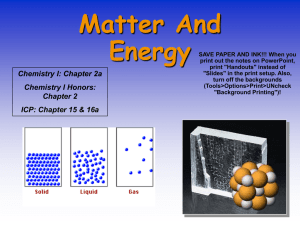
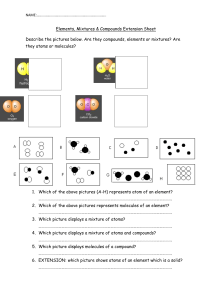
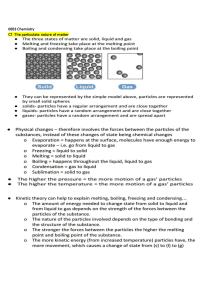
INTRODUCTION TO THE PARTİCULATE NATURE OF MATTER QUIZ 1 1-During the process of melting, a substance transitions from: a) A solid to a liquid state b) A liquid to a solid state c) A gas to a liquid state d) A liquid to a gas state 2-Which of the following statements is true regarding the particulate nature of matter? a) It only applies to organic compounds. b) It explains the behavior of matter at atomic and molecular levels. c) It primarily deals with the properties of liquids. d) It is unrelated to the behavior of matter. 3-What type of change is melting or freezing of a substance? a) A chemical change b) A physical change c) An electrical change d) A magnetic change 4-During which process does a substance transition from a gas to a liquid state? a) Boiling b) Melting c) Freezing d) Evaporation 5-Why is the particulate nature of matter important? a) It is only relevant for chemists. b) It helps us understand how matter behaves and chemical reactions. c) It only explains the behavior of gases. d) It defines the properties of solids. 6-What is the particulate nature of matter? a) It explains the properties of gases only. b) It describes matter as composed of atoms and molecules. c) It defines the properties of solids only. d) It relates to the speed of light and sound. 7-What is the fundamental difference between atoms and molecules? a) Atoms are always found in gases, while molecules are found in solids. b) Atoms are indivisible, while molecules consist of two or more atoms chemically bonded. c) Atoms and molecules are interchangeable terms. d) There is no difference between atoms and molecules. 8-What are the three fundamental states of matter, and what distinguishes them? a) Solid, liquid, gas; the difference lies in the spacing between particles. b) Solid, liquid, gas; the difference lies in molecular motion. c) Solid, liquid, gas; only thermal properties differ. d) Solid, liquid, gas; chemical properties differ. 9-What are elements and compounds, and how do they differ? a) Elements are composed of mixtures; compounds are pure substances. b) Elements are chemically simpler and consist of only one type of atom; compounds contain two or more different types of atoms. c) Elements are found only in gases; compounds are found only in solids. d) Elements and compounds are identical in meaning. 10-What is a mixture, and how does it differ from a pure substance? a) A mixture is a chemical combination of two or more substances, while a pure substance is a single element. b) A mixture is physically combined, while a pure substance is chemically bonded. c) A mixture is a pure substance, while a pure substance is a combination of elements. d) A mixture is only found in gases, while a pure substance is found in solids. 11-What is the term for the process during which a substance changes directly from a solid to a gas without passing through the liquid phase? a) Melting b) Freezing c) Sublimation d) Condensation 12-Which state of matter has particles that are tightly packed and vibrate in fixed positions? a) Gas b) Liquid c) Solid d) Plasma 13-What is the term for a mixture that has a uniform composition throughout and consists of a single phase? a) Homogeneous mixture b) Heterogeneous mixture c) Compound d) Element 14-What is the process during which a substance changes from a liquid to a gas at a temperature below its boiling point? a) Evaporation b) Condensation c) Sublimation d) Melting 15-What is the smallest particle of an element that retains its chemical properties? a) Molecule b) Atom c) Compound d) Ion 16-What is the term for the change of a substance from a gas to a liquid? a) Melting b) Freezing c) Condensation d) Evaporation 17-In which state of matter do particles have the most energy and move freely? a) Gas b) Liquid c) Solid d) Plasma 18-What is the term for the process of a substance changing directly from a solid to a gas without going through the liquid phase? a) Evaporation b) Melting c) Sublimation d) Condensation 19-Which of the following is an example of a heterogeneous mixture? a) Saltwater b) Air c) Orange juice with pulp d) Vinegar 20-What is the smallest unit of a compound that retains its chemical properties? a) Molecule b) Atom c) Element d) Ion