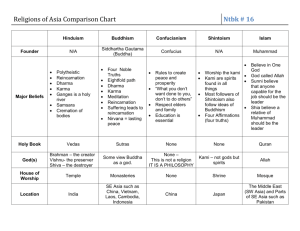
ANCIENT INDIA Hinduism No set theology Brahman – ultimate reality Polytheistic Gods are different manifestations of Brahman Maya – world is an illusion Atman - unchanging eternal self Samsara – reincarnation Cyclic nature of life Karma – cosmic justice Dharma – right behavior Goal is moksha: end to reincarnation Body passes through many castes based on dharma resulting in karma Caste system (Combination of 3 systems) 1. Traditional: Priest, warrior, tradesman, servant, untouchable 2. Jatis: occupation 3. Geographic Buddhism Siddhartha Gautama 563-483 BC founder Enlightenment Nontheistic – no creator, no unchanging divine reality Minimize suffering and gain inner peace Three marks of reality Change, impermanent personal identity, suffering Four noble truths To live is to suffer, Suffering comes from desire, End desire = end suffering Release from suffering via Eightfold path to nirvana Right: understanding, intention, speech, action, living, effort, meditation, and contemplation Several different schools of Buddhism Theravada Buddhism – Strict / conservative Mahayana Buddhism – Large vehicle Theravada Buddhism Way of the elders Strict/ conservative Strict adherence to Buddha's teachings Monastic Detachment / loss of desire through meditation Personal behavior important for release from reincarnation Merit to gain better rebirth Buddha is not divine Sri Lanka, Laos, Cambodia, Thailand, Myanmar (Burma) Mahayana Buddhism Large vehicle Less strict Broadened Buddhist ideal Common people – Lay, women, married Positive view of material world Buddhism is a quasi-religion Wisdom and compassion Heaven replaces nirvana Buddha was manifestation of divine reality Bodhisattva- one who stays in cycle of reincarnation to help others Rituals / devotions, temples on a grand scale China Jainism Mahavira “great man” 540 – 468 BC Final Jina “victor - Human who found way out of samsara Dualist philosophy jiva / ajiva Atheist Reincarnation Karma Extreme ahimsa Vegetarian Strict morality Austerity Gentle suicide Mauryan Dynasty 321 – 232 Along the Ganges River Centralized government / banking Created by marriage and conquest Chandragupta Maurya 332 – 298 Built infrastructure and insured quality for enterprises Capital at Pataliputra Kautilya the prime minister wrote Arthashastra Ashoka the Great 272 – 232 Great warrior who turned to peace Devout Buddhist Rock and pillar edicts