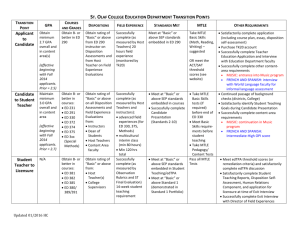
PMLSP 1 Medical Technology/Clinical Laboratory Science Education —----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Definition of Curriculum - Currere (latin) Known as the means and materials with which students interact for the purpose of achieving identified education outcomes Glossary of Education Reforms - knowledge and skills students are expected to learn which include learning standards and learning objectives they are expected to meet; units and lessons that teachers teach; assignments and projects; books, materials, videos, presentations, and readings; tests and assessments and other methods of evaluation John Dewey - Curriculum is a continuous reconstruction; moving from child’s present experience out into that represented by the organized bodies of truth we called as studies; the various studies that they experience Indiana Department of Education - planned interaction of students with instructional content, materials, resources, and processes for evaluating the attainment of education objectives Characteristics of an ideal Curriculum - - - Systematic and organized Explicitly states the outcomes (knowledge & skills) the learners/students have to achieve and learn through the use of planned instructional processes in a specific Period Consists of a planned process of measurement, assessment, and evaluation to gauge student learning Designed for students BSMT Curriculum - - - - - Four-year program consisting of general education and professional courses that students are expected to complete within the first 3 years; Fourth year is dedicated to internship in CHED-accredited training laboratories affiliated with their college/department CHED Memorandum Order No. 13 series of 2017 (Policies, Standards, and Guidelines for the BS in Medical Technology) Prerequisites for some courses (pathologist) CMO contains the goals, program outcomes, performance indicators, and the minimum course offerings Compliant with K-12 Program CHED - established on May 18, 1994 RA 7722, Higher Education Act of 1992 under the Office of the President of the Philippines that covers both public and private institutions PMLSP 1 Medical Technology/Clinical Laboratory Science Education —----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------TASK: Organize and appoint members of - aim to develop humane individuals the technical panel for each that have a deeper sense of self and discipline/program acceptance of others. Under CHED is the: ● ● Technical Committee for Medical Technology Education (TCMTE) - ● composed of leading academicians and practitioners responsible for assisting CHED in setting standards among institutions offering BS MT ● ● ● ● ● Number of units Lecture 1 unit = 1 hour/week 3 units lecture = 3 hours/week 3 hours x 18 weeks (one sem) = 54 hours Laboratory 1 unit lab = 3 hours/week TOTAL: 5 units (3 units lec, 2 units lab) Meaning, there is total of 3 hours for lecture and 6 hours for laboratory every week General Education Courses - aim to develop foundational knowledge, skills, values, and habits necessary for students to succeed in life; to positively contribute to society; to understand diversity of cultures; to gain bigger perspective and understanding of living with others; to respect differences in opinions; to realize and accept their weakness and improve on them; and to further hone their strengths Understanding the Self Readings in Philippine History Mathematics in Modern World Purposive Communication The Life and Works of Rizal Science, Technology, Society Art Appreciation Ethics Professional Courses - - taken for learners to develop knowledge, technical competence, professional attitude, and values necessary to practice and to meet the demands of the profession Critical-thinking skills decision-making skills, interpersonal skills, collaboration, and teamwork are also developed. ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Principles of Medical Laboratory Science Principles of Medical Laboratory Science II Community and Public Health for MT/MLS Cytogenetics Human Histology Histopathologic Techniques with cytology Clinical Bacteriology Clinical Parasitology Mycology and Virology Laboratory Management Medical Technology Laws and Bioethics Hematology 1 and 2 Clinical Microscopy PMLSP 1 Medical Technology/Clinical Laboratory Science Education —----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------● Clinical Chemistry 1 & 2 ● The academic institution is required ● Seminars 1 & 2 to conduct orientation to prospect ● Molecular Biology and interns regarding policies and Diagnostics guidelines as contained in the Internship Training Manual. Research Courses Number of Duty Hours Research 1: Introduction (basic concepts 32 hours per week not exceeding 1,664 and ethical principles) hours in a year. - More on proposal Research 2: Research Paper Writing and Presentation (methodology approved on Course No. of Hours Research 1, writing the research in format Clinical Chemistry 300 prescribed by the institution and international agencies for possible Clinical Microscopy 200 publication, and presentation of the finished and completed research in a formal forum) Microbiology 250 - More on experimentation Internship Program - For 4th year BS MT students Application of theoretical aspects of the profession into practice. Requirements: ● ● ● ● Successfully passed all academic requirements Physical and laboratory examinations CBC, Urinalysis, Fecalysis, CXR (chest x-ray) and/or sputum microsocopy(TB), HbsAg, HbsAb, (hepa) and Drug Test Hepatitis B proof of vaccination CHED-Accredited clinical laboratories affiliated with academic institutions on a 6-month or 1-year rotation.z Hematology 300 Blood Banking 200 Histopathology 100 Immunology and Serology 220 Laboratory Management 40 Phlebotomy 54 Licensure Examination - - Governed by Professional Regulation Commission (PRC) under the Office of the President: Professional Regulatory Board (PRB) for Medical Technology Professional Regulatory Board (PRB) ● All students experience to work in different sections of a clinical laboratory - 1 Chairperson (Pathologist) Dr. Marilyn A. Cabal-Barza PMLSP 1 Medical Technology/Clinical Laboratory Science Education —----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Failing to pass the MTLE 2 members (RMT) Dr. Grace J. Dela Calzada and Dr. Leila Lany M. Florento - MTLE is given twice a year (March and August) Grading System 20% Microbiology and Parasitology 20% - Hematology 20% - Blood Bank and Serology 20% Clinical Microscopy 10% 10% Criteria for Passing - General weighted average of 75% Have no rating below 50% in any major courses, and; Pass in at least 60% of the courses computed according to their relative weights Passing the MTLE - Learning Outcomes Clinical Chem Histopathology and MT Laws and Bioethics and Laboratory Management Certificate of Registration will only be issued for passers aging or above the age of 21 After 3 times of failing the MTLE, the examiner must enroll in a Refresher Course to be allowed to take the exam again If the examiner failed to pass but got a rating of 70-74% he/she may apply as medical lab technician define what the learner must achieve foundation of curriculum development and teaching methodologies that shape a program States the knowledge, skills, values, and ethics that graduates of the program should demonstrate. Learning Outcomes of BSMT 1. Demonstrate knowledge and technical skills needed to correctly perform lab testing. 2. Be endowed with professional attitude and values enabling them to work with colleagues. 3. Demonstrate critical thinking and problem solving skills when confronted with situations. 4. Actively participate in self-directed life-long learning activities. 5. Actively participate in research and community-oriented activities 6. Be endowed with leadership skills. 7. Demonstrate collaboration, teamwork, integrity, and respect when working in a multicultural environment. PMLSP 1 Medical Technology/Clinical Laboratory Science Education —----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Assessment - - Inherent in every learning activity Involves a planned, systematic, and organized way of testing, measuring, collecting, and obtaining necessary information to gain feedback on students’ progress against set standards per course and on the effectivity of teaching methodology The feedback comes from both students and teachers. Functions of Assessment Techniques - - - Provides feedback on the progress of students. Identifies flaws in the psychomotor skills and deficiencies in theoretical knowledge and conceptual skills. Serves as a diagnostic tool to determine the capabilities of students. Motivation to improve students’ skills. Provides information on students’ response to learning strategy. It provides info if the teacher needs to improve. It determines demonstrable changes in attitude and behavior of students. It determines whether learning has taken place. Types of Assessment Formative - Done to determine whether a student is achieving outcomes of the topic being discussed. - Done during and or/within the instructional process of a course i.e. quizzes, short-answer questions, reflection papers Summative - Done at the end of the instruction, grading period (prelim, midterms, finals) - Done to determine how well each student learned the tasks or how well the students attained learning outcomes. i.e. end of unit exam, end of term exam, research term paper, final projects Diagnostic - Given prior to instruction - It is a gauge what students already know and do not know about the topic at hand. Assessment Tools Lower-order thinking skills (LOTS) i.e. matching type, true or false Higher-order thinking skills (HOTS) i.e. enumeration, essay, case studies Sample Assessment Tools • Teacher-made written test • Reflection paper • Portfolios • Performance tasks • Oral exam and presentation • Rubrics Job Opportunities for BSMT Graduates - - Medtech/clinical laboratory scientist in a hospital-based or non-hospital-based lab Histotechnologist in an anatomical lab Researcher PMLSP 1 Medical Technology/Clinical Laboratory Science Education —----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Member of the academe - Perfusionist - Molecular scientist - Diagnostic product specialist - Public health practitioner - Health care leader Other Fields to Explore: • Molecular Biology • Public health and Epidemiology • Veterinary lab science • Food and industrial microbiology • Veterinary science • Forensic science • Nuclear medicine • Health facility administration • Quality Management