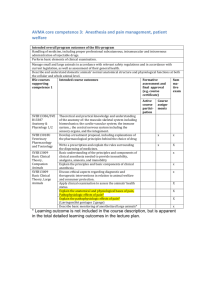
Anesthesia Comparison Chart Fill in the following table with the appropriate information. Think about why this information is important to know when you are caring for a patient undergoing each type of anesthesia. Think about how you will safely help the patient during the perioperative period. Moderate to Deep Sedation (formally called Monitored Anesthesia Care (MAC) General Anesthesia Regional Anesthesia Local Anesthesia involves a central nerve (spinal) or group of nerves (plexus) resulting in the loss of sensation in an area of the body by anesthetizing sensory pathways. rapid recovery and d/c without accompanying cognitive dysfunction. Can be used in pt’s w/co-morbidities Inhibits peripheral nerve conduction, and caused a loss of sensation at a desire site Confusion, metallic taste, dizziness taste, dizziness Pt has an increased risk of allergic rxn, skin rash, bradycardia, hypotension conscious sedation) Briefly describe the type of anesthesia. Used for procedures done outside of the OR. Short-term surgical, diagnostic, and therapeutic procedures used for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures done in or outside of the OR. ACP must be present good for surgical procedures that are of significant duration, need skeletal muscle relaxation, require uncomfortable operative positions. What are the benefits of using this type of anesthesia? Adequate sedation, reduction of fear and anxiety, amnesia, relief of pain and noxious stimuli, pt cooperation, stable vital signs, rapid recovery. ACP presence not needed; trained RN’s can perform Adverse rxn to medication, respiratory depression, bradycardia, hypotension, n/v Gives greatest flexibility to match sedation level to pt needs and procedural requirements Fast onset, fast elimination, fewer undesirable side effects. Leading to early discharge from PACU. Provides amnesia to pt. Pt. less responsive and may need airway management Hypotension, changes in HR, lowered temperature, respiratory depression, shivering, trembling, confusion, or hallucinations What risks are associated with this type of anesthesia? loss of sensation w/o loss of consciousness. What safety measures are completed to prevent or manage the risks? Resuscitation equipment readily available Resuscitation equipment readily available Airway safety temperature control, reorientation, Resuscitation equipment available Airway safety, emergency drugs, cardiac monitor/defibrillator monitor for allergic effect What type of patient would receive this type of anesthesia? reduction of dislocated joints in ED, pt needing minor therapeutic and diagnostic procedures (e.g., eye surgery, colonoscopy) Pt requiring full sedation. Pt that might have allergic rxn to medication Pt requiring full sedation. Pt that might have allergic rxn to medication Pt needing management of surgical pain, after surgery pain control. Used concurrent with MAC or moderate to deep sedation Pt that has an allergic rxn to regional anesthesia. Pt needing a minor procedure (e.g., skin growth) What type of patient should not use this type of anesthesia? Pt needing long surgical procedures, uncooperative pt due to intoxication, emotional lability, head injury, impaired cognition Pt with allergic rxns to IV anesthesia What post-anesthesia complications would you anticipate? Respiratory depression, hypotension, n/v Respiratory depression, hypotension, n/v, Respiratory depression, lowered body temperature, hypotension, changes in HR Respiratory paralysis Allergic rxns, irritation to injection site What nursing measures would you implement to prevent post-anesthesia complications? Monitor VS Monitor VS, Assessment, and management of physiologic problems Monitor VS, and closely monitor body temperature Elevation of upper body, monitor of BP, position changes Monitor VS, and s/s of allergic rxns Pt that has an allergic rxn to local anesthesia.