The Science of Water Evaporation: Mechanisms & Implications
advertisement

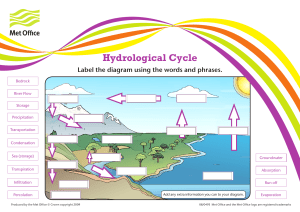
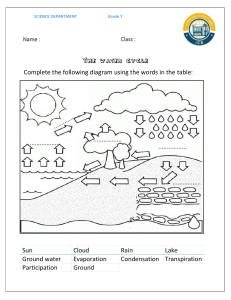
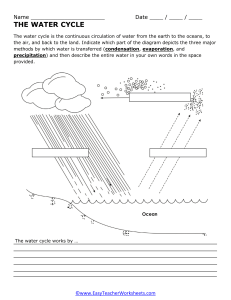
The Science of Water Evaporation Introduction Water is a fundamental substance that plays a vital role in our daily lives and the Earth's ecosystems. One of the most intriguing and essential phenomena related to water is evaporation. Evaporation is the process by which water changes from a liquid to a gaseous state. Understanding the mechanics and significance of water evaporation is crucial in various fields, including meteorology, ecology, and everyday applications. In this essay, we will explore the science behind water evaporation, including its mechanisms, factors influencing it, and its diverse implications. The Mechanisms of Water Evaporation Evaporation is a phase change process that occurs at the surface of a liquid, in this case, water. It is a result of the kinetic energy of water molecules. In a liquid, water molecules are in constant motion due to their thermal energy. Some molecules near the liquid's surface acquire sufficient energy to overcome the attractive forces of other water molecules and transition into the gaseous state. This transition is facilitated by the breaking of hydrogen bonds, which hold water molecules together. The process of water evaporation can be broken down into several key steps: 1. Energy Absorption: Heat from the environment, usually in the form of solar radiation, is absorbed by the water's surface. This energy increases the kinetic energy of water molecules, allowing them to move more rapidly. 2. Molecular Escape: As water molecules gain kinetic energy, some reach a critical velocity that enables them to break free from the liquid's surface and enter the air. 3. Vaporization: The molecules that escape the liquid form water vapor, which is the gaseous phase of water. These water vapor molecules mix with the surrounding air. 4. Diffusion and Mixing: Water vapor molecules disperse and mix with the surrounding air, gradually spreading away from the evaporation source. Factors Influencing Water Evaporation Several factors influence the rate of water evaporation: 1. Temperature: Higher temperatures provide more thermal energy to water molecules, increasing the rate of evaporation. 2. Humidity: The humidity of the surrounding air affects evaporation. In dry air, water molecules can evaporate more readily because there are fewer water vapor molecules competing for space. 3. Surface Area: A larger surface area exposed to air allows for more water molecules to escape, increasing the rate of evaporation. 4. Wind Speed: Air movement, such as wind, removes saturated air near the liquid's surface, allowing more water molecules to escape, thus accelerating the The Science of Water Evaporation 1 evaporation process. 5. Air Pressure: Lower air pressure at higher altitudes can lead to more rapid evaporation because water boils at a lower temperature, facilitating the transition from liquid to gas. Implications of Water Evaporation Water evaporation has numerous practical and ecological implications: 1. Weather Patterns: Evaporation is a critical component of the Earth's water cycle and plays a key role in weather patterns, including the formation of clouds, precipitation, and humidity. 2. Ecosystems: Evaporation affects the availability of water in ecosystems, impacting plant growth, soil moisture, and the distribution of species. 3. Industrial and Agricultural Processes: Many industrial and agricultural processes use evaporation to concentrate or separate substances in solution, such as salt production and wastewater treatment. 4. Cooling Systems: Evaporative cooling systems, like cooling towers, use water evaporation to dissipate heat and maintain machinery and buildings at optimal temperatures. Conclusion Water evaporation is a fundamental natural process with far-reaching implications in science, technology, and our everyday lives. Understanding the mechanisms and factors that influence water evaporation allows us to harness its power for practical applications and comprehend its role in shaping our environment. As we continue to study and appreciate this essential process, we can better manage water resources, predict weather patterns, and improve various industrial and agricultural practices. The Science of Water Evaporation 2