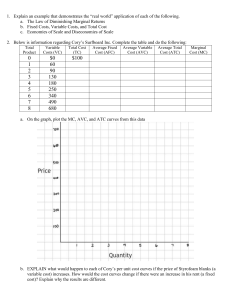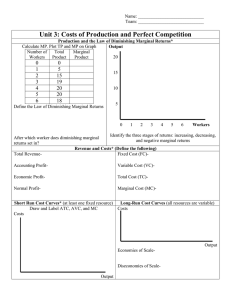
Microeconomics Behind the supply: Cost of production Short run (From the industry level analysis we are not towards the firm level analysis) session 10 September 2022 Why study cost structure – because it determines supply, and hence revenue and profit • Every firm has to make 3 key decisions to maximize profits Profits = Revenue - Costs – What price to set? – What quantity to produce? – When to enter and exit the industry? • Firms’ cost structure has implications for these decisions and hence, for the supply curve Costs Suppose two of you decide to start your own business. • One puts his own Rs 2,00,000 savings into it and also for gives up his job (implicit cost or opportunity cost) • The other has no job and take a loan of Rs 2,00,000 from a bank (explicit cost) • How would their balance sheet differ? • In Economics unlike accounting, we consider the implicit cost as well • Economic profit is thus lower than accounting profit. One may have profit in an accounting sense, but suffer an economic loss. Why are movies rarely based on original ideas/ innovative plots/formats? High fixed costs Fixed Cost • Costs of inputs whose use does not vary with the firm’s output level • Rent, insurance, interest cost, • Semi fixed - wages, advertising, telephone bill expenses so on – The short run is the time period in which at least one input (cost) is fixed. Solar panels Which type of costs is high? Let’s say a company spent $5 million building an airplane. Before the plane is complete, it is obsolete and no airline will buy it. Now the airlines want a different type of a plane. The company can finish the plane for another $1 million, or it can start over and build the new type of a plane for $3 million. What should the company do? Sitting through a bad movie because we have paid for it or overeating at all-you-can eat buffet are also an example of a sunk cost fallacy Some part of fixed costs is Sunk cost Expenditure that has been made and cannot be recovered. Because a sunk cost cannot be recovered, it should not influence the firm’s decisions. Because it has no alternative use, its opportunity cost is zero. Total cost = Fixed cost + Variable cost (Short run) Variable cost • Variable cost: costs of inputs that vary with the firm’s output level • Fuel, maintenance, electricity, transportation – The long run is the time period in which all inputs can be varied – all costs are variable costs In their calculation of profit, accountants typically do not take into account: A) variable costs. B) fixed costs. C) opportunity costs. D) explicit costs. When opportunity cost is positive, economic profit ______ accounting profit. A) is greater than B) is less than C) equals D) eliminates Total cost • In Economics, costs include Implicit cost (opportunity cost) and explicit cost • Total cost = Fixed cost + Variable cost • • • • Average cost = Total cost/total production Average Fixed cost = total fixed cost/total production Average Variable cost = total variable cost/total production Marginal cost = change in total cost/change in production Starting a business? Starting a fast-food restaurant. Rent is Rs 100 wages per worker Rs 10, raw material Rs 1 per unit of production Number Variable of Production Fixed cost Total Cost cost workers 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 55 120 190 200 210 215 218 AFC AVC ATC workers Production fixed cost Variable cost Total Cost AFC AVC ATC 0 0 100 0 100 1 55 100 65 165 1.82 1.18 3.00 2 120 100 140 240 0.83 1.17 2.00 3 190 100 220 320 0.53 1.16 1.68 4 200 100 240 340 0.50 1.20 1.70 5 210 100 260 360 0.48 1.24 1.71 6 215 100 275 375 0.47 1.28 1.74 7 218 100 288 388 0.46 1.32 1.78 Average total and average variation cost Cost of unit ATC AVC Quantity Average fixed cost and average Variable Cost Average fixed cost is the fixed cost per unit of output. Fixed cost per unit of output falls as output increases Average variable cost is the variable cost per unit of output. Variable cost per unit of output first falls and then rises • First, gains from specialization – the spreading effect • Then, the law of diminishing returns (holding fixed inputs constant) • Example: Restaurant Average Total Cost is total cost per unit of output To begin with both AFC and AVC fall so ATC cost also falls. After a point, AVC dominates, resulting in a U-shaped ATC curve Marginal Cost the Marginal Cost Curve first slopes downwards.. • Slope downward as a firm increases its production from zero up to some low level, sloping upward only at higher levels of production. • A firm that employs only a few workers often cannot reap the benefits of specialization of labor. This specialization can lead to increasing returns at first • Once there are enough workers, diminishing returns set in. ….and then upwards • Because there are diminishing returns to inputs in this example. As output increases, the marginal product of the variable input declines. • This implies that more and more of the variable input must be used to produce each additional unit of output as the amount of output already produced rises. • And since each unit of the variable input must be paid for, the cost per additional unit of output also rises. The Relationship Between the Average Total Cost and the Marginal Cost Curves Cost of unit If marginal cost is above average total cost, average total cost is rising. MC MC ATC H B A 1 A MC L M B 2 2 1 If marginal cost is below average total cost, average total cost is falling. Quantity Minimum cost output Cost of unit 2. … but diminishing returns set in once the benefits from specialization are exhausted and marginal cost rises. MC ATC AVC A - Minimum cost output A 1. Increasing specialization leads to lower marginal cost… Quantity 1985 – Coca cola company was faced with soaring prices of cane sugar 1-cent increase in the price of sugar raised its cost by $20 million. 1. What were the options for the company? 2. Is sugar a fixed or variable input? Rather than raise price, the company looked for cheaper input – corn sugar. Did the switch in the input lower – TC, VC, FC, ATC, AFC,AVC? Shark Tank – Off the Cob How much is the cost differential compared to the oldstyle corn chips? What is the price difference? What do you think is the price elasticity of demand? Barrel of Oil Produced Marginal Revenue Marginal Cost Average Costs 1 $50 $4 $34 2 50 6 20 3 50 11 17 4 50 17 17 5 50 23 18.20 6 50 29 20 7 50 36 22.29 8 50 50 25.75 9 50 90 32.89 10 50 124 What is the total cost of producing eight barrels of oil? A) $50 B) $206 C) $178 D) $336 42 What are the fixed costs of production for this firm? A) $34 B) $4 C) $30 D) $50 Shrinkflation is the process of items shrinking in size or quantity! - Video By tweaking the shape, Toblerone reduced its 400 gram bar down to 360 .The length and the price though remained the same (Feb 2018) Home work - Fill in the blanks Output VC 0 1 TC AVC AFC ATC 100 25 2 20 3 53.30 4 5 17.5 90 6 30 7 265 8 41.3 9 10 MC 35 425