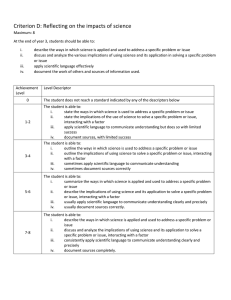
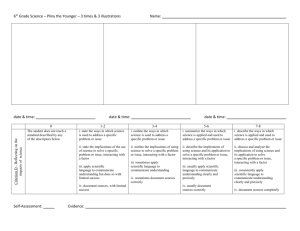
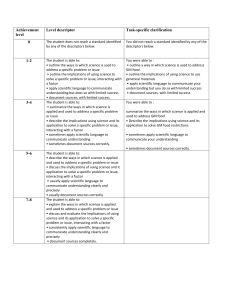
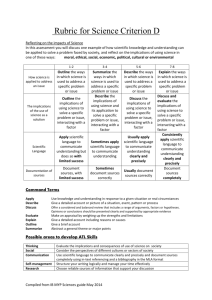
MYP 4 Biology Assessment Task Unit: How is life organised? Assessment criterion D (Reflecting on the impacts of science) Assessment task type: Research essay Deadline for submission into Managebac: 2nd June 2022 Introduction Although they vary in form and function, cells are the basic building blocks of life. The idea that cells are the unit of structure and function from which organisms are made is known as ‘the cell theory’. Cell theory states that: • cells are the building blocks of structure in living things • cells are the smallest unit of life • cells are made from other cells by division. Some scientists in the world are creating artificial cells. The assessment task ‘Will it be possible to create artificial life?’ (16marks) As a guide, ask yourself the following key questions; • Have there been attempts to create artificial cells/new organisms? • What ethical/cultural/political/environmental/economic issues does it raise? • Do you think that it will be possible to create new organisms artificially? Would this be desirable? In your research essay, you should; 1. explain the ways in which science is applied and used to address a specific problem or issue 2. discuss and evaluate the various implications of using science and its application to solve a specific problem or issue 3. apply scientific language effectively 4. document the work of others and sources of information used. Page 1 of 4 Criterion D: Reflecting on the impacts of science Maximum: 8 Students will be assessed on how well they: i. explain the ways in which science is applied and used to address a specific problem or issue ii. discuss and evaluate the various implications of using science and its application to solve a specific problem or issue iii. apply scientific language effectively iv. document the work of others and sources of information used. Level 0 Level Descriptor The student does not reach a standard identified by any of the descriptors below. The student is able to: 1-2 i. outline the ways in which science is used to address a specific problem or issue ii. outline the implications of using science to solve a specific problem or issue, interacting with a factor iii. apply scientific language to communicate understanding but does so with limited success iv. document sources, with limited success. The student is able to: 3-4 i. summarize the ways in which science is applied and used to address a specific problem or issue ii. describe the implications of using science and its application to solve a specific problem or issue, interacting with a factor iii. sometimes apply scientific language to communicate understanding iv. sometimes document sources correctly. The student is able to: 5-6 i. describe the ways in which science is applied and used to address a specific problem or issue ii. discuss the implications of using science and its application to solve a specific problem or issue, interacting with a factor iii. usually apply scientific language to communicate understanding clearly and precisely iv. usually document sources correctly. The student is able to: 7-8 Page 2 of 4 i. explain the ways in which science is applied and used to address a specific problem or issue ii. discuss and evaluate the implications of using science and its application to solve a specific problem or issue, interacting with a factor iii. consistently apply scientific language to communicate understanding clearly and precisely iv. document sources completely. Criterion D: Reflecting on the impacts of science 0 1-2 (MYP 5) Achievement Level Rubric 3-4 5-6 7-8 outline the ways in which science is used to address a specific problem or issue summarize the ways in which science is applied and used to address a specific problem or issue describe the ways in which science is applied and used to address a specific problem or issue explain the ways in which science is applied and used to address a specific problem or issue outline the implications of using science to solve a specific problem or issue, interacting with a factor describe the implications of using science and its application to solve a specific problem or issue, interacting with discuss the implications of using science and its application to solve a specific problem or issue, interacting with discuss and evaluate the implications of using science and its application to solve a specific problem or issue, interacting with a factor a factor a factor apply scientific language to communicate understanding but does so with limited success sometimes apply scientific language to communicate understanding usually apply scientific language to communicate understanding clearly and precisely consistently apply scientific language to communicate understanding clearly and precisely document sources, with limited success sometimes document usually document sources correctly sources correctly The student does not reach a standard identified by any of the descriptors Strand 4 Strand 3 Strand 2 Strand 1 The student is able to: Page 3 of 4 document sources completely GUIDANCE FOR WRITING ABOUT FACTORS Think about these definitions/questions when you evaluate the benefits and limitations of this application of science in regards to one of the world factors. ECONOMIC is defined as “pertaining to the production, distribution, and use of income, wealth, and commodities.” The costs and benefits of using science. Who pays or receives the benefit? Is it worth it? How much will it cost? Are the potential benefits worth the cost? Who pays for it, private companies, the Government, consumers? (eg. Obesity will cost governments millions but so does changing people’s eating habits and diet- is it worth attempting to deal with it?) SOCIAL is defined as “of or pertaining to the life, welfare, and relations of human beings in a community.” The people affected or involved, from a few people up to the global community. How will this application of science affect society, will it affect everyone or a select group? Will it unfairly affect one group of society over another? Will everyone have access to the science/solution or only the privileged (e.g An oil refinery is a local problem but global warming is truly global) ETHICAL is defined as “pertaining to or dealing with morals or the principles of morality; pertaining to right and wrong in conduct.” Is it right or wrong to use science in this way and if we do, how ought we to do it? (Aborting foetuses is something we have to do in a caring way even if we think it is right or wrong. Who decides whether it is right or wrong, the Government, religious groups, individuals? There are ways of doing things and often a law to guide us - animal testing is highly policed). POLITICAL is defined as “of, pertaining to, or involving the state or its government.” Is the government involved directly or are powerful groups trying to influence people or the government or the UN etc? Notice how much diet advice is given in books by non-experts. Why would the Government be for or against this the application of this science and how would it affect other countries? ENVIRONMENTAL is defined as “of, relating to, or associated with the environment.” Is the issue an environmental one in some way, directly or indirectly? (Pollution is direct but what about binge-drinking?) CULTURAL is defined as “of, relating to, or associated with the behaviors and beliefs characteristic of a particular social, ethnic, or age group.” A problem in one place is seen differently in another for reasons such as faith, tradition and different belief values. Would people from different cultures be affected the same way or have the same opinion on the scientific solution. Some religions are against certain medical procedures, from organ transplants to blood donations. Some cultures rely heavily upon the natural ecosystem to gain their food and shelter, others live in a manufactured society and are disconnected from the natural world. Certain religions have rules about how males and females should interact, or what foods to eat. Page 4 of 4