INTRAUTERINE CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICE
SK KARIUKI
DIAGNOSTIC MEDICAL ULTRASOUND{CLIMED & SURG}
IUD
• Intrauterine Contraceptive device
• Mode - Reversible
• Shape - T- shaped
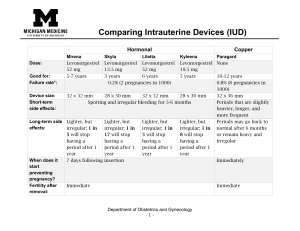
• Types – hormonal vs Non-hormonal
• Duration – up to 12 Yrs
TYPES
Hon-hormonal
copper: pure copper or alloyed with gold/silver
Non-significant
stainless steel: a.k.a. Chinese ring (manufacture ceased
in 2000)
polyethylene plastic: Lippes loop (discontinued in
1980s) 14
Hormonal, e.g. Mirena, Kyleena, Liletta, Skyla
MOA
Non-hormonal
Copper ions
• Spermicidal
• Decidualization of endometrium
Hormonal
Levonorgestriel
• Decidualization of endometrium
• Increased viscosity of cervical mucus
PREVENTS PREGNANCY BY;
Thinning the endometrial lining
Preventing sperm motility
Preventing implantation
26y/o F with Irregular heavy menses and IUD inserted 2/52 prior to the imaging
Displaced IUCD at the lower uterine segment
Removed and Reinserted
ROLE OF ULTRASOUND IN IUD;
• Before insertion
We check:
– Type of uterus.
– Rule out uterine malformations.
• After insertion
We check:
–
–
–
–
–
Infection – PID X3 Fold
Location to exclude expulsion, displacement, embedment and
perforation
after Difficult IUD placement
pregnancy-associated with IUCD
IUD retention/Lost IUD
COMPLICATIONS
• Iud Migration – different forms
• Spontaneous IUCD expulsion
• IUCD displacement >3-4 Increase Smx chances though may
migrate back, > 5mm is displaced and needs replacement
• IUCD embedment: penetration into the myometrium, but
not through the serosa
• IUCD perforation: penetration through myometrium and
serosa
• 3-fold increased risk of generalized pelvic
inflammatory disease (PID)
• pregnancy-associated with IUCD
• IUCD retention/lost IUD
• IUCD fragmentation
Partial perforation of IUD, patient underwent
laparotomy with IUD removal
IUD
Reference
• Radiopedia
• Rumack 5th edition
• My personal ultrasound images