How is unemployment measured? Discuss different types of unemployment.
advertisement

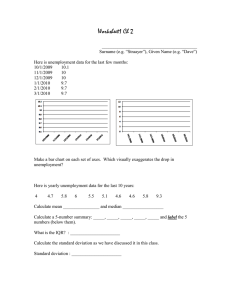
INDIVIDUAL ASSIGMENT Management Economics - ECON-5015-RLC Question 2 How is unemployment measured? Discuss different types of unemployment. Give examples to illustrate your answer. What is Unemployment? Unemployment is a term used to determine people in the labour force who are currently unemployed. It is often expressed as a rate which is called the unemployment rate and is measure by expressing the number of unemployed people in an economies labour force as a percentage of the entire labour force. (Lovewell, 2020) How is the unemployment rate measure? As discussed above, the unemployment rate is measured by expressing the number of unemployed people in the labour force as a percentage of the entire labour force. The labour force is calculated by the number of individuals who either have jobs or are actively seeking employment in the labour force population. (Individuals 15 years of age and older excludes individuals unable to be employed such as prisoners, psychiatric patients as well as members of the arms forces.) (Lovewell, 2020) The formula to measure the unemployment rate is as follows: 𝑈𝑛𝑒𝑚𝑝𝑙𝑜𝑦𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑟𝑎𝑡𝑒 (%) = 𝑢𝑛𝑒𝑚𝑝𝑙𝑜𝑦𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑖𝑛 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑙𝑎𝑏𝑜𝑢𝑟 𝑓𝑜𝑟𝑐𝑒 × 100 𝑙𝑎𝑏𝑜𝑢𝑟 𝑓𝑜𝑢𝑟𝑐𝑒 Different Types of Unemployment Unemployment can be sub-categories into 4 main types. They are as follows: 1. 2. 3. 4. Frictional unemployment Structural unemployment Cyclical Unemployment Seasonal Unemployment 1. Frictional Unemployment This type of unemployment is unemployment among people between jobs or people looking for their first job. An example of this type of unemployment is the unemployment that arises as a result of an executive of an organization leaving the organization for a new company they are to start as a assistant manager. During the transition period this employee will fall under frictional unemployment. (Lovewell, 2020) 2. Structural unemployment This type of unemployment is caused as a result of a mismatch between the people and inability for the unemployed to fill the available jobs as a result of inadequate skills, the advancement in technological requirement or a change in consumer needs. In simple terms, it is when the skills unemployed people have does not match the required skills for the available jobs. (Lovewell, 2020) An example for such unemployment is when a worker in a car manufacturing factory loses their employment due to automation of the workers tasks with the advancement of technology. 3. Cyclical Unemployment Cyclical unemployment is caused because of an economic recession. Unemployment tends to fall once the economic conditions improve. (Lovewell, 2020) For example, unemployment caused by the covid-19 pandemic in the hospitality industry because of wide-spread infections and lockdowns. However, as the economy improves unemployment spikes caused by the pandemic will fall. 4. Seasonal Unemployment This is common in industries where the demand is seasonal. Unemployment of this nature is caused when demand is low for the particular season and thereby forcing businesses to terminate employment for this period. (Lovewell, 2020) One such example is the unemployment faced by constructions workers during winter as construction becomes difficult with the weather conditions. References Lovewell, M. (2020). Understanding Economics - A Contemporary Perspective (8 ed.). Toronto, Canada: McGraw-Hill Ryerson.