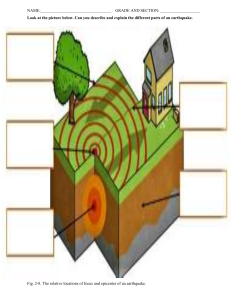
Name___________________________________________ Hall_________ Date_____________ Ms. Sameroff Objective: SWBAT identify characteristics of igneous rocks by completing a graphic organizer. DO NOW ACTIVITY #1 ACTIVITY #2 EXIT DO NOW 1. 2. 3. Using the information on the diagram explain the steps of the rock cycle. _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ VOCABULARY Use your worksheet to define the words below. 1 ACTIVITY #1 DIRECTIONS: Use writing lines or graphic organizer to explain the sequence of processes through which most sedimentary rocks are formed. ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ OR Sequence of processes weathering 2 3 Questions 1. What is coal? _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. When did the coal deposits of the eastern United States begin to form? What were environmental conditions like at the time? _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. What is peat? (Use this sentence starter. Peat is….) _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. What process caused the peat to become coal? _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. A type of coal called anthracite is classified by geologists as a metamorphic rock. It is much harder than sedimentary coal. Describe how you think anthracite forms. _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 VOCABULARY Directions: Use your worksheet to define the following words. ACTIVITY #1 12 THINK, PAIR, SHARE Why do you think your building will uphold the shaking of an earthquake? ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ Describe today’s lesson in 3-5 sentences. ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ 13 14 15 16 1. At least how long did aftershocks occur after the great Sumatra-Andaman earthquake? 2. How much ground movement occurred everywhere? Was it noticed everywhere? 3. From what did the quake result? 4. How long did the quake last? How long does a typical earthquake last? 5. Why have they never had such comprehensive data on an earthquake before? 6. How many people died as a result of the earthquake? 7. In addition to the earthquake, explain what else happened. 8. The quake was the result of two plate movements. Name those plates and state what those plates did. 9. How much was sea level worldwide raised as a result of the plate movement? 10. The quake made the Earth oscillate (go back and forth) like a bell. How long did the periods (time for one oscillation) last? 11. How big was the Sumatra earthquake? How big was an aftershock on March 28, 2005? 12. How big were the earthquakes in Chile in 1960, in Alaska in 1964 and in California in 1989? 13. Approximately, how much more powerful was the Sumatra earthquake than the one in California? (Remember, each increase by one in magnitude is a ten times increase in power.) 14. How much did the ground move in Sri Lanka, more than 1,000 miles from the Sumatra earthquake? 15. What happened in Alaska when the surface waves of the Sumatra earthquake reached Alaska? 17 Which 18 ACTIVITY #2 LIST OF RECENT EARTHQUAKES Date Richter Scale Damaged Caused: Primary and Secondary Effects SWBAT describe two possible effects of a major Earthquakes on buildings and cities. ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ 19 Describe today’s lesson in 3-5 sentences. ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________ 20 21 The effects of earthquakes are usually divided into two, primary and secondary. Primary effects occur as a direct result from the violent shaking of the ground. This may result in the collapse of buildings and many people may be killed. For example when an earthquake occurs deep cracks may open in the ground. These damage or destroy roads, bridges, dams and other structures. In the 1995 Japan earthquake many people lost their lives when a flyover collapsed. During the same earthquake, a number of fast trains were derailed and many people lost their lives or were injured. The image below shows a road completely damaged by the earthquake. 22 Secondary effects occur as a result of the primary effect. In the days following an earthquake, the people suffer for lack of food, water, sleep and other necessities. Many people are injured and others remain homeless. Disease will strike due to lack of hygiene. Often, foreign governments and international voluntary organisations immediately send doctors and workers who can help the victims. Other material necessities such as blankets, camps, food, water and medicine are also dispatched. The image below shows many people homeless after an earthquake. The effects of an earthquake can also be classified into social, economic and environmental. Examples of social impacts include people killed or injured, collapse of buildings, roads, bridges and railways damaged, water pipes may burst and water supplies contaminated, spread of disease, people may also need to be rehoused or live temporarily in camps. An earthquake can have huge consequences on the economy of the area. Trade with other areas may be hindered due to damage in infrastructure such as roads and bridges. Shops, factories and businesses may be destroyed and the cost for rebuilding the damaged settlement is usually very high. As a result of an earthquake we may also expect a number of environmental impacts. The built up area including important historical landmarks may be destroyed, As a result of gas leaks fires can spread damaging areas of woodland. Landslides may also occur and tsunamis often flood whole coastal areas. Although we ae not able to predict and prevent earthquakes, much is being done to reduce the damage caused by them. In earthquake-prone areas engineers are planning structures that are anti-seismic, that is resistant to tremors. Such measures together with exercise, preparation and planning help in reducing the damage caused by earthquakes. Some examples of building improvements resistant to earthquakes include: • Purposely manufactured springs or rubber shock-absorbers placed in the foundations of high buildings in order to absorb the impact of the movement of the ground. 23 • Steel frames with cross-bracing that can sway during earth tremors. • Computer controlled counter-weight on roofs which move to balance the effects of an earthquake. • Lightweight roofs designed to reduce damage and injury. The image below shows some of the main characteristics of an earthquake resistant building 24 1. What two factors do geologists take into account when they determine earthquake risk? _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Circle the letter of the location where 25 26 27 28 EXIT TICKET 1. Discuss the relationship between tsunamis and earthquakes. 29 ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Where do most tsunamis happen? ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Describe today’s lesson in 3-5 sentences. ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ 30 31 32 33 34 What’s the difference between a seismograph and seismogram? 35 ACTIVITY #1 36 37 38 39 40 ACTIVITY #2 41 _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ 1. After the lesson, now I understand… _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Something I still need help with… _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ 42 43 44 45 46 47 THINK, PAIR, SHARE Describe body waves and surface waves. _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ 48 ____________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. After the lesson, now I understand… ____________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. Something I still need help with… ____________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 49 50 51 52 1. What are the two different types of luster? 2. What is the range of hardness found on the chart? 53 3. What type of breakage is more common: cleavage or fracture? 4. What is the most common element found in the composition of minerals? 54 55 ACTIVITY #2 EXIT TICKET After the lesson, now I understand… ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ Something I still need help with… ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 56 57 58 EXIT TICKET What is the difference between an iconic and covalent bond? ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ What are the three subatomic particles found in atoms? ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ After the lesson, now I understand… ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ Something I still need help with… ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 59 In the same science fair, Tina asks the question “Does caffeine increase the heart rate of an earthworm?” I Test 1, she measures the heart rate by looking at the earthworm under a microscopes, the earthworm has a heart rate of 50 bpm (beats per minute). In Test 2, she places a few drops of caffeine on the earthworm’s skin and measures the rate again. In this test, the heart rate is 68 bpm. Student’s Mistake: 6) What is the manipulated variable in this___________________________________________________ experiment? ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ 7) What is the responding variable in this ___________________________________________________ experiment? _________________________ 8) Tina’s experiment should have included a hypothesis. In a complete sentence, suggest a hypothesis for Tina’s experiment. Student’s Mistake: ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ ___________________________ 60