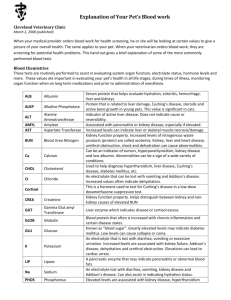
lOMoARcPSD|27030987 Values AND Markers - notes Nursing Process Ii (Broward College) Studocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university Downloaded by Steven Traffanstedt (steventraff@protonmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|27030987 VALUES AND MARKERS Hematology Values HEMATOCRIT (HCT) Normal Adult Female Range: 37 – 47% Optimal Adult Female Reading: 42% Normal Adult Male Range 40 – 54% Optimal Adult Male Reading: 47 Normal Newborn Range: 50 – 62% Optimal Newborn Reading: 56 HEMOGLOBIN (HGB) Normal Adult Female Range: 12 – 16 g/dl Optimal Adult Female Reading: 14 g/dl Normal Adult Male Range: 14 – 18 g/dl Optimal Adult Male Reading: 16 g/dl Normal Newborn Range: 14 – 20 g/dl Optimal Newborn Reading: 17 g/dl MCH (Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin) Normal Adult Range: 27 – 33 pg Optimal Adult Reading: 30 MCV (Mean Corpuscular Volume) Normal Adult Range: 80 – 100 f Optimal Adult Reading: 90 Higher ranges are found in newborns and infants MCHC (Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration) Normal Adult Range: 32 – 36 % Optimal Adult Reading: 34 Higher ranges are found in newborns and infants · R.B.C. (Red Blood Cell Count) Normal Adult Female Range: 3.9 – 5.2 mill/mcl Optimal Adult Female Reading: 4.55 Normal Adult Male Range: 4.2 – 5.6 mill/mcl Optimal Adult Male Reading: 4.9 Lower ranges are found in Children, newborns and infants W.B.C. (White Blood Cell Count) Normal Adult Range: 3.8 – 10.8 thous/mcl Optimal Adult Reading: 7.3 Higher ranges are found in children, newborns and infants. PLATELET COUNT Normal Adult Range: 130 – 400 thous/mcl Optimal Adult Reading: 265 Higher ranges are found in children, newborns and infants Downloaded by Steven Traffanstedt (steventraff@protonmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|27030987 NEUTROPHILS and NEUTROPHIL COUNT – this is the main defender of the body against infection and antigens. High levels may indicate an active infection. Normal Adult Range: 48 – 73 % Optimal Adult Reading: 60.5 Normal Children’s Range: 30 – 60 % Optimal Children’s Reading: 45 LYMPHOCYTES and LYMPHOCYTE COUNT – Elevated levels may indicate an active viral infections such as measles, rubella, chickenpox, or infectious mononucleosis. Normal Adult Range: 18 – 48 % Optimal Adult Reading: 33 Normal Children’s Range: 25 – 50 % Optimal Children’s Reading: 37.5 MONOCYTES and MONOCYTE COUNT – Elevated levels are seen in tissue breakdown or chronic infections, carcinomas, leukemia (monocytic) or lymphomas. Normal Adult Range: 0 – 9 % Optimal Adult Reading: 4.5 EOSINOPHILS and EOSINOPHIL COUNT – Elevated levels may indicate an allergic reactions or parasites. Normal Adult Range: 0 – 5 % Optimal Adult Reading: 2.5 BASOPHILS and BASOPHIL COUNT – Basophilic activity is not fully understood but it is known to carry histamine, heparin and serotonin. High levels are found in allergic reactions. Normal Adult Range: 0 – 2 % Optimal Adult Reading: 1 Advertisements REPORT THIS AD Electrolyte Values SODIUM – Sodium is the most abundant cation in the blood and its chief base. It functions in the body to maintain osmotic pressure, acid-base balance and to transmit nerve impulses. Very Low value: seizure and Neurologic Sx. Normal Adult Range: 135-146 mEq/L Optimal Adult Reading: 140.5 POTASSIUM – Potassium is the major intracellular cation. Very low value: Cardiac arythemia. Normal Range: 3.5 – 5.5 mEq/L Optimal Adult Reading: 4.5 Downloaded by Steven Traffanstedt (steventraff@protonmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|27030987 CHLORIDE – Elevated levels are related to acidosis as well as too much water crossing the cell membrane. Decreased levels with decreased serum albumin may indicate water deficiency crossing the cell membrane (edema). Normal Adult Range: 95-112 mEq/L Optimal Adult Reading: 103 CO2 (Carbon Dioxide) – The CO2 level is related to the respiratory exchange of carbon dioxide in the lungs and is part of the bodies buffering system. Generally when used with the other electrolytes, it is a good indicator of acidosis and alkalinity. Normal Adult Range: 22-32 mEq/L Optimal Adult Reading: 27 Normal Childrens Range – 20 – 28 mEq/L Optimal Childrens Reading: 24 CALCIUM – involved in bone metabolism, protein absorption, fat transfer muscular contraction, transmission of nerve impulses, blood clotting and cardiac function. Regulated by parathyroid. Normal Adult Range: 8.5-10.3 mEq/dl Optimal Adult Reading: 9.4 PHOSPHORUS – Generally inverse with Calcium. Normal Adult Range: 2.5 – 4.5 mEq/dl Optimal Adult Reading: 3.5 Normal Childrens Range: 3 – 6 mEq/dl Optimal Childrens Range: 4.5 Advertisements REPORT THIS AD ANION GAP (Sodium + Potassium – CO2 + Chloride) – An increased measurement is associated with metabolic acidosis due to the overproduction of acids (a state of alkalinity is in effect). Decreased levels may indicate metabolic alkalosis due to the overproduction of alkaloids (a state of acidosis is in effect). Normal Adult Range: 4 – 14 (calculated) Optimal Adult Reading: 9 Downloaded by Steven Traffanstedt (steventraff@protonmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|27030987 CALCIUM/PHOSPHORUS Ratio Normal Adult Range: 2.3 – 3.3 (calculated) Optimal Adult Reading: 2.8 Normal Children’s range: 1.3 – 3.3 (calculated) Optimal Children’s Reading: 2.3 SODIUM/POTASSIUM Normal Adult Range: 26 – 38 (calculated) Optimal Adult Reading: 32 Hepatic Enzymes AST (Serum Glutamic-Oxalocetic Transaminase – SGOT ) – found primarily in the liver, heart, kidney, pancreas, and muscles. Seen in tissue damage, especially heart and live Normal Adult Range: 0 – 42 U/L Optimal Adult Reading: 21 Normal Adult Range: 0 – 48 U/L Optimal Adult Reading: 24 Normal Adult Range: 20 – 125 U/L Optimal Adult Reading: 72.5 Normal Childrens Range: 40 – 400 U/L Optimal Childrens Reading: 220 Normal Adult Female Range: 0 – 45 U/L Optimal Female Reading: 22.5 Normal Adult Male Range: 0 – 65 U/L Optimal Male Reading: 32.5 Normal Adult Range: 0 – 250 U/L Optimal Adult Reading: 125 Normal Adult Range 0 – 1.3 mg/dl Optimal Adult Reading: .65 ALT (Serum Glutamic-Pyruvic Transaminase – SGPT) – Decreased SGPT in combination with increased cholesterol levels is seen in cases of a congested liver. We also see increased levels in mononucleosis, alcoholism, liver damage, kidney infection, chemical pollutants or myocardial infarction ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE – Used extensively as a tumor marker it is also present in bone injury, pregnancy, or skeletal growth (elevated readings. Low levels are sometimes found in hypoadrenia, protein deficiency, malnutrition and a number of vitamin deficiencies GGT (Gamma-Glutamyl Transpeptidase) – Elevated levels may be found in liver disease, alcoholism, bile-duct obstruction, cholangitis, drug abuse, and in some cases excessive magnesium ingestion. Decreased levels can be Downloaded by Steven Traffanstedt (steventraff@protonmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|27030987 found in hypothyroidism, hypothalamic malfunction and low levels of magnesium. LDH (Lactic Acid Dehydrogenase) – Increases are usually found in cellular death and/or leakage from the cell or in some cases it can be useful in confirming myocardial or pulmonary infarction (only in relation to other tests). Decreased levels of the enzyme may be seen in cases of malnutrition, hypoglycemia, adrenal exhaustion or low tissue or organ activity. BILIRUBIN, TOTAL – Elevated in liver disease, mononucleosis, hemolytic anemia, low levels of exposure to the sun, and toxic effects to some drugs, decreased levels are seen in people with an inefficient liver, excessive fat digestion, and possibly a diet low in nitrogen bearing foods Advertisements REPORT THIS AD Renal Related B.U.N. (Blood Urea Nitrogen) – Increases can be caused by excessive protein intake, kidney damage, certain drugs, low fluid intake, intestinal bleeding, exercise or heart failure. Decreased levels may be due to a poor diet, malabsorption, liver damage or low nitrogen intake. Normal Adult Range: 7 – 25 mg/dl Optimal Adult Reading: 16 Normal Adult Range: .7 – 1.4 mg/dl Optimal Adult Reading: 1.05 Normal Adult Female Range: 2.5 – 7.5 mg/dl Optimal Adult Female Reading: 5.0 Normal Adult Male Range: 3.5 – 7.5 mg/dl Optimal Adult Male Reading:5.5 Normal Adult Range: 6 -25 (calculated) Optimal Adult Reading: 15.5 CREATININE – Low levels are sometimes seen in kidney damage, protein starvation, liver disease or pregnancy. Elevated levels are sometimes seen in kidney disease due to the kidneys job of excreting creatinine, muscle degeneration, and some drugs involved in impairment of kidney function. URIC ACID – High levels are noted in gout, infections, kidney disease, alcoholism, high protein diets, and with toxemia in pregnancy. Low levels may be indicative of kidney disease, malabsorption, poor diet, liver damage or an overly acid kidney. BUN/CREATININE – This calculation is a good measurement of kidney and liver function. Protein Downloaded by Steven Traffanstedt (steventraff@protonmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|27030987 PROTEIN, TOTAL – Decreased levels may be due to poor nutrition, liver disease, malabsorption, diarrhea, or severe burns. Increased levels are seen in lupus, liver disease, chronic infections, alcoholism, leukemia, tuberculosis amongst many others. Normal Adult Range: 6.0 -8.5 g/dl Optimal Adult Reading: 7.25 Normal Adult Range: 3.2 – 5.0 g/dl Optimal Adult Reading: 4.1 Normal Adult Range: 2.2 – 4.2 g/dl (calculated) Optimal Adult Reading: 3.2 Normal Adult Range: 0.8 – 2.0 (calculated) Optimal Adult Reading: 1.9 ALBUMIN – major constituent of serum protein (usually over 50%). High levels are seen in liver disease(rarely) , shock, dehydration, or multiple myeloma. Lower levels are seen in poor diets, diarrhea, fever, infection, liver disease, inadequate iron intake, third-degree burns and edemas or hypocalcemia GLOBULIN – Globulins have many diverse functions such as, the carrier of some hormones, lipids, metals, and antibodies(IgA, IgG, IgM, and IgE). Elevated levels are seen with chronic infections, liver disease, rheumatoid arthritis, myelomas, and lupus are present, . Lower levels in immune compromised patients, poor dietary habits, malabsorption and liver or kidney disease. A/G RATIO (Albumin/Globulin Ratio) Advertisements REPORT THIS AD Lipids CHOLESTEROL – High density lipoproteins (HDL) is desired as opposed to the low density lipoproteins (LDL), two types of cholesterol. Elevated cholesterol has been seen in artherosclerosis, diabetes, hypothyroidism and pregnancy. Low levels are seen in depression, malnutrition, liver insufficiency, malignancies, anemia and infection. Normal Adult Range: 120 – 240 mg/dl Optimal Adult Reading: 180 Normal Adult Range: 62 – 130 mg/dl Optimal Adult Reading: 81 mg/dl Normal Adult Range: 35 – 135 mg/dl Optimal Adult Reading: +85 mg/dl Normal Adult Range: 0 – 200 mg/dl Optimal Adult Reading: 100 Normal Adult Range: 1 – 6 Optimal Adult Reading: 3.5 Downloaded by Steven Traffanstedt (steventraff@protonmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|27030987 LDL (Low Density Lipoprotein) – studies correlate the association between high levels of LDL and arterial artherosclerosis HDL (High Density Lipoprotein) – A high level of HDL is an indication of a healthy metabolic system if there is no sign of liver disease or intoxication. TRIGLYCERIDES – Increased levels may be present in artherosclerosis, hypothyroidism, liver disease, pancreatitis, myocardial infarction, metabolic disorders, toxemia, and nephrotic syndrome. Decreased levels may be present in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, brain infarction, hyperthyroidism, malnutrition, and malabsorption. CHOLESTEROL/LDL RATIO Thyroid THYROXINE (T4) – Increased levels are found in hyperthyroidism, acute thyroiditis, and hepatitis. Low levels can be found in Cretinism, hypothyroidism, cirrhosis, malnutrition, and chronic thyroiditis. Normal Adult Range: 4 – 12 ug/dl Optimal Adult Reading: 8 ug/dl Normal Adult Range: 27 – 47% Optimal Adult Reading: 37 % Normal Adult Range: 4 – 12 Optimal Adult Reading: 8 Normal Adult Range: .5 – 6 milU/L AACE (2003) target level: 0.3 to 3.04 T3-UPTAKE – Increased levels are found in hyperthyroidism, severe liver disease, metastatic malignancy, and pulmonary insufficiency. Decreased levels are found in hypothyroidism, normal pregnancy, and hyperestrogenis status. FREE T4 INDEX (T7) THYROID-STIMULATING HORMONE (TSH) – produced by the anterior pituitary gland, causes the release and distribution of stored thyroid hormones. When T4 and T3 are too high, TSH secretion decreases, when T4 and T3 are low, TSH secretion increases. Advertisements REPORT THIS AD Cardiac Creatine phosphokinase (CK) – Levels rise 4 to 8 hours after an acute MI, peaking at 16 to 30 hours and returning to baseline within 4 days 25-200 U/L 32-150 U/L < 12 IU/L if total CK is <400 IU/L <3.5% of total CK if total CK is >400 IU/L Downloaded by Steven Traffanstedt (steventraff@protonmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|27030987 140-280 U/L LDH-1 18%-33% LDH-2 28%-40% 10-42 U/L <1 < 0.4 CK-MB CK isoenzyme – It begins to increase 6 to 10 hours after an acute MI, peaks in 24 hours, and remains elevated for up to 72 hours. (LDH) Lactate dehydrogenase – Total LDH will begin to rise 2 to 5 days after an MI; the elevation can last 10 days. LDH-1 and LDH-2 LDH isoenzymes – Compare LDH 1 and LDH 2 levels. Normally, the LDH-1 value will be less than the LDH2. In the acute MI, however, the LDH 2 remains constant, while LDH 1 rises. When the LDH 1 is higher than LDH 2, the LDH is said to be flipped, which is highly suggestive of an MI. A flipped pattern appears 12-24 hours post MI and persists for 48 hours. SGOT – will begin to rise in 8-12 hours and peak in 18-30 hours Myoglobin – early and sensitive diagnosis of myocardial infarction in the emergency department This small heme protein becomes abnormal within 1 to 2 hours of necrosis, peaks in 4-8 hours, and drops to normal in about 12 hours. Troponin Complex – Peaks in 10-24 hours, begins to fall off after 1-2 weeks. Table of Cardiac markers Serum Markers of Myocardial Injury Detected Peak Falls Myoglobin 1-3 1-8 12-18 CK/CK-MB 3-8 12-16 24-48 MB Isoforms 1-6 4-8 12-48 Troponin Complex 3-6 10-24 cTnI: 5-9 days cTnT: 7-14 days Downloaded by Steven Traffanstedt (steventraff@protonmail.com)