diagramming method is the precedence diagramming method (PDM) 9 PK0-004 5.4 Assigning Resources Resources refer to human resources and/or consulting or contracting resources who will work on the tasks Assigning tasks among the team members according to their skills Determining and managing start and end dates of multiple tasks within a work package Resource calendar is used to describes the time frames in which resources are available PK0-004 10 5.5 Determining Task Durations Defining Duration Estimating Techniques 11 PK0-004 Defining Duration » When estimating duration Make sure that you are looking at the total elapsed time to complete the activity Be aware of the difference between workdays and calendar days 12 PK0-004 Estimating Techniques » Several techniques used to determine task duration estimates are: Analogous estimating is a technique that uses actual durations from similar tasks on a previous project. Expert judgment is a technique where the people most familiar with the work determine the estimate. Parametric estimating is a quantitatively based estimating method that multiplies the quantity of work by the rate. The Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) is a method that the U.S. Navy developed in the 1950s. It makes use of expected value. PK0-004 13 5.6 Creating the Project Schedule Milestones Displaying the Schedule The Critical Path Method Duration Compression Project-Scheduling Software Setting the Baseline and Obtaining Approval Quality Gates Establishing Governance Gates PK0-004 14 Milestones » Major accomplishments of the project and mark the completion of major deliverables in the project » Milestone charts are one method to display schedule information PK0-004 15 Displaying the Schedule » Most common way to display project schedules is a Gantt chart. » Network diagrams can also be used to display the project schedule. PK0-004 16 The Critical Path Method » Determines the amount of float time for each activity on the schedule » Determine which tasks can start late or can take more time than planned without impacting the project end date PK0-004 17 The Critical Path Method PK0-004 18 Activity Slack Earliest start schedule (ESS) PK0-004 19 Activity Slack Latest start schedule (LSS) PK0-004 20 What is the Critical Path? » Activities with zero slack cannot be delayed without affecting the entire project duration and are called critical activities. The critical path consists of a path of critical activities and is given by activities A, B, E and F. » The amount of slack (or float) associated with each activity is used to denote the free time of each activity within the ESS and LSS. It denotes the amount of time each activity can be delayed without violating the entire project duration. The slack of an activity can be calculated as the difference between its latest start and earliest start time, or alternatively, as the difference between its latest and earliest finishing time. PK0-004 21 Duration Compression » Refers to the state when calculation of the total project duration is longer than the target project completion date » Use duration compression scheduling techniques to shorten the planned duration of the project to help resolve schedule slippage » Two duration compression techniques are: Crashing Fast Tracking PK0-004 22 Project-Scheduling Software » Automatically calculate task durations, determine the critical path, and help balance resources » Provides with the ability to display a number of different views of the project PK0-004 23 Setting the Baseline and Obtaining Approval » Schedule baseline includes the baseline start and finish dates and resource assignments » Obtain sign-off on the project schedule from the stakeholders and the functional managers PK0-004 24 Quality Gates » Similar to milestones » Determine quality checks at strategic points in the project » Ensure that the work is accurate and meets quality standards PK0-004 25 Quality Gates PK0-004 26 Establishing Governance Gates » Used as approval points in the project » Include client sign-off, management approval, and legislative approval PK0-004 27 Summary » Many steps are involved in schedule planning. » Task definition is the foundation for developing a project schedule to complete the project deliverables » Sequencing is the process of identifying dependency relationships between project activities and sequencing them in proper order. » Dependencies are relationships between activities. » There are four types of logical relationships: finish-to-start, startto-start, start-to-finish, and finish-to-finish. » The critical path method (CPM) creates a schedule by determining float time. » Duration compression is the technique used to shorten a project schedule to meet a mandated completion date. PK0-004 28 Summary (continued) » Milestones mark major project events such as the completion of a key deliverable or project phase. » Gantt charts are a common method to display schedule data » Quality gates may be added to the schedule to determine whether the work so far is accurate and meets quality standards. » Governance gates include client sign-off, management approval, and legislative approval. PK0-004 29