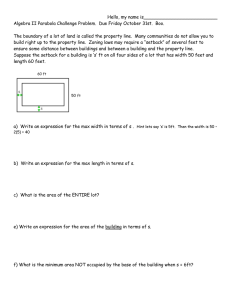
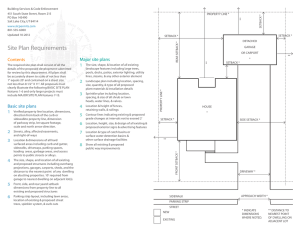
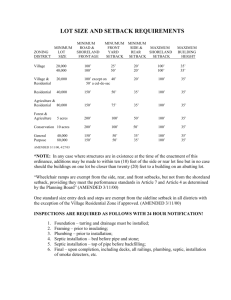
Step 1. Retrieve the plot plan or survey of the land. This document should feature property lines, easements, and existing structures. Step 2: Make sure to accurately measure the dimensions of the land. You can either use the provided survey or measure the land yourself. Step 3: Look up the setback regulations and requirements to determine the minimum distances needed for front, back, and side setbacks. - Calculate setback distances from property lines, nearby structures, and any natural features such as water bodies or slopes. Step 4: To mark the setback lines correctly, use stakes or marking flags to set the setback lines on the ground, based on your measurements. Make sure the lines are visible and distinguishable from the property boundaries. Step 5: it's important to consider other factors that could impact your setback plans. This includes things like utility easements, drainage requirements, or guidelines from a homeowners' association. If needed, adjust your setback lines to stay compliant with the regulations In Step 6, seek professional advice if you're uncertain about any aspect of setback requirements. A local architect, land surveyor, or zoning expert can offer guidance and help ensure compliance. Finally, in Step 7, obtain any necessary permits and approvals to ensure your setback plans are fully approved and legal. Once you have finalized your setback plan, submit the required documentation to the relevant building department or local authority to obtain the necessary permits and approvals before proceeding with construction.