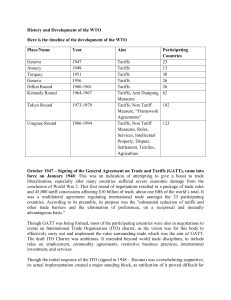
According to WTO (1998), the core principles of GATT now (WTO) include the most favored nation, tariff reduction, national treatment, tariff preferred, and transparency. The Most Favored Nation (MFN) rule is fundamental to the GATT's entire structure. According to Article I of the GATT, if one GATT (now WTO) member provides another country "more favorable treatment" (such as a decrease in the customs tax due to importation of a certain product), the other party must promptly and unconditionally reciprocate. The second fundamental premise is that members make commitments to indicate the maximum level of import duty, another charge, or condition that they will impose on certain types of products imported. Tariff preferred is also used to protect the interest of countries that are members of GATT and WTO. The idea of national treatment states that a product's domestic provider should only be protected by border action. Advantages of Import Substitution Disadvantages of Import Substitution Suitable for large domestic economy Inefficiency Due to heavy protectionism, ISI restricts the economy while protecting domestic businesses. Increased savings Minimize investment Firms sought minimize to maximize investments since profits and they were protected from foreign competitors and had a safe home market.