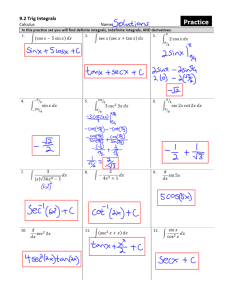
AP Physics 1 Scoring Guide Assignment #13 1. A 29.1-kg sledder is traveling along a level area with a speed of 8.96 m/s when she approaches a gentle incline which makes an angle of 12.5 degrees with the horizontal. If the coefficient of friction between the sled and the incline is 0.109, then what will be her speed at the bottom of the inclined plane, located 8.21 m above the top of the incline A 162.3 m/s B 30.3 m/s C 12.7 m/s D 0 m/s 2. A 50.0 kg crate is lifted to a height of 2.0 meters in the same time as a 25.0 kg crate is lifted to a height of 4 meters. The rate at which energy is used (i.e., power) in raising the 50.0 kg crate is ____ as the rate at which energy is used to lift the 25.0 kg crate. A twice as much B half as much C the same 3. A platform diver weighs 500 N. She steps off a diving board that is elevated to a height of 10 meters above the water. The diver will possess ___ Joules of kinetic energy when she hits the water. a. 10 b. 500 c. 510 d. 5000 e. more than 5000 . Copyright © 2020. The College Board. These materials are part of a College Board program. Use or distribution of these materials online or in print beyond your school’s participation in the program is prohibited. Page 1 of 29 AP Physics 1 Scoring Guide Assignment #13 A 10 B 500 C 510 D 5000 E more than 5000 4. A Watt is the standard metric unit of work. True or False A True B False 5. A physical situation is described below. Simplify the work-energy equation by canceling any zero terms and any energy terms (whether KE or PE) which are unchanging. Copyright © 2020. The College Board. These materials are part of a College Board program. Use or distribution of these materials online or in print beyond your school’s participation in the program is prohibited. Page 2 of 29 AP Physics 1 Scoring Guide Assignment #13 A PE + W = KE B PE + W = PE C PE + W = O D PE = PE + KE 6. What is the equation for kinetic energy? A 1/2 m v(squared) B mgh 7. A block is pushed up an incline that makes a angle with the horizontal, as shown in the figure. Once the block is pushed a distance of up the incline, the block remains at rest. What is the approximate change in the gravitational potential energy of the block-Earth system when the block is held at rest compared to its original location at the bottom of the incline? Copyright © 2020. The College Board. These materials are part of a College Board program. Use or distribution of these materials online or in print beyond your school’s participation in the program is prohibited. Page 3 of 29 AP Physics 1 Scoring Guide Assignment #13 A B C D 8. An object of mass is attached to a string of negligible mass and spun in a vertical circle of radius , as shown in the figure above. As the object’s height increases, its speed decreases such that the object-Earth system’s total mechanical energy remains constant. By how much does the object’s kinetic energy decrease in moving from point , the lowest point on the circle, to point , the highest point on the circle? Copyright © 2020. The College Board. These materials are part of a College Board program. Use or distribution of these materials online or in print beyond your school’s participation in the program is prohibited. Page 4 of 29 AP Physics 1 Scoring Guide Assignment #13 A B C D 9. A B C An object is released from rest near and above Earth’s surface from a distance of appropriate kinematic equation, a student predicts that it will take for the object to reach the ground with a speed of . After performing the experiment, it is found that the object reaches the ground after a time of . How should the student determine the actual speed of the object when it reaches the ground? Assume that the acceleration of the object is constant as it falls. Use but use the new time rather than other quantities are known. Solve for Use Solve for Use since all . since all other quantities are known. . since the conservation of mechanical energy applies in this scenario, and the initial height above the ground is known. Solve for . to determine the acceleration of the object as it falls since all other quantities are known. Then use quantities are known. Solve for 10. and the vertical acceleration equal to with the vertical acceleration equal to Use D . After applying the with since all other . An object initially at rest falls from a height until it reaches the ground. Two of the following energy bar charts represent the kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy of the object-Earth system at two positions. The first position is when the object is initially released, and the second position is when the object is halfway between its release point and the ground. Which two charts could represent the mechanical energy of the object-Earth system? Select two answers. Copyright © 2020. The College Board. These materials are part of a College Board program. Use or distribution of these materials online or in print beyond your school’s participation in the program is prohibited. Page 5 of 29 AP Physics 1 Scoring Guide Assignment #13 A B Copyright © 2020. The College Board. These materials are part of a College Board program. Use or distribution of these materials online or in print beyond your school’s participation in the program is prohibited. Page 6 of 29 AP Physics 1 Scoring Guide Assignment #13 C D Copyright © 2020. The College Board. These materials are part of a College Board program. Use or distribution of these materials online or in print beyond your school’s participation in the program is prohibited. Page 7 of 29 AP Physics 1 Scoring Guide Assignment #13 11. An experiment is conducted such that an applied force is exerted on a object as it travels across a horizontal surface in which frictional forces are NOT considered to be negligible. A graph of the net force exerted on the object as a function of the object’s distance traveled is shown. How could a student use the graph to determine the net work done on the object? A Multiply the average value of the applied force by the total distance the object traveled. B Multiply the slope of the best fit line by the total distance the object traveled. C Calculate the area bound by the line of best fit and the horizontal axis from D to . There is not enough information that is known or can be obtained from the graph to determine the net work done on the object. Copyright © 2020. The College Board. These materials are part of a College Board program. Use or distribution of these materials online or in print beyond your school’s participation in the program is prohibited. Page 8 of 29 AP Physics 1 Scoring Guide Assignment #13 12. The surface of an incline is coated with an experimental substance that is intended to reduce the frictional force between a block and the surface of the incline. A block is placed at the top of the incline at a height of , as shown in the figure. After the block is released from rest, the block slides down the incline and a motion detector at the bottom of the incline measures the block’s speed as after the block is no longer on the incline. Which of the following claims is correct about the experimental substance? The experimental substance reduced all the frictional force because all the gravitational potential energy of A the Earth-block system at the top of the incline was converted into the kinetic energy of the block at the bottom of the incline. B C The experimental substance did not reduce all the frictional force because some of the gravitational potential energy of the Earth-block system at the top of the incline was converted into nonmechanical energy. The effectiveness of the experimental substance cannot be determined because the speed of the block at the bottom of the inline, as measured by the motion detector, indicates that the block has more energy at this location than the Earth-block system had at the top of the incline. The effectiveness of the experimental substance cannot be determined without knowing the magnitude of the D frictional force between the block and the incline before and after the experimental substance was applied to the incline. A student is conducting an experiment to analyze the mechanical energy of a block-spring system. The student places a block of mass on a horizontal surface and attaches the block to a horizontal spring of negligible mass Copyright © 2020. The College Board. These materials are part of a College Board program. Use or distribution of these materials online or in print beyond your school’s participation in the program is prohibited. Page 9 of 29 AP Physics 1 Scoring Guide Assignment #13 and spring constant , as shown in the figure. There is negligible friction between the block and the horizontal surface. The other end of the spring is attached to a wall. The block-spring system is initially at the spring’s equilibrium position. 13. The student wants to collect data of the block-spring system that can be used to determine the work done on the spring by the block when the spring is compressed. Which of the following includes only the measuring devices that the student will need in order to collect the data? A Force probe and meterstick B Stopwatch and meterstick C Stopwatch and force probe D Force probe, stopwatch, and meterstick 14. Based on data collected from the experiment, the student creates the graph that shows the force exerted on the spring as a function of the distance the spring is compressed. How can the student use the data to experimentally determine the work done on the spring by the block? Copyright © 2020. The College Board. These materials are part of a College Board program. Use or distribution of these materials online or in print beyond your school’s participation in the program is prohibited. Page 10 of 29 AP Physics 1 Scoring Guide Assignment #13 A Determine the slope of the line of best fit through the data from B Determine the area bound by the line of best fit through the data and the horizontal axis from . C Use the maximum value of the force exerted on the spring and multiply that value by the maximum distance that the spring is compressed. D to . to This graph cannot be used to determine the work done by the block on the spring because the force exerted on the spring by the block is not constant. Copyright © 2020. The College Board. These materials are part of a College Board program. Use or distribution of these materials online or in print beyond your school’s participation in the program is prohibited. Page 11 of 29 AP Physics 1 Scoring Guide Assignment #13 15. A student conducts an experiment in which an object is released from rest and falls to the floor. In the experiment, frictional forces CANNOT be neglected. The student uses experimental data to create two graphs. Figure 1 is a graph of kinetic energy of the object as a function of time. Figure 2 is a graph of the object-Earth system’s gravitational potential energy as a function of time. How should the student use one or both graphs to determine how much the total mechanical energy changes after ? Copyright © 2020. The College Board. These materials are part of a College Board program. Use or distribution of these materials online or in print beyond your school’s participation in the program is prohibited. Page 12 of 29 AP Physics 1 Scoring Guide Assignment #13 A B C Calculate the magnitude of the difference between the final kinetic energy of the object and the final kinetic energy of the object by using the graph in Figure 1. Calculate the magnitude of the difference between the final gravitational potential energy of the system and the initial gravitational potential energy of the system by using the graph in Figure 2. Calculate the magnitude of the difference between the final kinetic energy of the object found from the graph in Figure 1 and the final gravitational potential energy of the object-Earth system found from the graph in Figure 2. Calculate the magnitude of the difference between the final kinetic energy of the object found from the graph D in Figure 1 and the initial gravitational potential energy of the object-Earth system found from the graph in Figure 2. A conveyor belt ramp of length is inclined at with respect to the horizontal and is used to move objects from one location to another location. When an object is placed on the conveyor belt, the object travels up the incline with a constant speed of . A motor is used to keep the conveyor belt moving. The mass of the objects that are placed on the conveyor belt are varied. 16. Suppose the motor breaks and a person must push an object of mass from the bottom of the incline to the top of the incline. The person can exert a force of on the object parallel to the incline. What is the approximate amount of work that the person does on the object to move it to the top of the incline? Assume that all frictional forces are negligible. Copyright © 2020. The College Board. These materials are part of a College Board program. Use or distribution of these materials online or in print beyond your school’s participation in the program is prohibited. Page 13 of 29 AP Physics 1 Scoring Guide Assignment #13 A B C D 17. A B C D 18. For the system that only includes the object, which of the following claims best describes what happens to the mechanical energy of the system while the object is moving from the bottom of the ramp to the top of the ramp? The mechanical energy of the object increases because the gravitational potential energy increases as the object moves up the ramp. The mechanical energy of the object decreases because the force due to gravity from Earth does negative work on the object as it moves up the ramp. The mechanical energy of the object is constant because the kinetic energy of the object is constant. A determination of the change of the mechanical energy of the object cannot be made without knowing the power of the motor that is used to move the conveyor belt. Object and object are placed on the incline such that the motor moves the conveyor belt. The mass of object is greater than the mass of object . After both objects have been placed on the conveyor belt and travel at a constant speed, how does the rate of change of the gravitational potential energy of the object –Earth system per unit of time compare to that for the object Copyright © 2020. The College Board. These materials are part of a College Board program. Use or distribution of these materials online or in print beyond your school’s participation in the program is prohibited. –Earth system ? Page 14 of 29 AP Physics 1 Scoring Guide Assignment #13 A B , because the speed of the conveyor belt remains constant and both objects move at the same constant speed. , because the speed of the conveyor belt remains constant and both objects move at a constant speed. C , because object has a greater mass than object . D , because object has a greater mass than object . 19. Two blocks of the same mass but made of different material slide across a horizontal, rough surface and eventually come to rest. A graph of the kinetic energy of each block as a function of position along the surface is shown. Which of the following is a true statement about the frictional force that is exerted on the two blocks? Copyright © 2020. The College Board. These materials are part of a College Board program. Use or distribution of these materials online or in print beyond your school’s participation in the program is prohibited. Page 15 of 29 AP Physics 1 Scoring Guide Assignment #13 A , since the force of friction is represented as the slope for each of the two curves. B , since the force of friction is represented as the inverse slope for each of the two curves. C D , since the force of friction is represented as the inverse of the area bound by each curve and the horizontal axis. , since the force of friction is represented as the area bound by each curve and the horizontal axis. A student conducts an experiment in which an object is released from rest above a motion detector so that data can be collected about the object’s motion as the object falls to the ground. The experiment is conducted near Earth’s surface. All frictional forces are considered to be negligible unless otherwise stated. 20. The student collects the data necessary to graph the object’s kinetic energy as a function of time, as shown. Which of the following graphs represents the sum of the kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy of the object-Earth system as a function of time? Copyright © 2020. The College Board. These materials are part of a College Board program. Use or distribution of these materials online or in print beyond your school’s participation in the program is prohibited. Page 16 of 29 AP Physics 1 Scoring Guide Assignment #13 A B Copyright © 2020. The College Board. These materials are part of a College Board program. Use or distribution of these materials online or in print beyond your school’s participation in the program is prohibited. Page 17 of 29 AP Physics 1 Scoring Guide Assignment #13 C D Copyright © 2020. The College Board. These materials are part of a College Board program. Use or distribution of these materials online or in print beyond your school’s participation in the program is prohibited. Page 18 of 29 AP Physics 1 Scoring Guide Assignment #13 21. The student wants to collect data to determine the work done by the force due to gravity on the object as it falls. Which of the following lists contains the fewest number of measuring devices, in addition to the motion detector, that the student can use? A Spring scale B Spring scale and meterstick C Stopwatch and meterstick D Spring scale, meterstick, and stopwatch 22. A graph of the net force exerted on an object as a function of position is shown for the object of mass as it travels a horizontal distance . Which expression represents the change in the kinetic energy of the object? Copyright © 2020. The College Board. These materials are part of a College Board program. Use or distribution of these materials online or in print beyond your school’s participation in the program is prohibited. Page 19 of 29 AP Physics 1 Scoring Guide Assignment #13 A B C D 23. A object is released from rest near and above Earth’s surface such that the object-Earth system’s gravitational potential energy as a function of time is shown in the graph. Which of the following graphs represents the kinetic energy of the object as a function of time? Assume all frictional forces are considered to be negligible. Copyright © 2020. The College Board. These materials are part of a College Board program. Use or distribution of these materials online or in print beyond your school’s participation in the program is prohibited. Page 20 of 29 AP Physics 1 Scoring Guide Assignment #13 A B C Copyright © 2020. The College Board. These materials are part of a College Board program. Use or distribution of these materials online or in print beyond your school’s participation in the program is prohibited. Page 21 of 29 AP Physics 1 Scoring Guide Assignment #13 D 24. A person starting from rest at point swings along a circular arc from a rope, as shown above. Point is at a lower height than point . What is the trajectory of the person when the person lets go of the rope at Point ? Copyright © 2020. The College Board. These materials are part of a College Board program. Use or distribution of these materials online or in print beyond your school’s participation in the program is prohibited. Page 22 of 29 AP Physics 1 Scoring Guide Assignment #13 A B C D Copyright © 2020. The College Board. These materials are part of a College Board program. Use or distribution of these materials online or in print beyond your school’s participation in the program is prohibited. Page 23 of 29 AP Physics 1 Scoring Guide Assignment #13 25. The small block shown in the figure above was released from rest at point that friction was considered to be negligible. The block reached point and , what kind of work did the track do on the block, and why? A B C D and slid down the track such with speed . Between points Positive work, because the block’s kinetic energy increased. Positive work, because a component of the gravitational force is directed along the track, making the block gain kinetic energy. Zero work, because the average force exerted by the track on the block is zero. Zero work, because the track does not exert a force on the block directed along the block’s direction of motion. Copyright © 2020. The College Board. These materials are part of a College Board program. Use or distribution of these materials online or in print beyond your school’s participation in the program is prohibited. Page 24 of 29 AP Physics 1 Scoring Guide Assignment #13 26. A planet orbits a star along an elliptical path, as shown in the figure above. How do the planet’s kinetic energy and the total mechanical energy of the star-planet system change as the planet moves from point X to point Y? A B C D Planet’s Kinetic Energy System’s Total Mechanical Energy Increases Remains the same Planet’s Kinetic Energy System’s Total Mechanical Energy Increases Increases Planet’s Kinetic Energy System’s Total Mechanical Energy Decreases Remains the same Planet’s Kinetic Energy System’s Total Mechanical Energy Decreases Decreases Copyright © 2020. The College Board. These materials are part of a College Board program. Use or distribution of these materials online or in print beyond your school’s participation in the program is prohibited. Page 25 of 29 AP Physics 1 Scoring Guide Assignment #13 27. Blocks and are connected by a string that passes over a pulley, as shown in the figure. Block has more mass than Block . The string and pulley have negligible mass, and the pulley rotates with negligible friction. After the blocks are released from rest, what happens to the mechanical energy of the system consisting of the two blocks and Earth? A decreases. B remains constant. C increases. D The change of cannot be determined without knowing the ratio of the blocks’ masses and their initial distances from Earth’s surface. Copyright © 2020. The College Board. These materials are part of a College Board program. Use or distribution of these materials online or in print beyond your school’s participation in the program is prohibited. Page 26 of 29 AP Physics 1 Scoring Guide Assignment #13 28. Figure 1 shows the kinetic energy as a function of time for a object that is released from rest and falls toward Earth’s surface. Figure 2 shows the kinetic energy as a function of time for a object that is released from rest and falls toward Earth’s surface. Both objects are released simultaneously from the same height. How much does the gravitational potential energy of the object-object-Earth system change from to ? A B C D 29. A student wants to approximate the amount of work that the force due to gravity does on the student as the student walks up a set of stairs. Which of the following measurements must the student collect in order to approximate the amount of work done by Earth on the student? Select two answers. Copyright © 2020. The College Board. These materials are part of a College Board program. Use or distribution of these materials online or in print beyond your school’s participation in the program is prohibited. Page 27 of 29 AP Physics 1 Scoring Guide Assignment #13 A The mass of the student. B The angle between the inclined portion of the stairs and the horizontal. C The total inclined length of the stairs. D The final vertical height above the initial vertical position. 30. An experiment is conducted such that an applied force is exerted on a object as it travels across a horizontal surface. A graph of the net force exerted on the object as a function of the object’s distance traveled is shown. How could a student use the graph to determine the work done by the applied force? Copyright © 2020. The College Board. These materials are part of a College Board program. Use or distribution of these materials online or in print beyond your school’s participation in the program is prohibited. Page 28 of 29 AP Physics 1 Scoring Guide Assignment #13 A Multiply the maximum value of the applied force by the total distance the object traveled. B Multiply the weight of the object by the total distance traveled by the object. C Calculate the slope of the line of best fit. D Calculate the area bound by the line of best fit and the horizontal axis from Copyright © 2020. The College Board. These materials are part of a College Board program. Use or distribution of these materials online or in print beyond your school’s participation in the program is prohibited. to . Page 29 of 29