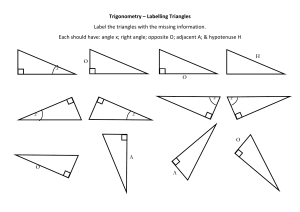
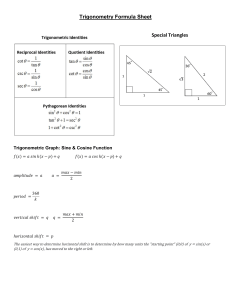
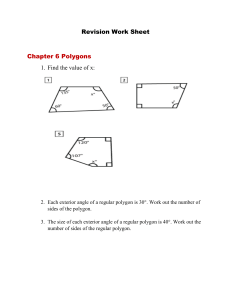
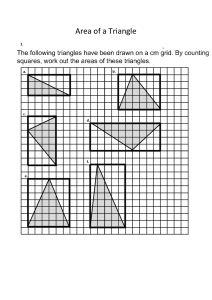
Review Trigonometry and Area 1. Trigonometry and Bearings Trigonometry in Right Triangles The symbols we use for these ratios are abbreviations for their full names: sine, cosine, tangent Example • Solve the triangle. Special Triangles • Certain right triangles have ratios that can be calculated easily from the Pythagorean Theorem. • For example, Special Triangles • Certain right triangles have ratios that can be calculated easily from the Pythagorean Theorem. Since they are used frequently, we mention them here. Identities Example 1. 2. 3. 4. Find the value of sin θ, if tan θ = ¾ and cos θ = ½. Find tan θ if sin θ = 4/3 and cos θ = 3/2 Find sin θ, if cos θ = 1/2 Find cosθ, if sin θ=16/5 Examples in real world • If an observer is looking at an object, then the line from the eye of the observer to the object is called the line of sight. • If the object being observed is above the horizontal, then the angle between the line of sight and the horizontal is called the angle of elevation. • If the object is below the horizontal, then the angle between the line of sight and the horizontal is called the angle of depression. Example • Find the height of a tree. A problem involving right triangles • From a point on the ground 500 ft from the base of a building, an observer finds that the angle of elevation to the top of the building is 24o and that the angle of elevation to the top of a flagpole atop the building is 27o. Find the height of the building and the length of the flagpole. Regular polygons • How can we determine the sum of angles inside the polygon? AREAS OF REGULAR POLYGONS • In regular hexagon ABCDEF inscribed in circle G, • GA and GF are radii from the center of the circle G to two vertices of the hexagon. • GH is drawn from the center of the regular polygon perpendicular to a side of the polygon. This segment is called an apothem. Area of regular polygons • Therefore • Since the hexagon is formed with 6 congruent triangles Example • Find the area of a regular pentagon with a perimeter of 40cm Example:Area of an Inscribed Polygon • Find the area of the shaded region. Assume that the triangle is equilateral.