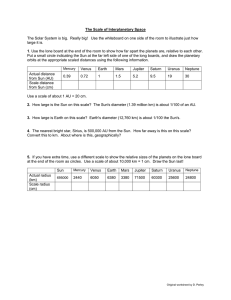
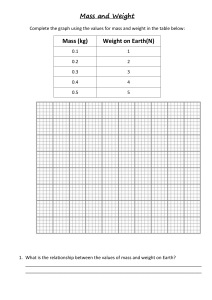
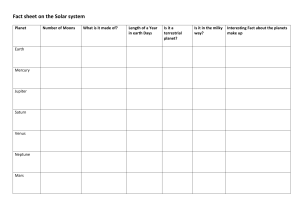
Different types of rocks 1. Igneous Rocks Formed when magma (molten rock beneath the Earth’s crust) cools and solidifies. A mixture of different minerals Large crystals can be formed (Examples: Obsidian, Granite, Basalt) 2. Sedimentary rocks Formed by the accumulation of sediments (little fragments of rocks). The weight of new sediments presses on older sediments, forming solid rocks Fossils can be formed Made of grains/particles Porous Has layers (Examples: Sandstone, Limestone, Shale) 3. Metamorphic rocks Formed by high temperatures and pressures underground Hard No gaps Not porous (Examples: Marble, Quartzite, Slate) Models of the Universe Geocentric Model: A model of the solar system/universe where Earth is at the centre Scientists who supported the model: Plato (400 BCE) Aristotle (400 BCE) Ptolemy (100 CE) Heliocentric model: A model of the solar system/universe where the Sun is at the centre Scientists who supported the model: Aristarchus (300 BCE) Copernicus (1542 CE) Kepler (1609 CE) Galileo (1610 CE) Discoveries of the planets and moons Known since ancient times (Visible with the naked eye) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Mercury Venus Mars Jupiter Saturn The Moon The Sun Uranus Discovered by Sir William Hershel in 1781. Neptune Discovered by Johann Gottfried Galle, Urbain Jean Joseph Le Verrier, John Couch Adams in 1846. Pluto Discovered by Clyde Tombaugh in 1930. The Galilean moons of Jupiter Moons of Jupiter discovered by Galileo Galilei in 1610 1. 2. 3. 4. Io Europa Ganymede Callisto The rings of Saturn Discovered by Galileo Galilei in 1610. Mountains and Craters on the Moon Discovered by Galileo Galilei in 1610. Order of the Solar System Position (Closest to furthest from the Sun) Sun, Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, (Asteroid belt), Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, Pluto Size (Biggest to smallest) Sun, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, Earth, Venus, Mars, Mercury Temperature (Hottest to coldest) Sun, Venus, Mercury, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, Pluto Brightness (Brightest to darkest from Earth) Sun, Venus, Jupiter, Mars, Mercury, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, Pluto Keys Keys are used to identify different species. A key is a set of questions about the organism you want to identify. Examples: Proton and Electron number Atomic number The number of protons in an atom Mass number The number of protons and neutrons in an atom Number of particles in an atom Protons = Mass – Neutrons Electrons = Protons Neutrons = Mass – Protons Electronic Structure Electrons are arranged in shells or orbitals around the nucleus of an atom Maximum number of electrons in each shell/orbital: 2,8,8 Structure of an Atom Approximated mass of subatomic particles Proton = 1 Neutron = 1 Electron = 0 Charge of subatomic particles Proton (+) Neutron (0) Electron (-) Sounds Loudness = Amplitude Pitch = Frequency Examples: Higher frequency = Shorter wavelength = Higher pitch Lower frequency = Bigger wavelength = Lower pitch Higher amplitude = Higher Loudness Lower amplitude = Lower Loudness Pollination and Fertilisation in Plants Pollination: The act of transferring pollen grains from the male anther of a flower to the female stigma Fertilisation: When a sperm cell fuses with an egg inside an ovule. This process develops a seed. Structure of a flower Parts of a female flower (Pistil) 1. Stigma Receives pollen Starts the fertilization process 2. Style Long, slender stalk Connects the stigma to the ovary 3. Ovule Forms seeds In the ovary Parts of a male flower (Stamen) 1. Anther Produces pollen Stores pollen 2. Filament Supports the anther Other parts of a flower 1. Petals Most colour part of a flower Attracts animals (pollinators) 2. Sepal Encloses and protects developing reproductive structures Green and leaf-like Common Pollinators Bees Wasps Moths Butterflies Flies Beetles Birds Seed Formation 1. Male and female nucleus fuses, producing a zygote 2. Zygote divides, forming an embryo 3. Ovule begins to change, forming into a seed *Fruits are the ovaries of plants Example: Structure of a seed 3 main components of a seed 1. Embryo Developed from fertilized egg Most important part of a seed 2. Endosperm/ Perisperm Contains nutrients Provides nutrients Supports the embryo during germination (sprouting of a seed) 3. Seed-coat Two layers: Testa (thick), Tegmen (thin) Protects the seed from sunlight & water Prevents loss of water and parasites Elements, compounds, and mixtures Elements The simplest substances that cannot be broken down into simpler formats Examples.: Oxygen (O), Iron (Fe), Carbon (C) Compounds The substances that contain atoms of two or more different elements and are chemically joined together Examples: Water (H20), Carbon Dioxide (CO2), Iron Oxide (Fe2O3) Mixtures Made when two or more substances are combined physically, but not chemically Examples: Air, Seawater, Mud *The components of a mixture can be easily separated Molecules Substances containing 2 or more atoms that are chemically joined together Examples: Oxygen air (O2), Water (H20), Nitrogen air (N2) Solutions A mixture containing a solvent and a solute Example: (Salt water: Salt is the solute; water is the solvent) Common methods for separation of mixtures 1. Chromatography Separating colours from a mixture 2. Distillation Separating mixtures comprised of two or more pure liquids. Liquids are vaporized, condensed, and isolated 3. Evaporation Separating mixtures with one or more dissolved solids Drives off liquid components from solid components 4. Filtration Separating out pure substances in mixtures comprised of particles through a filter Electricity, Circuits and Brightness of Bulbs Static Electricity Results of imbalances between negative and positive charges in an object The transfers of electrons between objects Examples: Lightning, Balloon and hair, Doorknobs and hands *Like charges repel, opposite charges attract *Coulombmeters can be used to find out if an object has positive or negative charge Conductors Materials that allow electricity to pass through them Examples: Copper, Iron, Mercury Insulators Materials that don’t allow electricity to pass through them Examples: Plastic, Rubber, Wood Electric Current Flow of electric charge Creates magnetic fields (Electromagnet) Measured in Amperes (Amp, A) Measured using ammeter Voltage The “pressure” from an electrical power source that pushes electrons through a conducting loop Measured in volts (V) Measured using voltmeter Higher voltage = Higher current Circuit types Parallel Circuit Comprises of branches Current divides Voltage is the same throughout circuit Current may vary throughout circuit Bulbs are usually brighter than in series circuits Series Circuit Current flows through each component Same current flows throughout circuit Bulbs are usually dimmer than in parallel circuits *Electrons flow from negative to positive *Current flows from positive to negative (opposite direction of electron flow) Digestive system Digestion: The breakdown of large molecules into small molecules so they can be absorbed Absorption: Movement of digested food molecules through the wall of the intestine, into the blood or lymph The digestive system is made up of the alimentary canal The alimentary canal: 1. Mouth Teeth chew food into smaller pieces Saliva breaks down starch to sugar 2. Oesophagus Food passes through 3. Liver Makes bile (helps with fat digestion) Bile flows into small intestine 4. Stomach Contain hydrochloric acid that kills micro-organism in food Stomach juices break down protein to amino acids 5. Gall bladder Stores bile 6. Pancreas Produces pancreatic juice (helps with protein, starch, and fat digestion) Pancreatic juice flows into small intestine 7. Small Intestine Breaks down starch, protein, and fat into smaller molecules Starch, protein, fat, water, vitamins, and minerals are absorbed Absorption happens through the walls of the small intestine 8. Large Intestine Undigested food pass through here Absorbs water Faeces is formed Teeth Hardest substances in the human body In the mouth Chews food into smaller pieces Types of teeth 1. Incisors Chisel shaped Sharp edges Used for bite off food 2. Canines More pointed than incisors Used the same way as incisors 3. Premolars Broad surfaces with ridges Used for crushing and grinding food 4. Molars Similar to premolars, but bigger Used for crushing and grinding food Structure of a tooth Crown 1. Enamel : A very hard covering, containing calcium 2. Dentine : A layer containing liver cells 3. Pulp Cavity : Containing blood vessels and nerves 4. Gum Root 5. Fibres : Help to hold tooth in jawbone 6. Jawbone 7. Blood supply : Supply blood Nutrients Protein Makes new cells Makes enzymes Makes antibodies Supply energy Carbohydrate Provide energy Examples: Starch, Sugar Fat Provides energy Stored in the body Provides insulation Make new cell membranes Vitamins and minerals Don’t provide energy Found in fruits and vegetables Fibre and water Keep food moving easily through the digestive system Found in fruits, vegetables, whole seeds 70% of our body is made up of water Diet Enzymes Biological catalysts (substances that speed up a chemical reaction, but is not changed itself) Helps break down large molecules into smaller ones Different types of animals Vertebrates Vertebrates are animals with backbones. They are classified into five groups called classes 1. Fish With fins Covered with scales Breathe using gills Lay eggs in water (Examples: Sardines, Salmon, Cod) 2. Amphibians Adults live on land, breathe using lungs 4 limbs Have smooth skin without scales Lay eggs in water The young are called tadpoles Tadpoles develop in water, breathe using gills (Examples: Frogs, Geckos, Toads) 3. Reptiles With scaly skins 4 legs (except for snakes) Some live on land, some in water Lay eggs on land (Examples: Snakes, Crocodiles, Dinosaurs) 4. Birds With wings, feather, and a beak Lay eggs on land (Examples: Eagles, Cockatiels, Chickens) 5. Mammals With hair Give birth to young Young are fed on milk from the mother (Examples: Humans, Chimpanzees, Wolves) Invertebrates invertebrates are animals without backbones. There are many different groups of invertebrates. Only a few are listed below. 1. Molluscs With a soft body Muscular foot to move around Some have shells (Examples: Slugs, Snails, Octopuses) 2. Annelids Worms with bodies Divided up into rings (segments) Don’t have legs Have tiny bristles called chaetae (Examples: Earthworms, Leech, Polychaete) 3. Arthropods With jointed legs Divided into segments Have a skeleton on the outside (Exoskeleton) Most common kinds of animals on Earth Several groups of arthropods are listed below: 1. Insects With 6 jointed legs Body divided into: Head, Thorax, Abdomen Most have 2 pairs of wings attached to thorax Legs are attached to thorax 1 pair of antennae on head (Examples: Locusts, Mosquitos, Cockroaches) 2. Arachnids 8 jointed legs Don’t have wings or antennae (Examples: Spiders, Scorpions, Ticks) 3. Crustaceans With tough exoskeleton More than 4 pairs of jointed legs 2 pairs of antennae (Examples: Lobsters, Crabs, Shrimps) 4. Myriapods Many pairs of jointed legs One pair of antennae (Examples: Centipedes, Millipedes, Symphyla) Conduction, convection, and radiation Conduction Transfer of heat from a hot place to a cooler one through a heat conductor. Example: Common heat conductors (Usually metals) Aluminium Bronze Copper Iron Convection Transfer of hear by the motion of a fluid (Example: Air, Water) Basic principle of heat convection Warmer fluids rise, cooler fluids sink Example: *Convection currents are the constant cyclical motion of air *Natural wind is caused by convection Radiation Transfer of heat through energy emitted by matter in the form of electromagnetic waves Example: *Heat is transferred from the Sun to Earth through radiation *Most heat transfers through radiation are in Infrared waves *Black surfaces absorb radiation *Shiny white/ Silver surfaces reflect radiation Energy (renewable or non-renewable) Renewable energy Energy that cannot be used up and can be replaced naturally Examples: 1. Wind Power Wind can turn a windmill, which turns a turbine and generates electricity 2. Water power Water can turn a mill wheel, which turns a turbine and generates electricity 3. Solar Energy The sun can be used to generate electricity using solar cells 4. Biofuels Biofuel can be fermented to produce liquid fuel for cars and trucks Non-renewable energy Energy that can be used up eventually Examples: 1. Coal Takes millions of years to form Combustible 2. Nuclear energy Split atoms to gain energy Radioactive material can be used up 3. Petroleum Takes millions of years to form Combustible 4. Natural gas Formed deep beneath the Earth’s surface Combustible Exothermic and endothermic Exothermic reactions Chemical reactions that release energy (heat) (Examples: Potassium + Water, Carbon + Oxygen, ) Endothermic reaction Chemical reactions that absorb energy (Examples: Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate + Citric Acid, Ice Melting) Moments The turning effect of a force Moment = Force x Distance from pivot Principle of Moments For a beam to be balanced: Clockwise moment = Anticlockwise moment Example: Moment B = 500N x 2m = 1000Nm Moment A = 1000N x 1m = 1000Nm Clockwise moment = Anticlockwise moment ; Moment A = Moment B, therefore the beam is balanced. Moment = Force x Distance Force = Moment / Distance Distance = Moment / Force Heart circulatory system Structure of a heart 1. Artery to lungs Sends deoxygenated blood to the lungs 2. Artery to body Sends oxygenated blood to the body 3. Vein from body Sends deoxygenated blood to the heart 4. Vein from lungs Sends oxygenated blood to the heart 5. Upper chamber Receive incoming blood 6. Valve Control the blood flow in the heart 7. Lower chamber Pump blood out of heat Blood Plasma Liquid part of the blood Contain many different substances dissolved Sugar is dissolved in plasma Red blood cells Small Contain reg pigment (Haemoglobin) Oxygenated Haemoglobin (Oxyhaemoglobin) is very bright red Deoxygenated Haemoglobin (Haemoglobin) is dull blueish-red White blood cells Larger than red blood cells Have a nucleus Defend against viruses and bacteria Produce enzymes and antibodies to kill bacterium Platelets Clot and seal wounds Blood vessels The tubes through which blood flows. There are 3 main types of blood vessels. Arteries Carries blood away from the heart Delivers blood to the body Thick, strong, elastic walls Have to withstand strong forces and pressures Capillaries Very tiny Thin walls made of one layer of cells Supply cells with things they need Take away waste products Veins Return blood to the heart Similar size to arteries Thinner walls Bigger space inside Contain valves Reactivity of Metals Reactivity series (Most reactive to least reactive) Potassium Sodium Lithium Calcium Magnesium Aluminium Zinc Iron Lead Copper Silver Gold Food Chain Trophic levels Producers 1st trophic level Usually plants Uses photosynthesis to create food (Examples: Grass, leaves, weed) Primary Consumers 2nd trophic level Herbivores Consumes producers (Examples: Caterpillars, insects, hummingbirds) Secondary Consumers 3rd trophic level 2nd level consumer Carnivores Consumes primary consumers Some are omnivores, which consume producers & primary consumers (Examples: Fox, frogs)