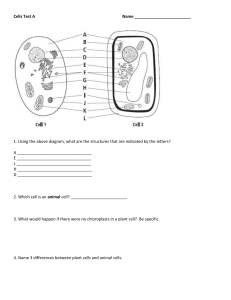
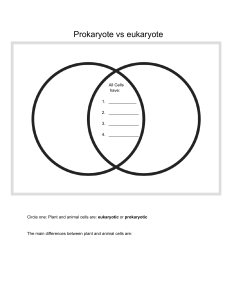
Chapter2 Cells Part1 Cells and Microscope are made up of Different types of Let’s compare animal cell with plant cell! What are organelles? • Definition: tiny structures that have specific functions in the cells. • Example: nucleus(细胞核),mitochondria(线粒体), chloroplast(叶绿体), vacuole(液泡). Similarity1: Both surrounded by cell membrane Function:form a barrier between the cell and its surroundings; control the exchange of substances(物质) . It is selectively/ partially permeable. Similarity2: Both have Cytoplasm (细胞质) Function: provide space for chemical reaction/enzymes and organelles inside the cell Similarity3: Both have nucleus(细胞核) Contain chromosomes(染色体) which carry genetic information and can be copied to the next generation. Function: control cell activities/growth/ division/ reproduction nucleolus核仁 nuclear pore 核孔 nuclear envelope 核膜 Chromosomes(染色体) in nucleus (染色体) Similarity4: Both have endoplasmic reticulum • structure: a complex of double membranes (内质网) • types: with ribosomes: rough ER to transport protein made by ribosomes without ribosomes:smooth ER to make fat (lipid) Similarity5: Both have ribosomes(核糖体) • Structure: very tiny, can only be seen under electron microscope • only organelle that prokaryotic cell has • Function: site of making protein Many cells need to be ‘paid' when they do their jobs! Similarity6:Both have mitochondria(线粒体) Singular: Mitochondrion Function: site of respiration (呼吸 作用) to provide energy. Difference1: All plant cells have cell wall cell membrane Cell wall is rigid and inflexible and is made up of cellulose (纤 维素). Function: Protect and support for the cell. Fully permeable Where does the juice of a lemon or orange come from? Difference2:Most Plant cell has vacuole(液泡) In animal cells vesicle In plant cells vacuole Most plant cells contain large permanent vacuoles. Function: 1. contain cell sap: store water, sugar, salts and so on; 2. help maintain cell shape. Why are most of the leaves green? Difference3: Most Plant cell has chloroplast Chloroplasts contain green pigment called chlorophyll to absorb light energy for photosyntheis Most plant cells have chloroplasts, but some only have chlorophyll Function: 1. the site of photosynthesis; 2. store starch. Comparison between plant and animal cell animal cell cell wall cell membrane cytoplasm nucleus chloroplast vacuole endoplasmic reticulum mitochondria ribosome plant cell Function ribosome Prokaryotic Cells VS Eukaryotic Cells bacterial cell • Organism does not have nucleus, called prokaryote, made up of prokaryotic cells. • e.g. bacteria • Organism has nucleus, called eukaryote, made up of eukaryotic cells. • e.g. animal, plant a layer of sugar nucleus eukaryotic cells prokaryotic cells form of genetic materials cell size organelles Exercise-01&02: How to observe cells? By microscope Light Microscope and Electron Microscope 光学显微镜 电子显微镜 Magnification of Microscope Exercise-03: An egg measured 6.5 cm in diameter. A student made a drawing of this egg and the diameter was measured as 19.5 cm. What was the magnification of the drawing? Part2 Specialised Cells Are all cells in your body same? Who is Mr.undifferentiate? speciliased cells • Stem cells: with the ability to develop into other kind of cells; • This process is called cell differentiation. Specialised Cells When cells are specialised: a. they do one particular job b. they develop a different shape c. special kinds of chemical change take place in their cytoplasm. Cells have special shape/feature for better carrying out its function. We call it ‘adapation’. Structures are adapted for functions. 1. Red Blood Cell (红细胞) Function: carry, transport,and release oxygen Adaptation: 1. Contain haemoglobin(血红蛋白): a protein which can combine with oxygen 2. No nucleus and other organelles: provide more ___________ for haemoglobin to bind with oxygen; more flexible shape to move through ____________ 3. biconvace shape: larger _____________ for oxygen to get through 2.Sperm and Egg Cells • acrsome(顶体): produce ________ to digest egg membrane • mid-piece: many mitochondria • __________: for movement • Much larger: more cytoplasm contains many _____________ Function: Reproduction (生殖) 3. Ciliated Cells (纤毛细胞) cilia 纤毛 Function: Remove mucus(粘液) away from lungs through bronchi (支气管) and trachea(气管). 4. Nerve Cells (神经细胞) nucleus nerve fibre Function: Conduction of nerve/ electrical impulse (电冲动) 5. Root Hair Cells (根毛细胞) Function: Absorb water and mineral salts (矿物盐) Adaptations of Root hair cells Root hair cells absorb water by________and minerals by____________ from soil Adaptation: 1. extensions to increase ______________ 2. thin wall for ______________ 3. concentrated cell sap for ________ 6. Xylem Vessels (木质部导管细胞) • Structure: 1. dead 2. thickened cell wall by lignin(木质素) to withstand pressure and prevent collapsing • Function: transport water and mineral salts upwards (栅栏叶肉细胞) 7. Palisade Mesophyll Cells (栅栏叶肉细胞) Adaptation: 1. just under the transparent cuticle: 2. arrange closely: 3. contain much more chloroplasts: Function: main place of photosynthesis Exercise-04&05: Exercise-06: Exercise-07: Part3 Levels of Organisation How can cells organise into living organisms? eukaryotic cell prokaryotic cell: bacteria VS Definition: A tissue is a group of cells with similar structures, working together to perform a shared function. Xylem and phloem are transporting tissues. Definition: An organ is a structure made up of a group of tissues, working together to perform a specific function. Plant Organs Special organs in plants: bulb:鳞茎 tuber:块茎 runner/stolon:匍匐茎 Definition: A system is a group of organs with related functions, working together to perform a body function. Human organ system 循环系统 神经系统 骨骼系统 呼吸系统 消化系统 肌肉系统 生殖系统 Do plants have organ system? 轴系统 根系统 Definition: An organism is formed by the organs and systems working together to produce an independent plant or animal. Exercise-08: Exercise-09&10: Checklist Checklist THANKS