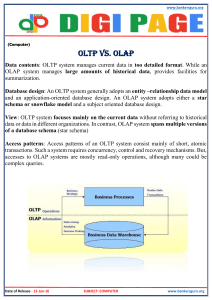
DSA5104 Principles of Data Management and Retrieval Lecture 0: Overview Data Is Ubiquitous Social Media E-Commerce Internet of Things (IoT) https://www.nist.gov/blogs/cybersecurity-insights/more-just-milestone-botnet-roadmap-towards-more-securable-iot-devices Big Data - Data Flooding in Smart Cities https://adtellintegration.com/smart-cities-infrastructure/ Teleco + Metro Data → Crowd Forcasting Caller Detail Records (CDR) [1] [1] Liang, Victor C., et al. "Mercury: Metro density prediction with recurrent neural network on streaming CDR data." ICDE 2016. Keppel Bay Tower - Singapore’s first Green Mark Platinum (Zero Energy) commercial building https://sleb.sg/UserFiles/Resource/GBIC/GBIC%20Demo%20Project/KBT%20GBIC%20Dashboard.pdf Keppel Bay Tower - Singapore’s first Green Mark Platinum (Zero Energy) commercial building https://sleb.sg/UserFiles/Resource/GBIC/GBIC%20Demo%20Project/KBT%20GBIC%20Dashboard.pdf Data Categorized by Data Types - Media Types Data Categorized by Data Types - Intrinsic Structure https://www.crowdstrike.com/blog/structured-unstructured-and-semi-structured-logging-explained/ Table & Record Caller Detail Records (CDR) [1] Structured Data § Data conforms to a set schema § Numerical, categorical and text data with well-defined schema Table name: instructor Column Data Type ID varchar(5) name varchar(20) not null dept_name varchar(20) salary numberic(8, 2) instructor Semi-Structured Data § Data with labels but no fixed schema § JSON, XML § CSV files with headers § Usage: § For data exchange https://e.nodegoat.net/CMS/upload/guide-import_person_csv_notepad.png Semi-Structured Data § XML - eXtensible Markup Language Semi-Structured Data § XML - eXtensible Markup Language Tag Closing tag note to from body Semi-Structured Data § XML - eXtensible Markup Language Tag Closing tag note to from body Semi-Structured Data § XML - eXtensible Markup Language Tag Closing tag note date to from body Semi-Structured Data § XML http://www.ling.helsinki.fi/~kjokinen/ICSLP06-DoD/Programme/GriolDavid06.pdf Semi-Structured Data § XML A prolog defines the XML version and the character encoding Element package has three attributes: destination, origin and version. http://www.ling.helsinki.fi/~kjokinen/ICSLP06-DoD/Programme/GriolDavid06.pdf Semi-Structured Data § XML A prolog defines the XML version and the character encoding Element package has three attributes: destination, origin and version. ASR XML SU http://www.ling.helsinki.fi/~kjokinen/ICSLP06-DoD/Programme/GriolDavid06.pdf Semi-Structured Data § JSON https://json.org/example.html Semi-Structured Data § JSON key/value pair seprated by commas Square brackets hold arrays Curly brackets hold objects https://json.org/example.html Semi-Structured Data § JSON § XML https://json.org/example.html Load JSON File Using Pandas data.json https://www.w3schools.com/python/pandas/pandas_csv.asp Load JSON File Using Pandas data.json https://www.w3schools.com/python/pandas/pandas_csv.asp Load JSON File Using Pandas data.json Jupyter Notebook Unstructured Data “I’m Hilda. I was born in 1990.” “My name is Max. I’m turning 20 this year.” Unstructured Data Natural Language Text Unstructured Data Natural Language Text Unstructured Data - Multimedia Content Image2Caption https://image2caption.pascalperle.de/ What is Big Data? § Big data sets are too large or complex to be processed by traditional methods. Consider that in a single minute (2022) there are: https://www.domo.com/data-never-sleeps Summary Structured Semi-Structured Unstructured Definition • Data with predefined schema • Data with flexible schema (e.g., XML) • Data without predefined schema Database Systems • Relational Database • MongoDB/HBase • No-SQL Databases • Object Store (S3) • Vector Database • SQL • XPath • XQuery • ElasticSearch for text • Search Vector Embeddings Query Languae • MySQL, PostgreSQL Data Warehouse & ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) https://rivery.io/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/ETL-Process-for-linkedin3.png Data Lake & Data Lakehouse Late 1980’s 2011 https://www.databricks.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/data-lakehouse-new-1024x538.png 2020 OLTP OLAP https://www.healthcatalyst.com/insights/database-vs-data-warehouse-a-comparative-review OLTP OLAP OLAP vs. OLTP Criteria Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) Online Transaction Processing (OLTP) Purpose • OLAP helps you analyze large volumes of data to support decision-making. • Data source • OLAP uses historical and aggregated data from • multiple sources. OLTP uses real-time and transactional data from a single source. Volume of data • OLAP has large storage requirements. Think terabytes (TB) and petabytes (PB). • OLTP has comparatively smaller storage requirements. Think gigabytes (GB). Response time • OLAP has longer response times, typically in seconds or minutes. • OLTP has shorter response times, typically in milliseconds Availability • OLAP systems can be backed up less frequently • since they don’t modify current data. OLTP systems require frequent or concurrent backups to help maintain data integrity. This is because they modify data frequently, which is the nature of transactional processing. Example applications • OLAP is good for analyzing trends, predicting • customer behavior, and identifying profitability. OLTP is good for processing payments, customer data management, and order processing. OLTP helps you manage and process real-time transactions. https://aws.amazon.com/compare/the-difference-between-olap-and-oltp/#:~:text=OLTP,Online%20analytical%20processing%20(OLAP)%20and%20online%20transaction%20processing%20(OLTP,processing%20and%20real%2Dtime%20updates. https://www.ibm.com/blog/olap-vs-oltp/ Course Schedule Week Topic (Subject to change) Note 1 • Overview • Introduction to Database Systems 2 • Relational Model • SQL I 3 • SQL II 4 • SQL III 5 • Database Design Using the Entity-Relationship (ER) Model 6 • Relational Database Design (Schema Refinement) Assignment Assignment Due Reading 7 Test 1 In person / Closed book Course Schedule Week Topic (Subject to change) Note 8 • Semi-structured Data Management Project 9 • Complex Data Types Project Proposal Due 10 • Big Data 11 • Document-Database: MongoDB 12 Test 2 NUS Well-Being Day - 10 Nov 2023 (Fri) 13 • Vector Database Project Due Reading • Project Presentaion • • • • • • • • XML XPath & XQuery Object Orientation Textual Data Spatial Data Key-value pairs MapReduce Spark SQL In person / Closed book Workload 01 Homework 02 Project 20% • Done individually • Week 3 - 6 03 Tests 40% • • • • Week 7 Test 1 (20%) Week 12 Test 2 (20%) Closed book In person (NO online alternative) 30% • • • • • 4-5 persons Week 7 - 13 Proposal 3% Final presentation 13% Final report 14% 04 Course Participation 10% • Class participation • Bonus points for assignment / project Late Policy For project / assignment § You will lose 20% of the total points every 24 hours late. § No submission is allowed beyond 72 hours. § Please contact the instructor ASAP if something comes up. § My email address: xyyang@nus.edu.sg Course Materials § Database System Concepts by Avi Silberschatz, Henry F. Korth and S. Sudarshan § Database Management Systems by Raghu Ramakrishnan and Johannes Gehrke Thank You